Abstract
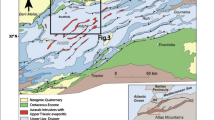
The aim of this study is to map and to identify the water erosion risks in the central High Atlas Mountains of Morocco. The approach is to integrate in the geographic information systems (GIS) for multi-criteria analyses, the geomorphometric variables (the gradient and the form of the slope) and the spectral indices derived from Landsat 5 Thematic Mapper (TM) data (form index, coloration index, and vegetation index). According to different weights for these variables, several scenarios of water erosion risk maps were produced and confronted with the ground truth for validation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bannari A, El-Harti A, Haboudane D, Bachaoui M, El-Ghmari A (2008) Intégration des variables spectrales et géomorphométriques dans un SIG pour la cartographie des zones exposées à l’érosion. Rev Télédétect 7:327–342
Baret F, Guyot G, Begue A, Maurel P (1988) Complemenîary of middle-infiared with visible and near-inhed reflectance for monitoring wheat canopies. Remote Sens Environ 26:213–225. doi:10.1016/0034-4257(88)90078-8
Bou Kheir R, Cerdan O, Abdallah C (2006) Regional soil erosion risk mapping in Lebanon. Geomorphology 82:347–359
Chikhaoui M, Bonn F, Merzouk A, Lacaze B, Mejjati AM (2007) Cartographie de la dégradation des sols à l’aide des approches de Spectral Angle Mapper et des indices spectraux en utilisant d es données ASTER. Rev Télédétect 7:343–357
Chikhaoui M, Lacaze B, Merzouk M, Madramootoo CA (2010) Étude de la dégradation des sols en milieu semi-aride à l’aide de l’approche neuronale et de données multi-sources. Rev Télédétect 10:139–150
Deschamps PY, Herman M, Tanré D (1981) Influence de l’atmosphère en télédétection des ressources terrestres, Modélisation et possibilités de correction. Actes du premier colloque international sur les signatures spectrales d’objets en télédétection, Avignon 8–11 Septembre, Société internationale de photogrammétrie et télédétection, Versailles, France, pp 543–558
Escadafal R, Bacha S (1996) Strategy for the dynamic study of desertification. Proceedings of the ISSS International Symposium Ouagadougou, Burkino Faso, pp 19–34
Escadafal R, Huete AR (1991) Étude des propriétés spectrales des sols arides appliquée à l’amélioration des indices de végétation obtenus par télédétection. C R Acad Sci Paris Ser 312:1385–1391
Escadafal R, Belghit A, Ben-Moussa A (1994) Indices spectraux pour la télédétection de la dégradation des milieux naturels en Tunisie aride. Actes du 6ème Symposium international sur les mesures physiques et signatures en télédétection, Val d’Isère (France) 17–24 janvier, ISPRS-CNES, pp 253–259
Evans LS (1972) General geomorphometry, derivations of altitude and descriptive statistics. In: Chorley RJ (ed) Spatial Analysis in Geomorphology. Methuen, London, pp 17–90
Feizizadeh B, Blaschke T, Rafiq L (2011) GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping: a case study in Bostanabad County, Iran. GI4DM conference, Antalya, Turkey
Fernandez RN, Schulze DG, Coffin DL, Van Scoyoc GE (1988) Color, organic matter, and pesticide absorption relationships in a soil landscape. Soil Sci Soc Am J 52:1023–1026. doi:10.2136/sssaj1988.03615995005200040023x
Ghanam M (2003) La désertification au Maroc – Quelle stratégie de lutte?. 2nd FIG Regional Conference, December 2–5, Marrakech, Morocco
Haboudane D (1999) Intégration des données spectrales et géomorphométriques pour la caractérisation de la dégradation des sols et l’identification des zones de susceptibilité à l’érosion hydrique, Thèse de doctorat (Ph.D), Département de Géographie et Télédétection, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Québec, Canada
Haboudane D, Bonn F, Royer A (2007) Evaluation and predictability of terrain susceptibility to hillslope erosion at the regional scale using DEM-derived indices and remotely sensed information. Rev Télédétect 7:373–391
Haboudane D, Bonn F, Royer A, Sommer S, Mehl W (2010) Land degradation and erosion risk mapping by fusion of spectrally based information and digital geomorphometric attributes. Int J Remote Sens 18:3795–3820. doi:10.1080/01431160110104638
Hill J, Mehl W, Altherr M (1994) Land degradation and soil erosion mapping in a Mediterranean ecosystem, In: Hill J and Mdgier J (eds) Imaging Spectrometry - a Tool for Environmental Observations, Brussels and Luxembourg. Printed in the Netherlands, pp 237–260
Kastner CJ, Slater PN (1982) In-flight radiometric calibration of advanced remote sensing systems. Proc SPIE 356:158–165
Kaufman YJ (1988) Atmospheric effects on spectral signature measurements and corrections. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 26:441–450
Krishna-Bahadur KC (2008) Mapping soil erosion susceptibility using remote sensing and GIS: a case of the Upper Nam Wa Watershed, Nan Province, Thailand. Environ Geol 57:695–705. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1348-3
Lal R (2001) Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad Dev 12:519–539. doi:10.1002/ldr.472
