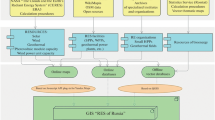
Abstract
The Mediterranean region presents a surplus in renewable energy but limited water availability. Desalination confronts water scarcity and secure appropriate quality and quantity of water for diverse applications such as irrigation and drinking. So, a challenge arises: How to establish and operate desalination plants minimizing their environmental footprint along with the corresponding life-cycle costs? This work paves the path towards a concrete and easy-to-implement response to this challenge. This is accomplished through an open-source publicly available Geographical Information System Platform that has been recently developed. Initially, the platform, called DES2iRES, determines the most favorable location for the establishment of a desalination plant based on renewable energy sources availability in its vicinity. Then, the platform takes a step forward and designs the optimal arrangement of the renewable energy source and desalination systems. In order to carry out these tasks effectively, three independent modules operate in parallel within the DES2iRES platform following an interoperable schema. In the present study, emphasis is given to the geo-information module although the main tasks carried out by the other modules are also described. The benefits of using the DES2iRES platform to design a desalination plant powered with renewable energy sources is demonstrated in a theoretical scenario for two study areas in Greece and Tunisia. Finally, constrains in extending platform’s operations are discussed along with future plans to cope those by incorporating diverse data sources to enhance the efficiency of the desalination plant design.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed FE, Hashaikeh R, Hilal N (2019) Solar power desalination – technology, energy and future outlook. Desalination 453:54–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2018.12.002
Amin I, Ali MEA, Bayoumi S, Oterkus S, Shawky H, Oterkus E (2020) Conceptual design and numerical analysis of a novel floating desalination plant powered by marine renewable energy for Egypt. J Mar Sci Eng 8:95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8020095
Antonyan M (2019) Energy footprint of water desalination. Master Thesis, University of Twente
Bartoszewski D, Piorkowski A, Lupa M (2019) The comparison of processing efficiency of spatial data for PostGIS and MongoDB databases. In: kozielski S, Mrozek D, Kasprowski P, Malysiak-Mrozek B, Kostrzewa D (eds) Beyond Databases, Architectures and Structures. Paving the road to smart data processing and analysis. Springer, Cham.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-19093-4_22.
Chandrasekharam D, Lashin A, Arifi NA, Al-Bassam AM, Varun C (2019) Geothermal energy for desalination to secure food security: case study in Djibouti. Energy Sustain Soc 9:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13705-019-0206-3
Choi Y, Suh J, Kim SM (2019) GIS-based solar radiation mapping, site evaluation, and potential assessment: a review. Appl Sci 9(9):1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091960
Copernicus Climate Change Service (2018) ERA5 Fifth generation of ECMWF atmospheric reanalyzes of the global climate. Copernicus Climate Change Service Climate Data Store. https://doi.org/10.24381/cds.bd0915c6. Accessed 10 December 2018.
DESiRES (2019) DES2iRES User Guide. http://desires.tuc.gr/wp-content/uploads/sites/159/2016/07/DES2iRES-users-guide.pdf. Accessed 20 April 2019.
Esmaeilion F (2020) Hybrid renewable energy systems for desalination. Appl Water Sci 10:84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-1168-5
Feijoo F, Lyer G, Binsted M, Edmonds J (2020) US energy system transitions under cumulative emissions budgets. Clim Chang. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-020-02670-0
Gelaro R, McCarty W, Suárez MJ, Todling R, Molod A, Takacs L, Randles C et al (2017) The Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2). J Clim 30:5419–5454. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0758.1
Global Modeling and Assimilation Office GMAO (2015) MERRA-2 tavg1_2d_slv_Nx: 2d,1-Hourly,Time-Averaged,Single-Level,Assimilation,Single-Level Diagnostics V5.12.4, Greenbelt, MD, USA, Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC). https://doi.org/10.5067/VJAFPLI1CSIV. Accessed 15 May 2019.
Gude VG (2017) Desalination and water reuse to address global water scarcity. Rev Environ SciBiothechnol 16:591–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-017-9449-7
Gude VG (2018) Renewable energy powered desalination handbook: application and thermodynamics. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-02851-3
Hristopulos DT (2015) Stochastic local interaction (SLI) model: bridging machine learning and geostatistics. Comput Geosci 85:26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2015.05.018
Hristopulos DT, Agou VD (2019) Stochastic local interaction model with sparse precision matrix for space-time interpolation. Spatial Statistics 100403:100403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spasta.2019.100403
Hristopulos DT, Pavlides A, Agou VD, Gkafa P (2020) Stochastic local interaction model: geostatistics without kriging. ArXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.02246. Accessed 14 Sept 2020.
