Abstract
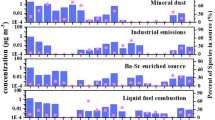
Premature deaths in China due to exposure to PM2.5-bound heavy metals (HMs) are notably more prevalent in rural areas than in urban ones. In suburban rural areas, electricity and natural gas have emerged as the primary energy sources. However, in remote rural locations far from urban centers, coal and biomass are still commonly used for cooking and heating. This disparity in energy use can lead to variations in health risks among populations and may cause significant discrepancies between implemented policies and actual conditions. Winter PM2.5 samples were collected from rural sites across the North China Plain. To identify the effects of air exposure on rural populations with different types of energy use, we employed probabilistic and source-specific risk assessment methods. Results showed that the average PM2.5 mass was 10.08 and 10.91 times higher than the World Health Organization's recommended guideline (15 μg/m3). This indicates a higher contamination burden in suburban rural areas. Children were found to be at higher risk of noncarcinogenic risks (NCR) but at a lower risk of carcinogenic risks (CR) compared to adults. Interestingly, the NCR and CR of HMs from coal and biomass combustion in remote rural areas were 2.68 and 2.47 times higher, respectively, than those in suburban rural areas. The widespread use of electricity and natural gas in suburban areas has decreased the health burden of HMs on residents when compared to the use of coal and biomass. Coal and biomass combustion was identified as the primary source of health risks in remote rural areas. In suburban rural areas, it is essential to reduce coal and biomass combustion, vehicle emissions, and industrial emissions. Our results provide valuable scientific insights for the prevention of air pollution throughout the rural energy transition process, not only in China but also in developing countries worldwide.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data available on request from the authors.
References
Amato F, Hopke PK (2012) Source apportionment of the ambient PM2.5 across St. Louis using constrained positive matrix factorization. Atmos Environ 46:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.09.062
AMBS (2021) Anyang city statistical yearbook 2021. Anyang Municipal Bureau of Statistics, Anyang
Begum BA, Kim E, Biswas SK, Hopke PK (2004) Investigation of sources of atmospheric aerosol at urban and semi-urban areas in Bangladesh. Atmos Environ 38:3025–3038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2004.02.042
Behrooz RD, Kaskaoutis DG, Grivas G, Mihalopoulos N (2021) Human health risk assessment for toxic elements in the extreme ambient dust conditions observed in Sistan, Iran. Chemosphere 262:127835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127835
Bell ML, Ebisu K, Leaderer BP, Gent JF, Lee HJ, Koutrakis P, Wang Y, Dominici F, Peng RD (2014) Associations of PM2.5 constituents and sources with hospital admissions: analysis of four counties in Connecticut and Massachusetts (USA) for persons >= 65 years of age. Environ Health Perspect 122:138–144. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1306656
Brown SG, Eberly S, Paatero P, Norris GA (2015) Methods for estimating uncertainty in PMF solutions: examples with ambient air and water quality data and guidance on reporting PMF results. Sci Total Environ 518:626–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.022
Chao S, Liu J, Chen Y, Cao H, Zhang A (2019) Implications of seasonal control of PM2.5-bound PAHs: an integrated approach for source apportionment, source region identification and health risk assessment. Environ Pollut 247:685–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.12.074
Chen R, Jia B, Tian Y, Feng Y (2021) Source-specific health risk assessment of PM2.5-bound heavy metals based on high time-resolved measurement in a Chinese megacity: insights into seasonal and diurnal variations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 216:112167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112167
Du W, Li X, Chen Y, Shen G (2018) Household air pollution and personal exposure to air pollutants in rural China—a review. Environ Pollut 237:625–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.054
Faraji Ghasemi F, Dobaradaran S, Saeedi R, Nabipour I, Nazmara S, Abadi RV, Arfaeinia H, Ramavandi B, Spitz J, Mohammadi MJ, Keshtkar M (2020) Levels and ecological and health risk assessment of PM2.5-bound heavy metals in the northern part of the Persian Gulf. Environ Sci Pollut R 27:5305–5313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07272-7
Feng J, Chan CK, Fang M, Hu M, He L, Tang X (2006) Characteristics of organic matter in PM2.5 in Shanghai. Chemosphere 64:1393–1400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.12.026
Feng J, Yu H, Liu S, Su X, Li Y, Pan Y, Sun J (2017) PM2.5 levels, chemical composition and health risk assessment in Xinxiang, a seriously air-polluted city in North China. Environ Geochem Health 39:1071–1083. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9874-5
Feng R, Xu H, He K, Wang Z, Han B, Lei R, Ho KF, Niu X, Sun J, Zhang B, Liu P, Shen Z (2021) Effects of domestic solid fuel combustion emissions on the biomarkers of homemakers in rural areas of the Fenwei Plain, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 214:112104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112104
