Abstract
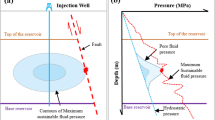
Production safety at the Shuang 6 gas storage facility is controlled by the fault block system underlying the facility. In this study, the “fault valve” theory, Coulomb fracture criterion, and current crustal stress conditions are considered as constraints for the Mohr’s circle stress calculation model, which is used to simulate and evaluate the fault stability beneath the facility. The stability margin of faults at the current maximum operating storage pressure and the formation fluid pressure (activation pressure) corresponding to fault activation are estimated, providing a basis for the upper limit of gas injection pressure for gas storage safety. The results show that the related internal faults at Shuang 6 gas storage are in a stable state under the current crustal stress and the highest gas storage pressure. The fault activation pressures of the Xing II and Xing III formations in the Shuangtaizi area exceed 8 MPa higher than the original formation pressures, and there is a large space available for additional gas storage capacity, including other regional storage groups.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown A (2003) Capillary effects on fault-fill sealing. Am Assoc Petrol Geol 87(3):381–395
Ding GS, Li WY (2002) Present situation and development trend of underground gas storage at home and abroad. Intl Petrol Econ 10(6):14–17 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ding GS (2011) Demand and challenges for underground gas storages in China. Nat Gas Ind 31(12):91–93 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ferrill DA, Stamatakos JA, Sims D (1999) Normal fault corrugation: implications for growth and seismicity of active normal faults. Struct Geol 21:1027–1038
Geraud Y, Diraison M, Orellana N (2006) Fault zone geometry of a mature active normal fault: a potential high permeability channel (Pirgaki fault, Corinth, Greece). Tectonophysics. 426:61–76
Gudmundsson A, Berg SS, Lyslo KB (2001) Skurtveit.E. Fracture networks and fluid transport in active fault zones. J Struct Geol 23(2-3):343–353
Koukouvelas IK, Papoulis D (2009) Fluid involvement in the active Helike normal Fault, Gulf of Corinth, Greece. Struct Geol 31:237–250
Lander RH, Walderhaug O (1999) Predicting porosity through simulating sandstone compaction and quartz cementation. AAPG Bull 83(9):433–449
Langhi L, Zhang Y, Gartrell A et al (2010) Evaluating hydrocarbon trap integrity during fault reactivation using geomechanical three-dimensional modeling: an example from the Timor Sea Australia. AAPG Bull 94(4):567–591. https://doi.org/10.1306/10130909046
Li XG, Min ZS (2020) comprehensive evaluation on operation and research on capacity expansion potential of Shuang 6 gas storage. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs 12(6):114–119 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li XG, Liu XZ (2020) Continuous Hydrocarbon Accumulation Properties and Patterns in Liaohe Fault-Depression. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs 27(1):1–8 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Losh S (1998) Oil migration in a major growth fault: structural analysis of the Pathfinder core, South Eugene Island Block 330, offshore Louisiana. AAPG Bull 82:1694–1710
Losh S, Eglinton LB, Schoell M, Wood JR (1999) Vertical and lateral fluid flow related to a large growth fault, South Eugene Island Block 330 Field, Offshore. AAPG Bull 83:244–276
Lu ZG (2016) Major Progress in China′s underground gas storage construction, Obstacles and Countermeasures. Sino-Global Energy 21(6):15–19 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lv XL (2018) Study on sealing of Shuang6 underground gas Storage in Liaohe. Oil field management. 220 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ma CL (2017) Classification and identification of the interlayer in block D of medium-thick viscous oil reservoirs in Liaohe Oilfield. J Geol 42(02):342–346 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Morris A, Ferrill DA, Henderson DB (1996) Slip-tendency analysis and fault reactivation. Geology. 23:275–278
Shan JF, Chen C, Zhou XL, Fang H (2021) Cenozoic tectonic evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation of Taian-Dawa fault zone, Liaohe Sag. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs 28(06):11–19 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Song XQ, Ma XM (2018) Geological and geophysical features and prospecting potential of Duocaima lead-zinc deposit. China’s Manganese Industry 10(5):51-54, 59 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Tong HM, Wang JJ, Zhao HT et al (2014) Mohr space and its application to the activation prediction of pre-existing weakness. Sci China Earth Sci 44(09):1948–1957 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wiprut D, Zoback MD (2000) Fault reactivation and fluid flow along a previously dormant normal fault in the northern North Sea. Geology. 28(7):595–598. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28%3C595:FRAFFA%3E2.O.CO;2
Xu JJ, Wang J (2016) Feasibility of B28-3 fault block in Banqiao area converted into underground gas storage. Petrochem Industry Appl 35(11):14–17 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang JM, Xu M (2003) Exploitation characteristics of condensate gas cap reservoir in Shuangliu well area. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs 10(4):41–42, 52 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang XJ, Xie QB, Zhou YL (2008) Diagenesis of reservoirs and predicting high-quality reservoirs in the Liaohe Western Depression. Gansu Geol 17(01):72–78 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng SY, Li SL, Liu XL, Liu ZM (2018) Brief introduction of world earth stress map (WSM) and its application in earthquake emergency. Recent Dev World Seismol 178:v–174 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Liaohe Oilfield for providing original data.
Funding
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (TD2019D001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santanu Banerjee
Highlights
1. The “fault valve” theory, Coulomb fracture criterion, and current crustal stress conditions are considered as constraints for the Mohr’s circle stress calculation model, which is used to simulate and evaluate the fault stability beneath the facility.
2. The fault activation pressures of the Xing II and Xing III formations in the Shuangtaizi area exceed 8 MPa higher than the original formation pressures, and there is a large space available for additional gas storage capacity, including other regional storage groups.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Meng, L., Fu, X. et al. Analysis of efficient operation conditions of the Shuang 6 gas storage in Shuangtaizi Oilfield, LiaoHe Basin, China. Arab J Geosci 15, 1486 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10624-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10624-2