Abstract
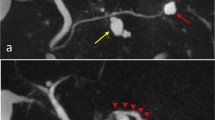
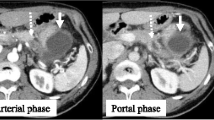
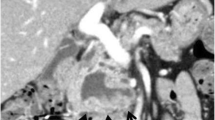
Acute pancreatitis reportedly occurs in about 15 % of cases of branch duct (BD)-intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs), with two-thirds of BD-IPMNs being located in the head or uncinate process of the pancreas. However, the surgical indications and optimal treatment methods for BD-IPMNs have not been established. A 59-year-old Japanese male with epigastralgia was admitted to our hospital. A multidetector row computed tomography (MDCT) scan disclosed grade I acute pancreatitis. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography disclosed a 1.5-cm BD-IPMN in the uncinate process. Two months after discharge, the epigastralgia recurred, and MDCT again revealed grade I pancreatitis. Due to the repeated episodes of pancreatitis, we performed ductal branch-oriented pancreatic resection. To detect the inferior branch of the Wirsung duct and avoid the development of a pancreatic fistula, we injected indigo carmine into the tumor which confirmed ligation of the inferior branch. Histopathologically, the tumor proved to be an adenoma. The postoperative course was uneventful in both the short- and long-term follow-up and, to date, there has been no recurrence of pancreatitis, or diabetes mellitus during the 6 years since pancreatectomy. This procedure is one of the methods that can be used for the successful resection of a BD-IPMN in the uncinate process that caused recurrent acute pancreatitis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IPMN:
-
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
- MDCT:
-
Multidetector row computed tomography
- AP:
-
Acute pancreatitis
- PD:
-
Pancreaticoduodenectomy
References
Steinberg W, Tenner S. Acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1198–210.
McGrath K, Slivka A. Diagnosis and management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;2(316–32):2.
Takeuchi K, Tsuzuki Y, Ando T, et al. A case of intraductal papillary-mucinous carcinoma of the pancreas with the onset of acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2002;49:838–41.
Rodriguez JR, Salvia R, Crippa S, et al. Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: observations in 145 patients who underwent resection. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:72–9 (quiz 309–310).
Yamaguchi K, Shimizu S, Yokohata K, et al. Ductal branch-oriented minimal pancreatectomy: two cases of successful treatment. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999;6(69–7):3.
Rosenberger LH, Stein LH, Witkiewicz AK, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) with extra-pancreatic mucin: a case series and review of the literature. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;16:762–70.
Hirooka Y, Goto H, Itoh A, et al. Case of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor in which endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy caused dissemination. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;18(1323–132):4.
Rotman N, Sastre B, Fagniez PL. Medial pancreatectomy for tumors of the neck of the pancreas. Surgery. 1993;113:532–5.
Sperti C, Pasquali C, Ferronato A, et al. Median pancreatectomy for tumors of the neck and body of the pancreas. J Am Coll Surg. 2000;190(711–71):6.
Warshaw AL, Rattner DW, Fernandez-del Castillo C, et al. Middle segment pancreatectomy: a novel technique for conserving pancreatic tissue. Arch Surg. 1998;133:327–31.
Nagai E, Ueki T, Chijiiwa K, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas associated with so-called “mucinous ductal ectasia”. Histochemical and immunohistochemical analysis of 29 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19:576–89.
Paik KY, Choi SH. Experience of limited pancreatic head resection for management of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in a single center. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(2904–290):7.
Takada T, Amano H, Ammori BJ. A novel technique for multiple pancreatectomies: removal of unicinate process of the pancreas combined with medial pancreatectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2000;7(49–5):2.
Tanaka M, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Adsay V, et al. International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2012;12:183–97.
Disclosures
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human/Animal Rights: All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008(5)
Informed Consent: Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natsume, T., Maruyama, T., Kobayashi, A. et al. Ductal branch-oriented pancreatic resection for an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in the uncinate process that caused recurrent acute pancreatitis: a case report of successful treatment. Clin J Gastroenterol 6, 476–479 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-013-0428-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-013-0428-4