Feng R, Xu H, Wang Z, He K, Shen Z, Sun J, Sun N (2022a) Characteristics, sources and health effect of trace components in indoor, outdoor, and personal exposure to PM2.5 samples in rural areas of Guanzhong, Shaanxi. Environ Chem 41(7):2334–2346 (In Chinese)
Feng X, Shao L, Jones T, Li Y, Cao Y, Zhang M, Ge S, Yang C, Lu J, BeruBe K (2022b) Oxidative potential and water-soluble heavy metals of size-segregated airborne particles in haze and non-haze episodes: impact of the “Comprehensive Action Plan” in China. Sci Total Environ 814(25):152774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152774
Guo L, Liu T, He G, Lin H, Hu J, Xiao J, Li X, Zeng W, Zhou Y, Li M, Yu S, Xu Y, Zhang H, Lv Z, Zhang J, Ma W (2021) Short-term mortality risks of daily PM2.5-bound metals in urban region of Guangzhou, China, an indication of health risks of PM2.5 exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 228(25):113049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113049
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Han Q, Wang M, Cao J, Gui C, Liu Y, He X, He Y, Liu Y (2020) Health risk assessment and bioaccessibilities of heavy metals for children in soil and dust from urban parks and schools of Jiaozuo, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110157
Han Q, Liu Y, Feng X, Mao P, Sun A, Wang M, Wang M (2021a) Pollution effect assessment of industrial activities on potentially toxic metal distribution in windowsill dust and surface soil in central China. Sci Total Environ 759:144023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144023
Han X, Li S, Li Z, Pang X, Bao Y, Shi J, Ning P (2021b) Concentrations, source characteristics, and health risk assessment of toxic heavy metals in PM2.5 in a Plateau City (Kunming) in Southwest China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(21):11004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111004
Hassan H, Latif MT, Juneng L, Amil N, Khan MF, Fujii Y, Jamhari AA, Hamid HHA, Banerjee T (2021) Chemical characterization and sources identification of PM2.5 in a tropical urban city during non-hazy conditions. Urban Clim 39:100953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2021.100953
Heidari M, Darijani T, Alipour V (2021) Heavy metal pollution of road dust in a city and its highly polluted suburb; quantitative source apportionment and source-specific ecological and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 273:129656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129656
Hu R, Wang S, Aunan K, Zhao M, Chen L, Liu Z, Hansen MH (2019) Personal exposure to PM2.5 in Chinese rural households in the Yangtze River Delta. Indoor Air 29:403–412. https://doi.org/10.1111/ina.12537
Huang H, Jiang Y, Xu X, Cao X (2018) In vitro bioaccessibility and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric particulate matters from three different functional areas of Shanghai, China. Sci Total Environ 610:546–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.074
Huang J, Wu Y, Sun J, Li X, Geng X, Zhao M, Sun T, Fan Z (2021) Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J Hazard Mater 415:125629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125629
Hus CY, Chi KH, Wu CD, Lin SL, Hsu WC, Tseng CC, Chen MJ, Chen YC (2021) Integrated analysis of source-specific risks for PM2.5-bound metals in urban, suburban, rural, and industrial areas. Environ Pollut 275:116652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116652
IARC (2016) Agents classified by the IARC monographs, vol 1–129. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Jimenez E, Linares C, Rodriguez LF, Bleda MJ, Diaz J (2009) Short-term impact of particulate matter (PM2.5) on daily mortality among the over-75 age group in Madrid (Spain). Sci Total Environ 407:5486–5492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.06.038
Jin X, Cai X, Yu M, Song Y, Wang X, Kang L, Zhang H (2020) Diagnostic analysis of wintertime PM2.5 pollution in the North China Plain: the impacts of regional transport and atmospheric boundary layer variation. Atmos Environ 224:117346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117346
Kong SF, Li L, Li XX, Yin Y, Chen K, Liu DT, Yuan L, Zhang YJ, Shan YP, Ji YQ (2015) The impacts of firework burning at the Chinese Spring Festival on air quality: insights of tracers, source evolution and aging processes. Atmos Chem Phys 15:2167–2184. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-2167-2015
Kong L, Tan Q, Feng M, Qu Y, An J, Liu X, Cheng N, Deng Y, Zhai R, Wang Z (2020) Investigating the characteristics and source analyses of PM2.5 seasonal variations in Chengdu, Southwest China. Chemosphere 243:125267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125267
Lai S, Xie Z, Song T, Tang J, Zhang Y, Mi W, Peng J, Zhao Y, Zou S, Ebinghaus R (2015) Occurrence and dry deposition of organophosphate esters in atmospheric particles over the northern South China Sea. Chemosphere 127:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.015
Li F, Yan J, Wei Y, Zeng J, Wang X, Chen X, Zhang C, Li W, Chen M, Lü G (2021) PM2.5-bound heavy metals from the major cities in China: Spatiotemporal distribution, fuzzy exposure assessment and health risk management. J Clean Prod 286:124967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124967
Liu L (2013) Geographic approaches to resolving environmental problems in search of the path to sustainability: the case of polluting plant relocation in China. Appl Geogr 45:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.08.011
