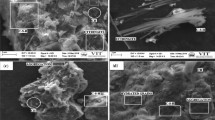
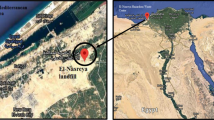
Abstract
One of Egypt’s major environmental issues is the disposal of solid waste. Natural clay is commonly employed to produce impermeable liners in solid waste landfills. Leachate from the waste mass can significantly affect the geotechnical properties of clay liners. In this study, the impact of hazardous industrial solid waste leachate (HISWL) on the geotechnical properties of clayey soil was investigated by using a natural clay artificially mixed with HISWL at various concentrations (0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100%) to assess the potential of utilizing this clay as a barrier to line the hazardous industrial solid waste landfill. Changes in the clay structure were interpreted by detailed analyses using X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The results revealed that there was a 10.53% percentage decrease (PD) in the plasticity index (IP) of 100% HISWL-contaminated clay. The mixing of natural clay with 75% and 100% HISWL reduced the optimum moisture content (OMC) with a PD of 12% and 20%, respectively. The maximum dry density (MDD) of 25% HISWL-contaminated clay remained unaffected, whereas there was a slight percentage increase (PI) of 3.74% in the MDD of 100% HISWL-contaminated clay. The permeability coefficient (k) of 100% HISWL-contaminated clay significantly decreased with a PD of 78.31%. The angle of internal friction (φ) significantly decreased from 23.7° (for the natural clay samples) to 16.3° (for the 100% HISWL-contaminated samples) with a PD of 31.22%. The cohesion decreased from 33 to 22 kN/m2 at 25% HISWL concentration with a PD of 33.33%. The compression index (CC) of the clay decreased at different concentrations of HISWL. This study recommends utilizing the used clay as a liner in the event that a new hazardous waste landfill is constructed in Egypt, due to its availability and effectiveness.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Fares RA, Al-Jarallah RS (2011) Geo-environmental site characterization at a waste disposal site using traditional geotechnical in-situ techniques: the State of Kuwait. Kuwait J Sci Eng 38(1B):55–77
APHA (2005) American public health association. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. USA, Washington DC
Arasan S, Yetimoǧlu T (2008) Effect of inorganic salt solutions on the consistency limits of two clays. Turkish J Eng Environ Sci 32(2):107–115
El-salam MA, Abu-zuid GI (2014) Impact of landfill leachate on the groundwater quality: a case study in Egypt. J Adv Res 6:579–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2014.02.003
Emami S, Negahdar A, Zarei M (2019) Investigating the influence of the leachate from the municipal solid waste on the mechanical and environmental properties of soil around the landfill (case study: the municipal landfill located in Ardabil—Iran). Arab J Sci Eng 44(10):8417–8428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03962-z
Francisca FM, Glatstein DA (2010) Long term hydraulic conductivity of compacted soils permeated with landfill leachate. Appl Clay Sci 49(3):187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.05.003
Ganiyu SA, Are KS, Olurin OT. (2020). Assessment of geotechnical and physico-chemical properties of age-long greywater-contaminated soils in basement complex areas, Southwest Nigeria, Appl. Water Sci 10(114). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01201-7
Gratchev I, Towhata I (2016) Compressibility of soils containing kaolinite in acidic environments. KSCE J Civ Eng 20(2):623–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-015-0141-6
Hakan A, Akar R (2016) Swelling and hydraulic conductivity of bentonites permeated with landfill leachates. Appl Clay Sci 142:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.09.029
Harun SN, Ali Rahman Z, Rahim SA, Lihan T, Idris WMR (2013) Effects of leachate on geotechnical characteristics of sandy clay soil. AIP Conf Proc 1571:530–536. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4858709
Ismail S, Tawfik A. (2015). Treatment of hazardous landfill leachate using Fenton process followed by a combined (UASB/DHS) system. Water Sci. Technol. 73(5). https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.655
Ismail S, Tawfik A (2016) Performance of passive aerated immobilized biomass reactor coupled with Fenton process for treatment of landfill leachate. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 111:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.04.010
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing. China Environ Pollut 152(3):686–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.056
Khodary SM, Negm AM, Tawfik A. Geotechnical properties of the soils contaminated with oils, landfill leachate , and fertilizers. Arab J Geosci 2018;11(13):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3372-7
Shan LJ, Xue Q, Wang P, Liu L (2013) Influence of leachate pollution on mechanical properties of compacted clay: a case study on behaviors and mechanisms. Eng Geol 167:128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.10.013
