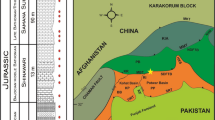
Abstract
The development of source rocks is closely related to palaeoproductivity and preservation conditions. This study examined the developmental characteristics of fossils and typomorphic minerals in different strata in the Lower Congo Basin. This study utilized thin section examination, SEM (scanning electron microscope), cathodoluminescence and chemical element analysis. The results show that there are strata rich in fossils, phosphate and pyrite in the Madingo Formation. The palaeontological record reflects the level of palaeoproductivity. The appearance of phosphate minerals is closely related to upwelling, which can bring nutrients from the subsurface. Pyrite develops in anoxic water environment, so it can be used to identify palaeoredox conditions. The Madingo Formation is rich in organic matter, which results from its high palaeoproductivity and good preservation conditions. The microstructures of sedimentary rocks and typomorphic minerals are examined, and the sedimentary characteristics and preservation conditions of organic matter in shale are comprehensively discussed. This study provides suitable tools to determine the formation mechanism and the complex heterogeneous distribution of source rocks and has great significance for oil exploration in the Lower Congo Basin.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abouelresh MO, Slatt RM (2012) Lithofacies and sequence stratigraphy of the barnett shale in east-central fort worth basin, texas. AAPG Bulletin 96:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1306/04261110116
Algeo TJ, Kuwahara K, Sano H, Bates S, Lyons T, Elswick E, Hinnov L, Ellwood B, Mosera J, Maynard B (2011) Spatial variation in sediment fluxes, redox conditions, and productivity in the Permian–Triassic Panthalassic Ocean. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 308:65–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.07.007
Babangida MSY, Wan HA, Abubakar MB, Hakimi MH, Mustapha KA, Adegoke AK (2014) Organic geochemical characteristics of cretaceous lamja formation from yola sub-basin, northern benue trough, ne nigeria: implication for hydrocarbon-generating potential and paleodepositional setting. Arab J Geosci 8:7371–7386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1713-3
Babangida MSY, Wan HA, Abubakar MB, Hakimi MH, Adegoke AK (2015) Geochemical characterisation of Early Cretaceous lacustrine sediments of Bima Formation, Yola Sub-basin, Northern Benue Trough, NE Nigeria: organic matter input, preservation, paleoenvironment and palaeoclimatic conditions. Mar Pet Geol 61:82–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.12.010
Brand U, Morrison JO (1987) Diagenesis and pyritization of crinoid ossicles. Can J Earth Sci 24:2486–2498. https://doi.org/10.1139/e87-233
Brownfield ME, Charpentier RR (2006) Geology and total petroleum systems of the Gulf of Guinea Province of West Africa, West Africa. U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2207-C. http://pubs.usgs.gov/bul/2207/C/. Accessed 13 Nov 2018
Burwood R, Cornet PJ, Jacobs L, Paulet J (1990) Organofacies variation control on hydrocarbon generation: a Lower Congo Coastal Basin (Angola) case history. Org Geochem 16:320–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6380(90)90052-2
Burwood R, Leplat P, Mycke B, Paulet J (1992) Rifted margin source rock deposition; a carbon isotope and biomarker study of a West African lower cretaceous “Lacustrine” section. Org Geochem 19:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6380(92)90026-T
Burwood R, Witte SMD, Mycke B, Paulet J (1995) Petroleum geochemical characterisation of the Lower Congo Coastal Basin Bucomazi Formation. In: Petroleum Source Rocks. Casebooks in Earth Sciences. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Cramp A, Collins M, West R (1988) Late Pleistocene-Holocene sedimentation in the NW Aegean Sea: a palaeoclimatic palaeoceanographic reconstruction. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 68:61–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-0182(88)90017-X
Das A, Krishnaswami S (2007) Elemental geochemistry of river sediments from the Deccan Traps, India: implications to sources of elements and their mobility during basalt–water interaction. Chem Geol 242:232–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.03.023
Demaison GJ, Moore GT (1980) Anoxic environments and oil source bed genesis. AAPG Bull 8:1179–1209. https://doi.org/10.1306/2F91945E-16CE-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Dineley DL, Rust BR (1968) Sedimentary and paleontological features of the Tertiary–Cretaceous rocks of Somerset Island, Arctic Canada. Can J Earth Sci 5:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1139/e68-077
Eshet Y, Almogi A (1996) Calcareous nannofossils as paleoproductivity indicators in Upper Cretaceous organic-rich sequences in Israel. Mar Micropaleontol 29:37–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-8398(96)00006-0
Fiedler PC, Philbrick V, Chávez FP (1991) Oceanic upwelling and productivity in the eastern tropical Pacific. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1834–1850. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1991.36.8.1834