Liu K, Ren J (2020) Seasonal characteristics of PM2.5 and its chemical species in the northern rural China. Atmos Pollut Res 11:1891–1901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.08.005
Liu P, Zhang C, Mu Y, Liu C, Xue C, Ye C, Liu J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2016) The possible contribution of the periodic emissions from farmers’ activities in the North China Plain to atmospheric water-soluble ions in Beijing. Atmos Chem Phys 16:10097–10109. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-10097-2016
Liu J, Chen Y, Chao S, Cao H, Zhang A, Yang Y (2018a) Emission control priority of PM2.5-bound heavy metals in different seasons: a comprehensive analysis from health risk perspective. Sci Total Environ 644:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.226
Liu Y, Wang Q, Zhuang W, Yuan Y, Yuan Y, Jiao K, Wang M, Chen Q (2018b) Calculation of Thallium’s toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index: a case study. Chemosphere 194:562–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.002
Liu P, Zhang Y, Wu T, Shen Z, Xu H (2019) Acid-extractable heavy metals in PM2.5 over Xi’an, China: seasonal distribution and meteorological influence. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:34357–34367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06366-6
Ma W, Tai L, Qiao Z, Zhong L, Wang Z, Fu K, Chen G (2018) Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator: a case study in North China. Sci Total Environ 631–632:348–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.011
Massey DD, Kulshrestha A, Taneja A (2013) Particulate matter concentrations and their related metal toxicity in rural residential environment of semi-arid region of India. Atmos Environ 67:278–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.11.002
Men C, Liu R, Wang Q, Guo L, Miao Y, Shen Z (2019) Uncertainty analysis in source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust based on positive matrix factorization model and geographic information system. Sci Total Environ 652:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.212
Men C, Liu R, Wang Q, Miao Y, Wang Y, Jiao L, Li L, Cao L, Shen Z, Li Y, Crawford-Brown D (2021) Spatial-temporal characteristics, source-specific variation and uncertainty analysis of health risks associated with heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 278:116866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116866
Paatero P, Tapper U (1994) Positive matrix factorization: a non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 5:111–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/env.3170050203
Paatero P, Eberly S, Brown SG, Norris GA (2014) Methods for estimating uncertainty in factor analytic solutions. Atmos Meas Tech 7:781–797. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-7-781-2014
Peng X, Shi G, Liu G, Xu J, Tian Y, Zhang Y, Feng Y, Russell AG (2017) Source apportionment and heavy metal health risk (HMHR) quantification from sources in a southern city in China, using an ME2-HMHR model. Environ Pollut 221:335–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.083
Quan J, Tie X, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Li X, Gao Y, Zhao D (2014) Characteristics of heavy aerosol pollution during the 2012–2013 winter in Beijing, China. Atmos Environ 88:83–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.01.058
Sah D, Verma PK, Kandikonda MK, Lakhani A (2019) Pollution characteristics, human health risk through multiple exposure pathways, and source apportionment of heavy metals in PM10 at Indo-Gangetic site. Urban Clim 27:149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2018.11.010
Simoneit BRT, Schauer JJ, Nolte CG, Oros DR, Elias VO, Fraser MP, Rogge WF, Cass GR (1999) Levoglucosan, a tracer for cellulose in biomass burning and atmospheric particles. Atmos Environ 33(2):173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(98)00145-9
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (2011) Exposure factors handbook, Final edn. U.S. Environment Protection Agency, Washington, DC (EPA/600/R-09/052F). USEPA
Wang S, Li G, Gong Z, Du L, Zhou Q, Meng X, Xie S, Zhou L (2015) Spatial distribution, seasonal variation and regionalization of PM2.5 concentrations in China. Sci China Chem 58:1435–1443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5468-9
Wang F, Wang J, Han M, Jia C, Zhou Y (2019a) Heavy metal characteristics and health risk assessment of PM2.5 in students’ dormitories in a university in Nanjing, China. Build Environ 160:106206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106206
Wang M, Han Q, Gui C, Cao J, Liu Y, He X, He Y (2019b) Differences in the risk assessment of soil heavy metals between newly built and original parks in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China. Sci Total Environ 676:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.396
Wang B, Li Y, Tang Z, Cai N, Zhang N, Liu J (2021a) The heavy metals in indoor and outdoor PM2.5 from coal-fired and non-coal-fired area. Urban Clim 40:101000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2021.101000
Wang Y, Guo G, Zhang D, Lei M (2021b) An integrated method for source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils and model uncertainty analysis. Environ Pollut 276:116666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116666
