Abstract
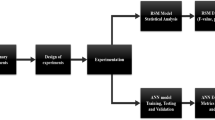
Mathematical models are powerful tools for the operational control of the extraction stage of the raw sugar manufacturing process. There are no simple mathematical models to quickly and accurately predict the output variables of the extraction stage. Most of the mathematical models developed in this regard have adequate robustness and a high level of description but includes variables that are not well known or difficult to determine. In this work, new mathematical models are developed and validated through multiple linear regression, using data obtained through rigorous experimentation. Applying these mathematical models, the brix and pol of the mixed juice and the moisture, pol, and brix of bagasse can be predicted. Through “hidden extrapolation” analysis, the application intervals of the models are defined. This analysis technique is of great importance and is not often referred to in works on mathematical modelling applied to industrial processes. All mathematical models are applicable for the following conditions: an imbibition water temperature between 40 and 80°C, an imbibition rate on fibre between 80 and 290%, a primary juice brix between 17.6 and 23.0°Bx, and a primary juice pol between 15.1 and 19.2%. The mathematical models are also validated with experimental data obtained at the industrial level in another sugar mill, showing adequate predictive capability. These mathematical models have the advantage and the novelty compared to those referred to by other authors of only involving variables that are easy to determine and of considering the effect of the temperature of the imbibition water.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, Mumtaz, Ravinesh C. Deo, Nathan J. Downs, and Tek Maraseni. 2018. Cotton yield prediction with Markov Chain Monte Carlo-based simulation model integrated with genetic programing algorithm: A new hybrid copula-driven approach. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 263: 428–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2018.09.002.
Arnoud, Wienese. 1995. The effect of imbibition and cane quality on the front end mass balance. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 69: 181–185.
Chantasiriwan, Somchart. 2013. Numerical model of sugar mills with compound imbibition. Proceedings Australian Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 35: 1–6.
Christodoulou, Pascal. 2003. Sugars and Carbohydrates. In Extraction optimization in food engineering, ed. Constantina Tzia and George Liadakis, 235–304. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Fox, John, and Weisberg Sanford. 2019. An R companion to applied regression. California: SAGE.
Gharekhani, Maryam, Ata Allah Nadiri, Rahman Khatibi, and Sina Sadeghfam. 2021. An investigation into time-variant subsidence potentials using inclusive multiple modelling strategies. Journal of Environmental Management 294: 112949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112949.
Gross, Juergen, and Uwe Ligges. 2015. Package ´´nortest´´:Tests for Normality. 1.0–4: CRAN.
Harrell, Frank. 2015. Regression modeling strategies: With applications to linear models, logistic and ordinal regression, and survival analysis. New York: Springer.
Hernández-Chover, Vicent, Lledó Castellet-Viciano, and Francesc Hernández-Sancho. 2019. Cost analysis of the facilities deterioration in wastewater treatment plants: A dynamic approach. Sustainable Cities and Society 49: 101613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101613.
Hugot, Emile. 2014. Imbibition. In Handbook of Cane Sugar Engineering, ed. E. Hugot, 223–245. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4832-3190-7.50028-3.
Kent, Geoff. 1997. Modelling the extraction processes of milling trains. Proceedings of the Australian Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 19: 315–321.
Kent, Geoff. 2001. A model to estimate milling unit throughput. Proceedings of the Australian Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 23: 457–460.
Kent, Geoff. 2011. The effect of added water temperature on milling train operation and performance. Sugar Tech 13: 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-011-0062-8.
Kent, Geoff. 2019. Understanding milling tandem control. Proceedings of the International Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 30: 1936–1943.
Kulkarni, Digambar. 1996. Cane sugar manufacture in India. New Delhi: STAI.
Kuznetsova, Alexandra, Per B. Brockhoff, and Rune H. B. Christensen. 2017. lmertest package: Tests in linear mixed effects models. Journal of Statistical Software 82: 1–26. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v082.i13.
Liu, Jin, and Stephen R. Smith. 2020. A multi-level biogas model to optimise the energy balance of full-scale sewage sludge conventional and THP anaerobic digestion. Renewable Energy 159: 756–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.06.029.
Lloyd, Tony, Steve Eastment, and Priest Mitchell. 2010. Milling train maceration control utilising NIR technology. Proceedings of the Australian Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 32: 688–695.