Fisher ISJ, Hudson JD (1987) Pyrite formation in Jurassic shales of contrasting biofacies. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 26:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1987.026.01.04
Fu X, Wang J, Chen W, Feng X, Wang D, Song C, Zeng SQ (2016) Elemental geochemistry of the early Jurassic black shales in the Qiangtang Basin, eastern Tethys: constraints for palaeoenvironment conditions. Geol J 51:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.2642
Holbourn AEL, Kaminski MA (1995) Lower Cretaceous benthic foraminifera from DSDP Site 263: micropalaeontological constraints for the early evolution of the Indian Ocean. Mar Micropaleontol 26:425–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-8398(95)00011-9
Jansen JHF, Giresse P, Moguedet G (1984). Structural and sedimentary geology of the Congo and Southern Gabon continental shelf; a seismic and acoustic reflection survey. Neth J Sea Res 17:364–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/0077-7579(84)90056-5
Jiří K, Vojtěch J, Pedro O, Jiří S, Ulrich S (2018) Did the circum-rodinia subduction trigger the neoproterozoic rifting along the congo–kalahari craton margin? Int J Earth Sci 107:1859–1894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-017-1576-4
Kochenov AV, Baturin GN (2002) The paragenesis of organic matter, phosphorus, and uranium in marine sediments. Lithol Miner Resour 37:107–120. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014816315203
Konitzer SF, Davies SJ, Stephenson MH, Leng MJ (2014) Depositional controls on mudstone lithofacies in a basinal setting: implications for the delivery of sedimentary organic matter. J Sediment Res 84:198–214. https://doi.org/10.2110/jsr.2014.18
Latimer JC, Filippelli GM (2001) Terrigenous input and paleoproductivity in the Southern Ocean. Paleoceanography 16:627–643. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000pa000586
Lei S, Feng Q, Shen J, Ito T, Chen ZQ (2016) Proliferation of shallow-water radiolarians coinciding with enhanced oceanic productivity in reducing conditions during the Middle Permian, South China: evidence from the Gufeng Formation of western Hubei Province. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 444:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.11.031
Li YC (2015) Main controlling factors for the development of high quality lacustrine hydrocarbon source rocks in offshore China. China Offshore Oil and Gas 27:1–9. https://doi.org/10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2015.03.001
Liu F, Cai J, Lv BQ, Liu JF (2011) Sedimentary characters of Wufeng Formation upwelling facies source rock in Lower Yangtze area. Journal of Tongji University 39:440–444 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2011.03.024
Liu B, Wang Y, Su X, Zheng H (2013) Elemental geochemistry of northern slope sediments from the South China Sea: Implications for provenance and source area weathering since Early Miocene. Chem Erde-Geochem 73:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2012.11.005
Loucks RG, Ruppel SC (2007) Mississippian barnett shale: lithofacies and depositional setting of a deep-water shale-gas succession in the fort worth basin, texas. AAPG Bull 91:579–601. https://doi.org/10.1306/11020606059
Marcano G, Anka Z, Di Primio R (2013) Major controlling factors on hydrocarbon generation and leakage in South Atlantic conjugate margins: a comparative study of Colorado, Orange, Campos and Lower Congo basins. Tectonophysics 604:172–190. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsjgs.156.1.0105
Mort HP, Adatte T, Föllmi KB, Keller G, Steinmann P, Matera V, Berner ZA, Stüben D (2007) Phosphorus and the roles of productivity and nutrient recycling during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2. Geology 35:483–486. https://doi.org/10.1130/G23475A.1
Nikitenko BL, Reolid M, Glinskikh L (2013) Ecostratigraphy of benthic foraminifera for interpreting Arctic record of Early Toarcian biotic crisis (Northern Siberia, Russia). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 376:200–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.03.003
Oluboyo AP, Gawthorpe RL, Bakke K, Hadler-Jacobsen F (2014) Salt tectonic controls on deep-water turbidite depositional systems: Miocene, southwestern Lower Congo Basin, offshore Angola. Basin Res 26:597–620. https://doi.org/10.1111/bre.12051
Pedersen TF, Calvert SE (1990) Anoxia vs. productivity: what controls the formation of organic-carbon-rich sediments and sedimentary rocks? AAPG Bull 74:454–466. https://doi.org/10.1306/0C9B2821-1710-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Philippe M, Stefan H, Howard T (1999). Chlorophyll degradation. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:67–95. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.67
Rajasekaran G (2006) Influence of microfossils and pyrites on the behaviour of oceanbed sediments. Ocean Eng 33:517–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2005.02.015