Wang W, Chen C, Liu D, Wang M, Han Q, Zhang X, Feng X, Sun A, Mao P, Xiong Q, Zhang C (2022) Health risk assessment of PM2.5 heavy metals in county units of northern China based on Monte Carlo simulation and APCS-MLR. Sci Total Environ 843:156777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156777
Widziewicz K, Loska K (2016) Metal induced inhalation exposure in urban population: a probabilistic approach. Atmos Environ 128:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.12.061
Wu X, Wu Y, Zhang S, Liu H, Fu L, Hao J (2016) Assessment of vehicle emission programs in China during 1998–2013: achievement, challenges and implications. Environ Pollut 214:556–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.042
Wu J, Li J, Teng Y, Chen H, Wang Y (2020) A partition computing-based positive matrix factorization (PC-PMF) approach for the source apportionment of agricultural soil heavy metal contents and associated health risks. J Hazard Mater 388:121766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121766
Xie Y, Zhao B, Zhao Y, Luo Q, Wang S, Zhao B, Bai S (2017) Reduction in population exposure to PM2.5 and cancer risk due to PM2.5-bound PAHs exposure in Beijing, China during the APEC meeting. Environ Pollut 225:338–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.02.059
Xie Y, Liu Z, Wen T, Huang X, Liu J, Tang G, Yang Y, Li X, Shen R, Hu B, Wang Y (2019) Characteristics of chemical composition and seasonal variations of PM2.5 in Shijiazhuang, China: impact of primary emissions and secondary formation. Sci Total Environ 677:215–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.300
Xie Y, Lu H, Yi A, Zhang Z, Zheng N, Fang X, Xiao H (2020) Characterization and source analysis of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 at a background site in central China. Atmos Res 239:104881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.104881
Xu H, Cao J, Chow JC, Huang RJ, Shen Z, Chen LW, Ho KF, Watson JG (2016) Inter-annual variability of wintertime PM2.5 chemical composition in Xi’an, China: evidences of changing source emissions. Sci Total Environ 545–546:546–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.070
Xu M, Liu Z, Hu B, Yan G, Zou J, Zhao S, Zhou J, Liu X, Zheng X, Zhang X, Cao J, Guan M, Lv Y, Zhang Y (2022) Chemical characterization and source identification of PM2.5 in Luoyang after the clean air actions. J Environ Sci 115:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.06.021
Yan RH, Peng X, Lin W, He LY, Wei FH, Tang MX, Huang XF (2022) Trends and challenges regarding the source-specific health risk of PM2.5-bound metals in a Chinese megacity from 2014 to 2020. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c06948
Zhang J, Zhou X, Wang Z, Yang L, Wang J, Wang W (2018) Trace elements in PM2.5 in Shandong Province: source identification and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 621:558–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.292
Zhang X, Eto Y, Aikawa M (2021) Risk assessment and management of PM2.5-bound heavy metals in the urban area of Kitakyushu, Japan. Sci Total Environ 795:148748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148748
Zhao Z, Lv S, Zhang Y, Zhao Q, Shen L, Xu S, Yu J, Hou J, Jin C (2019) Characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Jiaxing, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:7497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04205-2
Zhao X, Zhao X, Liu P, Ye C, Xue C, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Liu C, Liu J, Chen H, Chen J, Mu Y (2020) Pollution levels, composition characteristics and sources of atmospheric PM2.5 in a rural area of the North China Plain during winter. J Environ Sci 95:172–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.03.053
Zhao S, Liu S, Hou X, Sun Y, Beazley R (2021) Air pollution and cause-specific mortality: a comparative study of urban and rural areas in China. Chemosphere 262:127884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127884
Zhi M, Zhang X, Zhang K, Ussher SJ, Lv W, Li J, Gao J, Luo Y, Meng F (2021) The characteristics of atmospheric particles and metal elements during winter in Beijing: size distribution, source analysis, and environmental risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.111937
Zíková N, Wang Y, Yang F, Li X, Tian M, Hopke PK (2016) On the source contribution to Beijing PM2.5 concentrations. Atmos Environ 134:84–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.03.047
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 42177070): Migration processes of pathogenic bacteria at the subsurface media interface in livestock manure return areas and their driving mechanisms.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WW, XZ: investigation, conceptualization, writing, formal analysis, data curation and editing; MW, MW, QH: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, project administration and review; CC, DL: investigation, experimental analysis, data curation, review; QX, CZ: experimental analysis, data curation, investigation and experimental analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Wang, M., Wang, M. et al. Quantifying the Health Risks of PM2.5-Bound Heavy Metals for Rural Populations with Different Energy Use Types During the Heating Season. Expo Health (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-023-00590-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-023-00590-9