Lüdecke, Daniel, Mattan Ben-Shachar, Indrajeet Patil, and Dominique Makowski. 2020. Extracting, computing and exploring the parameters of statistical models using R. Journal of Open Source Software 5: 2445. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02445.
Lüdecke, Daniel, Mattan Ben-Shachar, Indrajeet Patil, Philip Waggoner, and Dominique Makowski. 2021. Performance: An R Package for assessment, comparison and testing of statistical models. Journal of Open Source Software 6: 3139. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03139.
Maindonald, John, and John Braun. 2010. Data analysis and graphics using R–an example-based approach. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Mann, Anthony, Omkar Thaval, Ross Broadfoot, and John Mcfeaters. 2015. Improving factory performance using an integrated sugar factory model. Proceedings of the Australian Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 37: 305–315.
Meyers, Lawrence, Glenn Gamst, and Anthony Guarino. 2016. Applied multivariate research: Design and iterpretation. California: Sage.
Montgomery, Douglas, and George Runger. 2018. Applied statistics and probability for engineers. New York: Wiley.
Montgomery, Douglas, Elizabeth Peck, and Geoffrey Vining. 2021. Introduction to linear regression analysis. New York: Wiley.
Mullor, Rubén, Julio Mulero, and Mario Trottini. 2019. A modelling approach to optimal imperfect maintenance of repairable equipment with multiple failure modes. Computers & Industrial Engineering 128: 24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2018.12.032.
Ohno, Hiroshi, and Akitoshi Suzumura. 2021. Electrolyte recommender system for batteries using ensemble Bayesian optimization. IFAC Journal of Systems and Control 16: 100158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacsc.2021.100158.
Priego, Quesada, and Rosario Palmer. 2018. Multi regression analysis of skin temperature variation during cycling exercise. Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics 27: 962–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-68195-5_105.
Razali, Nornadiah M., and Yap B. Wah. 2011. Power comparisons of shapiro-wilk, kolmogorov-smirnov, lilliefors and anderson-darling tests. Journal of Statistical Modeling and Analytics 2: 21–33.
Rein, Peter. 1975. A statistical analysis of the effect of cane quality on extraction performance. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 49: 43–48.
Rein, Peter. 2007. Sugar cane engineering. Berlin: Bartens.
Rumánková, Lenka, Luboš Smutka, Mansoor Maitah, and Irena Benešová. 2019. The Interrelationship between sugar prices at the main world sugar commodities markets. Sugar Tech 21: 853–861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-019-00739-4.
Sejati, Andri E., Sitti Kasmiati, and Fahrudi A. Ikhsan. 2019. The relationship between learning process interactions and student’s learning outcomes in environmental sustainability matter geography-social science education subject. In IOP conference series: Earth and environmental science 382: 012026. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/382/1/012026.
Suresh, Kumar, and Krishna Priya. 2011. Forecasting sugarcane yield of tamilnadu using ARIMA models. Sugar Tech 13: 23–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-011-0071-7.
Thaval, Omkar, Geoff Kent. 2012a. An enhanced mill extraction model. Proceedings of the Australian Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 34: 308–318.
Thaval, Omkar, Geoff Kent. 2012b. Modelling the flow of cane constituents in the milling process. Proceedings of the South African sugar technologists’ association 85: 435–453.
Thaval, Omkar, and Geoff Kent. 2013. Advanced computer simulation of the milling process. International Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 28: 1595–1607.
Thaval, Omkar, and Geoff Kent. 2015. Modelling milling train performance. Proceedings of the Australian Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 37: 292–304.
Vandchali, Rezaei, Stephen Cahoon Hadi, and Shu-Ling. Chen. 2021. The impact of supply chain network structure on relationship management strategies: An empirical investigation of sustainability practices in retailers. Sustainable Production and Consumption 28: 281–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.04.016.
Wienese, Arnoud. 1990. Mill settings and extraction. Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association 64: 154–157.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the important support given by Asociación de Técnicos Azucareros de Cuba (ATAC)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. Data collection was performed by JS, JLO, and HLR. The mathematical processing of the experimental data for developing the mathematical models was carried out by all authors. The analysis of the results was performed by JS and JLO. The manuscript was written by JS and JAD. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Serrano, J., Orozco, J.L., Dueñas, J. et al. Obtaining Mathematical Models to Predict the Behaviour of the Extraction Stage of the Raw Sugar Production Process. Sugar Tech 25, 777–787 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-022-01236-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-022-01236-x