Madeira J, Bédidi A, Cervelle B, Pouget M, Flay N (1997) Visible spectrometric indices of hematite (Hm) and goethite (Gt) content in lateritic soils: the application of a Thematic Mapper image for soil-mapping in Brasilia, Brazil. Int J Remote Sens 18:2835–2852. doi:10.1080/014311697217369
Maimouni S, Bannari A, El Harti A, El-Ghmari A (2011) Potentiels et Limites des Indices Spectraux pour Caractériser la Dégradation des Sols en Milieu Semi-aride. Can J Remote Sens 37(3):285–301. doi:10.5589/m11-038
Maimouni S, El-Harti A, Bannari A, Bachaoui M (2012) Water erosion risk mapping using derived parameters from DEM and Remotely Sensed data. Geo-Spat Inf Sci 15(3):157–169. doi:10.1080/10095020.2012.715855
Margate DE, Shrestha DP (2001) The use of hyperspectral data in identifying ‘desert-like’ soil surface features in Tabernas area, southeast Spain. Actes du Symposium Asiatique de Télédétection, 5–9 novembre, Centre de télédétection et de traitement d’images (CRISP), Université nationale de Singapour, Singapour, vol. 1, pp 736–741
Mathieu R, Pouget M (1998) Relationships between satellite-based radiometric indices simulated using laboratory reflectance data and typic soil colour of an arid environment. Remote Sens Environ 66:17–28
Merzouk A, Rayan J, Kacemi M (1994) A perspective on soil erosion in Morocco’s dry land semi-arid zone. Acte du colloque international des sciences du sol : « Science du sol au développement », Maroc, 6–8 Avril
Moore ID, Gessler PE, Nielson GA, Peterson GA (1993) Soil attribute prediction using terrain analysis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 2:443–452
Mougenot B, Cailleu D (1995) Identification par télédétection des sols dégradés d’un domaine sahélien au Niger. Actes du Symposium International AISS (groupe de travail RS et DM), Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, 6–10 février, 169–179
Moukhchane M (1999) Contribution à l’étude de l’érosion hydrique dans le Rif occidental. Applications des méthodes expérimentales du 137Cs et de la susceptibilité magnétique des bassins versants Nakhla, El-Hachef et Smir, Thèse de Doctorat d’Etat, Universite A. Essaadi, Tétouan, Maroc
Nagarajan M, Singh S (2009) Assessment of groundwater potential zones using GIS technique. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 37:169–177. doi:10.1007/s12524-009-0012-z
NASA (2006) Earth observing 1 (EO-1) user’s guide. http://eol.usgs.gov/userGuide/index.html
Nekhay O, Arriaza M, Boerboom L (2009) Evaluation of soil erosion risk using analytic network process and GIS: a case study from Spanish Mountain Olive Plantation. J Environ Manag 90:3091–3104. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.04.022
Post DF, Horvath EH, Lucas WM, White SA, Ehasz MJ, Batchily AK (1994) Relation between soil color and Landsat reflectance on semiarid rangelands. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:1809–1816
Rahman MDR, Shi ZH, Chongfa C (2009) Soil erosion hazard evaluation—an integrated use of remote sensing, GIS and statistical approaches with biophysical parameters towards management strategies. Ecol Model 220:1724–1734. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.04.004
Rouse JW, Haas RW, Schell JA, Deering DW, Harlan JC (1974) Monitoring the vernal advancement and retrogradation (Greenwave effect) of natural vegetation. NASA/GSFCT Type III Final Report, Greenbelt, MD, USA
Roy B (1985) Méthodologie multicritère d’aide à la décision. Économica, Paris
Tanré D (1982) Interaction rayonnement-aérosols: applications à la télédétection et au calcul du bilan radiatif, Thèse de doctorat d’Etat. Université des sciences et techniques de Lille, Lille
Teillet PM, Santer RP (1991) Terrain elevation and sensor altitude dependence in semi-analytical atmospheric code. Can J Remote Sens 17:36–44
Theilen-Willige B (2010) Detection of local site conditions influencing earthquake shaking and secondary effects in Southwest-Haiti using remote sensing and GIS-methods. Nat Hazard Earth Syst Sci 10:1183–1196. doi:10.5194/nhess-10-1183-2010
Thompson JA, Bell J (1996) Color index for identifying hydric conditions for seasonally saturated mollisols in Minnesota. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1979–1988
Torrent J, Schwertmann U, Fechter H, Alferez F (1983) Quantitative relationships between soil color and hematite content. Soil Sci 136:354–358. doi:10.1097/00010694-198312000-00004
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses—a guide to conservation planning, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington D.C., Agriculture Handbook
Zhuo L, Liu Y, Wu J, Wang J (2008) Quantitative mapping of soil organic material using field spectrometer and hyperspectral remote sensing. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci Beijing, China 37:901–906
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bachaoui, B., Bachaoui, E.M., Maimouni, S. et al. The use of spectral and geomorphometric data for water erosion mapping in El Ksiba region in the central High Atlas Mountains of Morocco. Appl Geomat 6, 159–169 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-014-0130-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12518-014-0130-3