Mansouri H, Jorkesh Z, Ajalloeian R, Sadeghpour AH (2017) Investigating effects of water salinity on geotechnical properties of fine-grained soil and quartz in a sandstone case study: Ajichay project in Northwest Iran. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76(3):1117–1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0920-4
Met İ, Akgün H (2015) Geotechnical evaluation of Ankara clay as a compacted clay liner. Environ Earth Sci 74(4):2991–3006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4330-x
Michaels AS., Lin CS (1954) Permeability of kaolinite. Ind. Eng. Chem.,46(6): 1239-1246. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50534a041
Mishra AK, Ohtsubo M, Li L, Higashi T. (2005). Effect of salt concentrations on the permeability and compressibility of soil-bentonite mixtures. J. Fac. Agr., Kyushu Univ 50(2):837–849
Nayak S, Sunil BM, Shrihari S (2007) Hydraulic and compaction characteristics of leachate-contaminated lateritic soil. Eng Geol 94:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.05.002
Nguyen XP, Cui YJ, Tang AM, Deng YF, Li XL, Wouters L (2013) Effects of pore water chemical composition on the hydro-mechanical behavior of natural stiff clays. Eng Geol 166:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.08.009
Oztoprak S, Pisirici B (2011) Effects of micro structure changes on the macro behaviour of Istanbul (Turkey) clays exposed to landfill leachate. Eng Geol 121(3–4):110–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2011.05.005
Raghab SM, Abd AM, Meguid E, Hegazi HA (2013) Treatment of leachate from municipal solid waste landfill. Hous Build Natl Res Cent HBRC J 9(2):187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbrcj.2013.05.007
Raj P. (2005). Mechanical, cementing and chemical stabilization. In Ground improvment techniques (p. 190)
Ramadan AR, Kock P, Nadim A (2005) Nasreya: a treatment and disposal facility for industrial hazardous waste in Alexandria, Egypt: phase I. Waste Manag Res 23(2):167–170. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X05053689
Rao NS, Mathew PK (1995) Effects of exchangeable cations on hydraulic conductivity of a marine clay. Clay Clay Miner 43(4):433–437. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.1995.0430406
Renou S, Givaudan JG, Poulain S, Dirassouyan F, Moulin P (2008) Landfill leachate treatment: review and opportunity. Hazard Mater 150(3):468–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.09.077
Roque AJ, Didier G (2006) Calculating hydraulic conductivity of fine-grained soils to leachates using linear expressions. Eng Geol 85(1–2):147–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.09.034
Schmitz RM (2006) Can the diffuse double layer theory describe changes in hydraulic conductivity of compacted clays ? Geotech Geol Eng 24:1835–1844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-005-3365-2
Shackelford CD, Benson CH, Katsumi T, Edil TB, Lin L. (2000). Evaluating the hydraulic conductivity of GCLs permeated with non-standard liquids. Geotext Geomembr 18(2–4): 133–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-1144(99)00024-2
Shin H, Santamarina JC (2013) The role of particle angularity on the mechanical behavior of granular mixtures. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng 139(2):83. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000768
Sridharan A, Rao SM, Murthy NS (1988) Liquid limit of kaolinitic soils. Geotechnique 38(2):191–198
Sujatha ER, Gurucharan R, Ramprasad CS, Sornakumar V. (2013) Impact of municipal solid waste dumping on the geotechnical properties of soil and groundwater in Ariyamangalam, Trichy, India. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 18 (Bund. K):2119–2132
Sunil BM, Shrihari S, Nayak S (2009) Shear strength characteristics and chemical characteristics of leachate-contaminated lateritic soil. Eng Geol 106(1–2):20–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.12.011
Wang Y-H, Siu W-K (2006) Structure characteristics and mechanical properties of kaolinite soils. I surface charges and structural charaterizations Can Geotech J 43(6):601–617. https://doi.org/10.1139/t06-027
Xie L, Han K, Ma Y, Zhou J (2013) An electrification mechanism of sand grains based on the diffuse double layer and hertz contact theory. Appl Phys Lett 103(10):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4819948
Acknowledgments
All authors would like to thank gratefully all the reviewers for their constructive comments and helpful suggestions. The first author would like to thank the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education (MoHE) for providing her the financial support (Ph.D. scholarship) for this research as well as the Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology (E-JUST) and the Soil Mechanics and Foundation Laboratory, Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University for offering the facilities and tools needed to conduct this work. All authors would like to thank the reviewers for their valuable and constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zeynal Abiddin Erguler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khodary, S.M., Elwakil, A.Z., Fujii, M. et al. Effect of hazardous industrial solid waste landfill leachate on the geotechnical properties of clay. Arab J Geosci 13, 706 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05699-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05699-8