Abstract
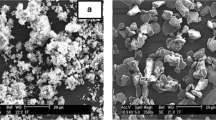
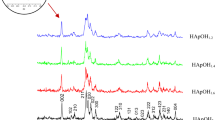
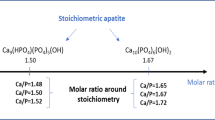
Bone ash-derived hydroxyapatite (HA) ceramics were prepared by pressureless sintering and hot pressing, and their dissolution behavior was examined in buffered water. HA powder was obtained by soaking bone ash in a 0.1M NaOH solution at 80 °C, followed by calcination at 1000 °C to completely remove the organic material. The crystal structure of the HA powder with a particle size of approximately 1 μm was mainly hydroxyapatite with a minimal amount of α-tricalcium phosphate. To improve densification, the powder was hot-pressed at 1000 °C for 0.5 h under a pressure of 30 MPa in an Ar atmosphere. The sintered density of the hot-pressed HA was 95 % of the theoretical density, which is much higher than the 70% obtained for the pressureless-sintered compact. In the porous HA ceramics obtained by pressureless sintering, dissolution occurred adjacent to the pores rather than in the dense part, which increased the residual porosity. On the other hand, the hot-pressed HA showed grain boundary dissolution followed by particle loosening.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Aoki, Science and Medical Applications of Hydroxyapatite, Japanese Association of Apatite Science, Japan (1991).
W. Suchanek and M. Yoshimura, J. Mater. Res. 13, 94 (1998).
G. S. Johnson, M. R. Mucalo, and M. A. Lorier, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 11, 427 (2000).
K. Haberko, M. M. Bucko, J. B. Miecznik, M. Haberko, W. Mozgawa, T. Panz, A. Pyda, and J. Zarebski, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 537 (2006).
D. Tadic and M. Epple, Biomaterials 25, 987 (2004).
Y. S. Kim, J. E. Kim, J. H. You, and H. T. Kim, J. Kor. Ceram. Soc. 41, 921 (2004).
C. Y. Ooi, M. Hamdi, and S. Ramesh, Ceram. Int. 33, 1171 (2007).
R. Murugan, S. Ramakrishna, and K. P. Rao, Mater. Lett. 60, 2844 (2006).
C. K. Lee, J. S. Choi, Y. J. Jeon, H. G. Byun, and S. K. Kim, J. Kor. Fish Soc. 30, 652 (1997).
M. R. Mucalo, D. L. Foster, B. Wielage, S. Steinhaeuser, H. Mucha, D. Knighton, and J. Kirby, J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2, 96 (2004).
S. J. Lee, Y. S. Yoon, M. H. Lee, and N. S. Oh, Mater. Lett. 61, 1279 (2007).
C. J. Liao, F. H. Lin, K. S. Chen, and J. S. Sun, Biomaterials 20, 1807 (1999).
D. S. Seo and J. K. Lee, Met. Mater. Int. 15, 265 (2009).
A. Royer, J. C. Viguie, M. Heughebaert, and J. C. Heughebaert, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 4, 76 (1993).
S. Nakamura, R. Otsuka, H. Oaki, M. Akao, N. Miura, and T. Yamamoto, Thermochim. Acta 165, 57 (1990).
C. V. Paganelli, A. H. Rahn, and O. D. Wangensteen, Respir. Physiol. 25, 247 (1975).
S. Raynaud, E. Champion, D. Bernache-Assolant, and D. Tetard, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 9, 221 (1998).
G. Daculsi, R. Z. LeGeros, and D. Mitre, Calcif. Tissue Int. 45, 95 (1989).
S. Wen and Q. Liu, Microsc. Res. Tech. 40, 177 (1998).
A. E. Porter, S. M. Best, and W. Bonfield, Key Eng. Mater. 240–242, 505 (2003).
T. Nonami, and F. J. Wakai, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 103, 648 (1995).
D. S. Seo, H. Kim, and J. K. Lee, Solid State Phenomena 121–123, 1241 (2007).
E. H. Kim, Y. C. Kim, S. H. Han, S. J. Yang, J. W. Park, and H. K. Seok, J. Kor. Inst. Met. & Mater. 47, 13 (2009).
G. Georgiou, J. C. Knowles, J. E. Barralet, Y. M. Kong, and H. E. Kim, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 15, 705 (2004).
National Prion Diseases Pathology Center, http://www.cjdsurveillance.com (2009).
G. Göller, F. N. Oktar, L. S. Ozyegin, E. S. Kayali, and E. Demirkesen, Mater. Lett. 58, 2599 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, D.S., Kim, Y.G. & Lee, J.K. Sintering and dissolution of bone ash-derived hydroxyapatite. Met. Mater. Int. 16, 687–692 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-0825-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-0825-x