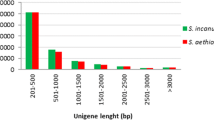
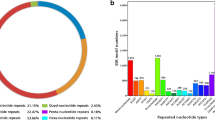
Abstract
EST-SSR markers were developed from Pongamia pinnata transcriptome libraries. We have successfully utilised EST-SSRs to study the genetic diversity of Indian P. pinnata germplasms and transferability study on legume plants. P. pinnata is a non-edible oil, seed-bearing leguminous tree well known for its multipurpose benefits and acts as a potential source for medicine and biodiesel preparation. Moreover, the plant is not grazable by animal and wildly grown in different agro climatic condition of India. Recently, it is much used in reforestation and rehabilitation of marginal and coal mined land in different part of India. Due to increasing demand for cultivation, understanding of the genetic diversity is important parameter for further breeding and cultivation program. In this investigation, an attempt has been undertaken to develop novel EST-SSR markers by analyzing the assembled transcriptome from previously published Illumina libraries of P. pinnata, which is cross transferrable to legume plants. Twenty EST-SSR markers were developed from oil yielding and secondary metabolite biosynthesis genes. To our knowledge, this is the first EST-SSR marker based genetic diversity study on Indian P. pinnata germplasms. The genetic diversity parameter analysis of P. pinnata showed that the Gangetic plain and Eastern India are highly diverse compared to the Central Deccan and Western germplasms. The lowest genetic diversity in the Western region may be due to the pressure of lower precipitation, high-temperature stress and reduced groundwater availability. Nevertheless, the highest genetic diversity of Gangetic plain and Eastern India may be due to the higher groundwater availability, high precipitation, higher temperature fluctuations and growing by the side of glacier-fed river water. Thus, our study shows the evidence of natural selection on the genetic diversity of P. pinnata germplasms of the Indian subcontinent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal G, Jhanwar S, Priya P, Singh VK, Saxena MS, Parida SK, Garg R, Tyagi AK, Jain M (2012) Comparative analysis of kabuli chickpea transcriptome with desi and wild chickpea provides a rich resource for development of functional markers. PLoS ONE 7:e52443. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052443
Aggarwal RK, Hendre PS, Varshney RK, Bhat PR, Krishnakumar V, Singh L (2006) Identification, characterization and utilization of EST-derived genic microsatellite markers for genome analyses of coffee and related species. Theor Appl Genet 114:359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0440-x
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Browse J (2009) Jasmonate passes muster: a receptor and targets for the defence hormone. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:183–205. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.043008.092007
Chabane K, Ablett GA, Cordeiro GM, Valkounn J, Henry RJ (2005) EST versus genomic derived microsatellite markers for genotyping wild and cultivated barley. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52:903–909. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-003-6112-7
Chen YN, Zilliacus H, Li WH, Zhang HF, Chen YP (2006) Ground-water level affects plant species diversity along the lower reaches of the Tarim river, Western China. J Arid Environ 66:231–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2005.11.009
Chen H, Liu L, Wang L, Wang S, Somta P, Cheng X (2015) Development and validation of EST-SSR markers from the transcriptome of adzuki bean (Vigna angularis). PLoS ONE 10:e0131939. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0131939
Dutta S, Kumawat G, Singh BP, Gupta DK, Singh S, Dogra V, Gaikwad K, Sharma TR, Raje RS, Bandhopadhya TK, Datta S, Singh MN, Bashasab F, Kulwal P, Wanjari KB, Varshney R, Cook DR, Singh NK (2011) Development of genic-SSR markers by deep transcriptome sequencing in pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan L.) Millspaugh]. BMC Plant Biol 11:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-17
Garcia RA, Rangel PN, Brondani C, Martins WS, Melo LC, Carneiro MS, Borba TC, Brondani RP (2011) The characterization of a new set of EST-derived simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers as a resource for the genetic analysis of Phaseolus vulgaris. BMC Genet 12:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-12-41
Gupta S, Tripathi KP, Roy S, Sharma A (2010) Analysis of unigene derived microsatellite markers in family solanaceae. Bioinformation 5:113–121
Huang J, Lu X, Yan H, Chen S, Zhang W, Huang R, Zheng Y (2012) Transcriptome characterization and sequencing-based identification of salt-responsive genes in Millettia pinnata, a semi-mangrove plant. DNA Res 19:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dss004
Huang J, Guo X, Hao X, Zhang W, Chen S, Huang R, Gresshoff PM, Zheng Y (2016) De novo sequencing and characterization of seed transcriptome of the tree legume Millettia pinnata for gene discovery and SSR marker development. Mol Breed 36:75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0503-x
Kesari V, Rangan L (2010) Development of Pongamia pinnata as an alternative biofuel crop-current status and scope of plantations in India. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 13(3):127–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-010-0064-1
Kesari V, Krishnamachari A, Rangan L (2008) Systematic characterisation and seed oil analysis in candidate plus trees of biodiesel plant, Pongamia pinnata. Ann Appl Biol 152:397–404. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2008.00231.x
Kesari V, Sudarshan M, Das A, Rangan L (2009) PCR amplification of the genomic DNA from the seeds of Ceylon ironwood, Jatropha, and Pongamia. Biomass Bioenergy 33:1724–1728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2009.08.005
Kesari V, Das A, Rangan L (2010a) Physico-chemical characterization and antimicrobial activity from seed oil of Pongamia pinnata, a potential biofuel crop. Biomass Bioenerg 34(1):108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2009.10.006
Kesari V, Madurai Sathyanarayana V, Parida A, Rangan L (2010b) Molecular marker-based characterization in candidate plus trees of Pongamia pinnata, a potential biodiesel legume. AoB Plants. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plq017
