Abstract
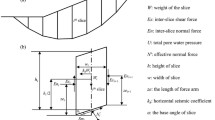
Geotechnical body is often heterogeneous in both of the natural and artificial slopes, and the layered slope is a special case. The previous studies have discussed in depth the stability of a layered slope. However, the research on the local stability of a layered slope with a focus on interlayer sliding is still insufficient. Due to the difference on the strength of soils in the adjacent upper and lower layers, it is possible for the local stability with the sliding along the interface between the adjacent two layers. Meanwhile, compared with the global stability of a layered slope, a complex sliding model should be adopted to simulate the local stability for the reason of its failure pattern affected by the forces on the interface of the two adjacent layers. Thus, this work establishes two failure modes of a layered slope, i.e., the global stability and the local stability with a focus on interlayer sliding. Then, on basic of the proposed limit equilibrium (LE) stress method, the formulas for calculating the slope factor of safety (FOS) under the two failure modes are derived. After comparison and analysis on some slope examples, the feasibility of the proposed method is verified. Furthermore, the parameter analysis is performed on a layered slope composed of soils with two layers, where the shear strength of soil in the upper layer is weaker than that in the lower layer. Thereby, the stability charts of a layered slope under different conditions are drawn. Moreover, the scopes for the global and local stability of a layered slope are respectively identified in these charts.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cho SE (2009) Infiltration analysis to evaluate the surficial stability of two-layered slopes considering rainfall characteristics[J]. Eng Geol 105(1):32–43
Deng DP, Zhao LH, Li L (2015) Limit equilibrium slope stability analysis using the nonlinear strength failure criterion[J]. Can Geotech J 52(5):563–576
Deng DP, Zhao LH, Li L (2016) Limit equilibrium method for slope stability based on assumed stress on slip surface[J]. J Cent South Univ 23(11):2972–2983
Deng DP, Li L, Zhao LH (2017a) LEM for stability analysis of 3D slopes with general-shaped slip surfaces[J]. Int J Geomech 17(10):1–12
Deng DP, Li L, Zhao LH (2017b) Limit equilibrium method (LEM) of slope stability and calculation of comprehensive factor of safety with double strength-reduction technique[J]. J Mt Sci 14(11):2311–2324
Deng DP, Li L, Zhao LH (2017c) Method of generation and model of calculation of arbitrary curved slip surfaces for three-dimensional convex and concave slopes[J]. Int J Geomech 17(11):1–17
Han TC, Dou HQ, Gong XN, Zhang J, Ma SG (2014) A rainwater redistribution model to evaluate two-layered slope stability after a rainfall event[J]. Environ Eng Geosci 20(2):163–176
Kumar J, Samui P (2006) Stability determination for layered soil slopes using the upper bound limit analysis[J]. Geotech Geol Eng 24(6):1803–1819
Lee YS, Cheuk CY, Bolton MD (2008) Instability caused by a seepage impediment in layered fill slopes[J]. Can Geotech J 45(10):1410–1425
Lim K, Li AJ, Lyamin AV (2015) Three-dimensional slope stability assessment of two-layered undrained clay[J]. Comput Geotech 70(10):1–17
Liu YQ, Li HB, Xiao KQ, Li JC, Xia X, Liu B (2014) Seismic stability analysis of a layered rock slope[J]. Comput Geotech 55(1):474–481
Liu LL, Cheng YM, Wang XM, Zhang SH, Wu ZH (2017) System reliability analysis and risk assessment of a layered slope in spatially variable soils considering stratigraphic boundary uncertainty[J]. Comput Geotech 89(9):213–225
Malvick EJ, Kutter BL, Boulanger RW, Kulasingam R (2006) Shear localization due to liquefaction-induced void redistribution in a layered infinite slope[J]. J Geotech Geoenviron 132(10):1293–1303
Morgenstern NR, Price VE (1965) The analysis of the stability of general slip surfaces[J]. Géotechnique 15(1):79–93
Peng XY, YU PC, Zhang YB, Chen GQ (2018) Applying modified discontinuous deformation analysis to assess the dynamic response of sites containing discontinuities[J]. Eng Geol 246(11):349–360
Prakash I (1985) Solution of base stability analysis in layered soils[J]. J Geotech Eng 111(8):1027–1032
Qian ZG, Li AJ, Merifield RS, Lyamin AV (2015) Slope stability charts for two-layered purely cohesive soils based on finite-element limit analysis methods[J]. Int J Geomech 15(3):1–14
Qin CB, Chian SC (2017) Kinematic stability of a two-stage slope in layered soils[J]. Int J Geomech 17(9):1–12
Song Q, Yanful EK (2011) Laboratory and numerical modeling of water balance in a layered sloped soil cover with channel flow pathway over mine waste rock[J]. Environ Earth Sci 62(1):1–17
Sun JP, Zhao ZY (2013) Stability charts for homogenous soil slopes[J]. J Geotech Geoenviron 139(12):2212–2218
Tsai TL, Chiang SJ (2013) Modeling of layered infinite slope failure triggered by rainfall[J]. Environ Earth Sci 68(5):1429–1434
Zeng P, Jimenez R, Jurado-Pina R (2015) System reliability analysis of layered soil slopes using fully specified slip surfaces and genetic algorithms[J]. Eng Geol 193(7):106–117
Zhang JF, Li ZG, Qi T (2005) Mechanism analysis of landslide of a layered slope induced by drawdown of water level[J]. Sci China 48(S1):136–145
Zhang YB, Chen GQ, Zheng L, Li YG, Wu J (2013) Effects of near-fault seismic loadings on run-out of large-scale landslide: a case study[J]. Eng Geol 166(11):216–236
Zhang YB, Xu Q, Chen GQ, Zhao JX, Zheng L (2014) Extension of discontinuous deformation analysis and application in cohesive-frictional slope analysis[J]. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 70(9):533–545
Zhang YB, Wang JM, Xu Q, Chen GQ, Zhao JX, Zheng L, Han Z, Yu PC (2015) DDA validation of the mobility of earthquake-induced landslides[J]. Eng Geol 194(8):38–51
Funding
This project was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51608541).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: David Giles
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Dp., Li, L. Failure modes and a calculation method for a stability analysis on a layered slope with a focus on interlayer sliding. Arab J Geosci 12, 182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4308-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4308-1