Jia X, Klemes JJ, Varboanov PS, Alwi RSW (2019) Analyzing the energy consumption, GHG emission, and cost of seawater desalination in China. Energies 12:463. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12030463
Kabeel AE, Abdelgaied M (2019) Minimizing energy consumption in reverse osmosis desalination using renewable energy sources: A review. AIP Conference Proceeding 2133.https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5120148.
Kennelly P (2008) Terrain maps displaying hill-shading with curvature. Geomorphology 102:567–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.05.046
Koutroulis E, Kolokotsa D (2010) Design optimization of desalination systems power supplied by PV and W/G energy sources. Desalination 258:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.03.018
Larsen MAD, Drews M (2019) Water use in electricity generation for water-energy nexus analyses: the European case. Sci Total Environ 651:2044–2058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.045
Lupp M (2008) Open Geospatial Consortium. In: Shekhar S, Xiong H (eds) Encyclopedia of GIS. Springer, Boston. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-35973-1
Magagna D, HidaldoGonvalez I, Bidoglio G, Peteves S, Adamovic M, Bisselink B, De Felice M, De Roo A, Dorati C, Ganora D, Medarac H, Pistocchi A, Van De Bund W, Wanham D (2019) Water-Energy Nexus in Europe, Publications Office of the Europen. Union, Luxemburg. https://doi.org/10.2760/968197
Malisovas A, Koutroulis E (2020) Design optimization of RES-Based desalination systems cooperating with smart grids. IEEE Syst J. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2020.2968842
Moreira F, Antunes AM, Freitas MAV (2019) Trend in wind-power desalination for water supply. J Environ Prot 10(6):807–820. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2019.106048
Oliveira MC, Iten M, Matos HA, Michels J (2019) Water-Energy nexus in typical industrial water circuits. Water 11(4):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040699
Pánek J, Burian J (2020) Online visualisation. In: Pászto V, Jürgens C, Tominc P, Burian J (eds) Spationomy. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26626-4_10
Sovacool B, Martiskainen M, Hook A, Baker L (2019) Decarbonization and its discontents: a critical energy justice perspective on four low-carbon transitions. Clim Chang 155:251–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-019-02521-7
Strobl C (2008) PostGIS. In: Shekhar S, Xiong H (eds) Encyclopedia of GIS. Springer, Boston. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-35973-1
Tsiourtis NX (2008) Criteria and procedure for selecting a site for a desalination plant. Desalination 221(1-3):114–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.073
Voutchkov N, Kaiser G, Stover R, Leinhart J, Awerbuch L (2019) Sustainable management of desalination plant concentrate.International Desalination Agency, https://idadesal.org/e-library/white-papers/.Accessed 22 May 2020.
Walton M (2018) Energy has a role to play in achieving universal access to clean water and sanitation. International Energy Agency.https://www.iea.org/commentaries/energy-has-a-role-to-play-in-achieving-universal-access-to-clean-water-and-sanitation. Accessed 22 May 2020.
World Bank (2019) The role of desalination in an increasingly water-scarce world. World Bank, Washington. https://doi.org/10.1596/31416
WWAP (UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme) (2019) The United Nations World Water Development Report 2019: Leaving No One Behind. UNESCO, Paris
Zarzo D, Prats D (2017) Desalination and energy consumption: What can we expect in the near future? Desalination 427:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.10.046
Zekri S (2020) Water Policies in MENA Countries.Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-29274-4.
Funding
The work presented in this paper has been implemented within the framework of the research project DES2iRES: DESign of DESalination systems based on optimal usage of multiple Renewable Energy Sources (ERANETMED NEXUS-14-049) supported by the ERA-NET Initiative Euro-Mediterranean Cooperation through ERANET joint activities and beyond (ERANETMED) under the topic ERANETMED Energy-Water nexus. In Greece, this work was funded by the Operational Program Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation 2014–2020 (co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund) and managed by the Greek General Secretariat of Research and Technology, Ministry of Education, Research, and Religious Affairs of Greece under the project DES2iRES (T3EPA-00017) of the ERANET action. In Tunisia, this work was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education Scientific Research and TIC TUNISIA. This support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hesham El-Askary
This paper was selected from the 1st Conference of the Arabian Journal of Geosciences (CAJG), Tunisia 2018
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrakis, G., Tripolitsiotis, A., Koutroulis, E. et al. Geo-informatics for optimal design of desalination plants using renewable energy sources: the DES2iRES platform paradigm. Arab J Geosci 13, 1012 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06026-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06026-x