Abstract
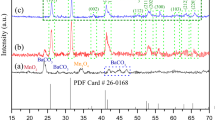
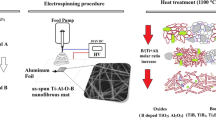
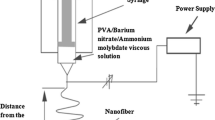
Barium titanate (BaTiO3, BT) nanofibers with a diameter range of 160 nm to 300 nm were prepared by drying electrospun BT/polyvinylpyrrolidone (BT/PVP) composite fibers for 1 h at 80 °C in vacuum with a subsequent calcination in air for 1 h at a temperature range of 650 °C to 750 °C. The morphology and crystal structure of calcined BT nanofibers were characterized with the aid of XRD, FT-IR, SEM, and TEM. The XRD and FR-IR measurements confirm that BT nanofibers with a diameter of about 160 nm and a tetragonal perovskite structure were present in the electrospun fibers after calcination for 1 h at 750 °C. The FR-IR analysis of the BT fibers reveals that the intensity level of the O-H stretching vibration bands (at 3430 cm−1 and 1425 cm−1) become weaker as the calcination temperature is increased and that a broad band at 570 cm−1, which represents the Ti-O vibration, appears sharper and narrower after calcination at 750 °C due to the formation of metal oxide bonds. In contrast, BT fibers prepared by a refluxing process in a nitrogen atmosphere show a dramatic change in crystal structure: the tetragonal structure changes to a cubic perovskite structure, probably due to the suppression of carbonate contamination. Thus, the calcination temperature and atmosphere appear to have a significant influence on the crystal structure of BT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Yuh, J.C. Nino, and W.M. Sigmund, Mater. Lett. 59, 3645 (2005).
J. Yuh, L. Perez, W.M. Sigmund, and J.C. Nino, Physica E 37, 254 (2007).
J.T. McCann, J.I.L. Chen, D. Li, Z. Ye, and Y. Xia, Chem. Phys. Lett. 424, 162 (2006).
H. Kozuka and A. Higuchi, J. Mater. Res. 16, 3116 (2001).
M. Nikiforov, H. Liu, H. Craighead, and D. Bonnell, Nano Lett. 6, 896 (2006).
M. Kim, S. Jeon, S. Jeong, I. Kim, J. Song, Electron. Mater. Lett. 4, 189 (2008).
D. Y. Lee, B. Kim, S. Lee, M. Lee, Y. Song, and J. Lee, J. Kor. Phys. Soc. 48, 1686 (2006).
Y. Kim, D. Y. Lee, M. Lee, N. Cho, S. Lee, and Y. Song, J. Kor. Phys. Soc. 53, 421 (2008).
D.Y. Lee, J. Cho, N. Cho, M. Lee, S. Lee, and B. Kim, Thin Solid Films 517, 1256 (2008).
S. Moon and N. Cho, Met. Mater. Int. 13, 329 (2007).
S. Lee, N. Cho, and D.Y. Lee, J. Euro. Ceram. Soc. 27, 3651 (2007).
S. Bae, S. Lee, S. Cho, and D.Y. Lee, J. Kor. Ceram. Soc. 41, 247 (2004).
D.Y. Lee, I. Park, M. Lee, K.J. Kim, and S. Heo, Sens. Actuators A 133, 117 (2007).
D. Y. Lee, S. Lee, M. Lee, J. Lee, B. Kim, Y. Song, and N. Cho, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 28, 294 (2008).
M. M. Hohman, M. Shin, G. Rutledge, and M. P. Brenner, Phys. Fluids 13, 2201 (2001).
H. Fong, I. Chun, and D. H. Reneker, Polymer 40, 4585 (1999).
S. Maensiri, W. Nuansing, J. Klinkaewnarong, P. Laokul, and J. Khemprasit, J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 297, 578 (2006).
J. Yuh, L. Perez, W. M. Sigmund, and J. C. Nino, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn. 42, 323 (2007).
S. Agarwal and G. L. Sharma, Sensor. Actuat. B-Chem. 85, 205 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.Y., Lee, MH., Cho, NI. et al. Effect of calcination temperature and atmosphere on crystal structure of BaTiO3 nanofibers. Met. Mater. Int. 16, 453–457 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-0616-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-0616-4