Kumar B, Kumar U, Yadav Hemant K (2015) Identification of EST–SSRs and molecular diversity analysis in Mentha piperita. Crop J 3:335–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.02.002
Mall RK, Gupta A, Singh R, Singh RS, Rathore LS (2006) Water resourcesand climate change: an Indian perspective. Curr Sci 90:1610–1626
McConn M, Browse J (1996) The critical requirement for linolenic acid is pollen development, not photosynthesis, in an Arabidopsis mutant. Plant Cell 8:403–416. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.8.3.403
Met Office (2011) Climate: Observations, projections and impacts-India. Hadley Center, UK Met Office: Exeter, UK
Metz J, Ribbers K, Tielborger K, Muller C (2014) Long- and medium-term effects of aridity on the chemical defense of a widespread Brassicaceae in the Mediterranean. Environ Exp Bot 105:39–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2014.04.007
Riar DS, Rustgi S, Burke IC, Gill KS, Yenish JP (2011) EST-SSR development from 5 lactuca species and their use in studying genetic diversity among L. serriola Biotypes. J Hered 102:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esq103
Savadi SB, Fakrudin B, Nadaf HL, Gowda MVC (2012) Transferability of sorghum genic microsatellite markers to peanut. Am J Plant Sci 3:4. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2012.39142
Shelke RG, Rangan L (2019) Isolation and characterisation of Ty1-copia retrotransposons from Pongamia pinnata. Trees. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-019-01878-7
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy: the principles and pratice of numerical classification. Freeman, San Francisco, p 573
Sorkheh K, Prudencio AS, Ghebinejad A, Dehkordi MK, Erogul D, Rubio M, Martinez-Gomez P (2016) In silico search, characterization and validation of new EST-SSR markers in the genus Prunus. BMC Res Notes 9:336. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-016-2143-y
Sreeharsha RV, Mudalkar S, Singha KT, Reddy AR (2016) Unravelling molecular mechanisms from floral initiation to lipid biosynthesis in a promising biofuel tree species, Pongamia pinnata using transcriptome analysis. Sci Rep 6:34315. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34315
Thiel T, Michalek W, Varshney R, Graner A (2003) Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 106:411–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1031-0
Toth G, Gaspari Z, Jurka J (2000) Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes: survey and analysis. Genome Res 10:967–981
Ul Haq S, Kumar P, Singh RK, Verma KS, Bhatt R, Sharma M, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2016) Assessment of functional EST-SSR markers (sugarcane) in cross-species transferability, genetic diversity among poaceae plants, and bulk segregation analysis. Genet Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7052323
Wang Z, Yu G, Shi B, Wang X, Qiang H, Gao H (2014) Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers based on rna-sequencing of Medicago sativa and in silico mapping onto the M. truncatula genome. PLoS ONE 9:e92029. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092029
Warner K, Ranger N, Surminski S, Arnold M, Linnnerooth-Bayer J, Michel-Kerjan E, Kovacs P, Herweijer C (2009) Adaptation to climate change: linking disaster risk reduction and insurance. United Nations International Strategy for Disaster Reduction Secretariat (UNISDR): Geneva, Switzerland. 18
Yadav HK, Alok R, Asif MH, Shrikant M, Sawant SV, Rakesh T (2011) EST-derived SSR markers in Jatropha curcas L.: development, characterization, polymorphism, and transferability across the species/genera. Tree Genet Genomes 7:207–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0326-6
Yamauchi T, Shiono K, Nagano M, Fukazawa A, Ando M, Takamure I, Mori H, Nishizawa NK, Kawai-Yamada M, Tsutsumi N, Kato K, Nakazono M (2015) Ethylene biosynthesis is promoted by very-long-chain fatty acids during Lysigenous aerenchyma formation in rice roots. Plant Physiol 169:180–193. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.00106
Yan Z, Wu F, Luo K, Zhao Y, Yan Q, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhang J (2017) Cross-species transferability of EST-SSR markers developed from the transcriptome of Melilotus and their application to population genetics research. Sci Rep 7:17959
Zhang K, Wu Z, Tang D, Lv C, Luo K, Zhao Y, Liu X, Huang Y, Wang J (2016) Development and identification of SSR markers associated with starch properties and N2-carotene content in the storage root of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Front Plant Sci 7:223. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00223
Zheng G, Tian B, Zhang F, Tao F, Li W (2011) Plant adaptation to frequent alterations between high and low temperatures: remodelling of membrane lipids and maintenanceof unsaturation levels. Plant, Cell Environ 34(9):1431–1442. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02341.x
Zhu H, Song P, Koo DH, Guo L, Li Y, Sun S, Weng Y, Yang L (2016) Genome wide characterization of simple sequence repeats in watermelon genome and their application in comparative mapping and genetic diversity analysis. BMC Genom 17:557. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2870-4
Acknowledgements
RGS thank Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), Government of India for student fellowship. Authors thank Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering IIT Guwahati for all infrastructural support and facilities. Thanks also to BIF facility supported by Department of Biotechnology (DBT) Govt. of India for computing facility (BT/BI/12/064/2012 NER-BIF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RGS and LR conceived and designed the experiments. RGS performed the experiments; RGS and SB analyzed the data. LR contributed to reagents/materials/analysis tools. LR, RGS and SB wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shelke, R.G., Basak, S. & Rangan, L. Development of EST-SSR markers for Pongamia pinnata by transcriptome database mining: cross-species amplification and genetic diversity. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26, 2225–2241 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00889-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-020-00889-w