Roberts E, Jelsma HA, Hegna T (2015) Mesozoic sedimentary cover sequences of the Congo Basin in the Kasai Region, Democratic Republic of Congo. In: Geology and Resource Potential of the Congo Basin. Regional Geology Reviews. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Sachse VF, Delvaux D, Littke R (2012) Petrological and geochemical investigations of potential source rocks of the central Congo Basin, Democratic Republic of CongoSource Rock Characterizations in the Central Congo Basin. AAPG Bull 96:245–275. https://doi.org/10.1306/07121111028
Schieber J (2002) Sedimentary pyrite: a window into the microbial past. Geology 30(6):531–534. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2002)0302.0.CO;2
Simpson SL, Apte SC, Batley GE (2000) Effect of short-term resuspension events on the oxidation of cadmium, lead, and zinc sulfide phases in anoxic estuarine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 34:4533–4537. https://doi.org/10.1021/es991440x
Slack JF, Selby D, Dumoulin JA (2015) Hydrothermal, biogenic, and seawater components in metalliferous black shales of the Brooks Range, Alaska: synsedimentary metal enrichment in a carbonate ramp setting. Econ Geol 110:653–675. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.110.3.653
Slatt RM, Rodriguez ND (2012) Comparative sequence stratigraphy and organic geochemistry of gas shales: commonality or comcidence? J Nat Gas Sci Eng 8:68–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2012.01.008
Valle PJ, Gjelberg JG, Hellandhansen W (2001) Tectonostratigraphic development in the Eastern Lower Congo Basin, offshore Angola, West Africa. Mar Pet Geol 18:909–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-8172(01)00036-8
Vecoli M, Riboulleau A, Versteegh GJM (2009) Palynology, organic geochemistry and carbon isotope analysis of a latest Ordovician through Siliirian clastic succession from borehole Ttl, Ghadamis Basin, southern Tunisia, North Africa: Palaeoenvironmental inteipretation. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 273:378–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.05.015
Wang L, Wang Z, Yu S, Ngia NR (2016) Seismic responses and controlling factors of Miocene deepwater gravity-flow deposits in Block A, Lower Congo Basin. J Afr Earth Sci 120:31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.04.015
Wilkin RT, Barnes HL (1997) Pyrite formation in an anoxic estuarine basin. Am J Sci 297:620–650. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.297.6.620
Wilkin RT, Barnes HL, Brantley SL (1996) The size distribution of framboidal pyrite in modern sediments: an indicator of redox conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:3897–3912. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(96)00209-8
Wit MCJD, Jelsma HA (2015) Geology and resource potential of the Congo Basin. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Yang R, He S, Wang X, Hu Q, Hu D, Yi J (2016) Paleo-ocean redox environments of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng and the first member in Lower Silurian Longmaxi formations in the Jiaoshiba area, Sichuan Basin. Can J Earth Sci 53:24–37. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjes-2015-0210
Zhang BM, Zhang SC, Bian LZ, Jin ZJ, Wang DR (2007) Developmental modes of the Neoproterozoic-Lower Paleozoic marine hydrocarbon source rocks in china. Chin Sci Bull 52:77–91 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-6018-4
Zhang CJ, Liu GX, Zeng HC, Zhang GL (2012) Depositional environments and controlling factors of Permian source rocks in western Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Geosci 23:626–635 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2012.04.626
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank key Laboratory of Tectonics and Petroleum Resources of Ministry of Education for providing technical support. The link to data used in the paper: DOI: 10.17632/k43kyd6swz.2.
Funding
This study is supported by the China National Offshore Oil Corporation Research Institute of Program under Grant (No. CRI2015FW001); China National Research and Development Project under Grant (No. 2017ZX05032); Major National Science and Technology Programs in the “Thirteenth Five-Year” plan period under Grant (No. 2016ZX05048); and Study on identification and prediction technology of source rocks in key area of West Africa–South America sea national oil and gas projects in the “Thirteenth Five-Year” plan period under Grant (No. 2017ZX05032-001-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Santanu Banerjee
Highlights
• The Madingo Formation is rich in fossils, phosphate and pyrite. Phosphate and pyrite can be used as typomorphic minerals.
• The sedimentary environment in the Madingo Formation exhibited high productivity and a reducing environment, which is good for source rock development and preservation.
• Source rock heterogeneity is studied.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Yang, X., Shi, W. et al. Characterization of fossils and typomorphic minerals and its implications for source rocks in the Lower Congo Basin. Arab J Geosci 13, 933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05949-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05949-9