Abstract
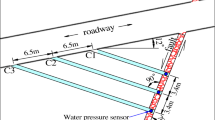
In order to measure permeability coefficient K of fault zone under coal mine quickly, the traditional borehole water pressure test method should be improved. After analyzing the principle of pressure water test in borehole, a new test method suit for borehole water pressure test under coal mine was proposed. In the new method, the time T was measured, and the calculating method was also changed from inverse algorithm to forward algorithm. According to the existing parameters and hydrogeologic conditions of fault zone, an empirical value of permeability coefficient Kc was set and then seven setting values were obtained. P-T figures of seven setting values were drawn by computer, and seven P-T figures were converted to K-T figures; the permeability coefficient could be read directly from the K-T figures. The new method was a fast experimental and calculating method to obtain permeability coefficient by borehole pressure water test on the fault zone in situ. The results were in good agreement with the low permeability coefficient of 7.5 × 10−8 and 8.0 × 10−8 m/s obtained by pressure water test in new borehole. And, the results were also in good agreement with the results of pumping test. This indicated that the pressure water test in the new borehole and the calculating method are accurate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haakon F (2010) Structural geology. Cambridge University Press
Hamm S, Kim M, Cheong J, Kim J, Moon S, Kim T (2007) Relationship between hydraulic conductivity and fracture properties estimated from packer test and borehole data in a fractured granite. Eng Geol 92:73–87
Hua X, Zhang W, Jiao D (2011) Assessment method of water-inrush induced by fault activation and its application research. Procedia Eng 26:441–448
Huang Z, Jiang Z, Zhu S, Qian Z, Cao D (2014) Characterizing the hydraulic conductivity of rock formations between deep coal and aquifers using injection tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 71:12–18
Kazmierczak JB, Laouafa F, Ghoreychi M, Lebon P, Barnichon JD (2007) Influence of creep on water pressure measured from borehole tests in the Meuse/Haute-Marne Callovo-Oxfordian argillites. Phys Chem Earth 32:917–921
Kitagawa Y, Fujimori K, Koizumi N (2007) Temporal change in permeability of the Nojima faults zone by repeated water injection experiments. Tectonophysics 443:183–192
Liao Z, Wei Y, Guo Z, Jia L, Long Y (2012) A method of determining permeability coefficient based on MATLAB software[J]. J Water Res Water Eng 02:175–178 (in Chinese)
Rao G, Lin A, Yan B, Jia D, Wu X (2014) Tectonic activity and structural features of active intracontinental normal fautls in the Weihe Graben, central China. Tectonophysics 636:270–285
Specification of borehole water pressure test in hydraulic and electric engineering. Chinese Hydraulic Standard. SL31-2003
Xiao C, Liang X, Cui J, Lan Y, Zhang J, Li S, Liang R, Zheng C (2005) Whole curve matching method for aquifer parameters determination. J Jiling Univ (Earth Sci Ed) 35(6):73–77 (in Chinese)
Yamano M, Goto S (2005) Long-term monitoring of the temperature profile in a deep borehole: temperature variations associated with water injection experiments and natural groundwater discharge. Phys Earth Planet Inter 152:326–334
Yi W, Yuan H (2011) A quantitative evaluation method of permeability coefficient of fault in coal mine. Chinese Patent. CN102243163B
Yokoyama T, Sano O, Hirata A, Ogawa K, Nakayama Y, Ishida T, Mizuta Y (2014) Development of borehole-jack fracturing technique for in situ stress measurement. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 7:9–19
Zhang Q, Li J, Liu B, Chen X (2011) Dirctional drainage grouting technology of coal mine water damage treatment. Procedia Eng 26:264–270
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the financial supporting from Important National Science and Technology Specific Projects (2011ZX05060-006), and Scientific and Technical Foundation of China National Coal Association (MTKJ2009-296).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, W., Wang, E. Experimental research on measurement of permeability coefficient on the fault zone under coal mine in situ. Arab J Geosci 9, 253 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2282-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2282-9