Abstract
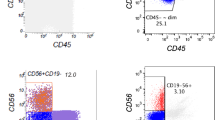
Subclinical PNH can be present in patients with bone marrow failure like aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Such clone may have prognostic and therapeutic implications. In literature around 1–10% MDS cases have shown a PNH clone, however, data from India is relatively scarce. A high sensitivity PNH assay was employed using a single tube combination of FLAER, CD157, CD64, CD15 and CD45 antibodies in adult patients of MDS at presentation. A clone size of > 0.01% was taken as significant. A total of 30 patients were included. PNH clone was present in 30% cases. Correlation done between PNH clone size and LDH values showed moderately positive correlation (r = 0.735, p = 0.001, r2 = 0.541). As per this study a LDH cut off of 247 IU is likely to predict a PNH clone (> 1%) with moderate sensitivity and specificity. High sensitivity PNH assay is able to detect small PNH clone. Calculating the cut-off of LDH to predict PNH positivity can help us judiciously prescribe this test in MDS patients in resource constrained settings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bessler M, Mason PJ, Hillmen P, Miyata T, Yamada N, Takeda N, Luzzatto L, Kinoshita T (1994) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is caused by somatic mutations in the PIG-A gene. EMBO J 13:110–117
Borowitz MJ, Craig FE, Digiuseppe JA, Illingworth AJ, Rosse W, Sutherland DR, Wittwer CT, Richards SJ (2010) Guidelines for the diagnosis and monitoring of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and related disorders by flow cytometry. Cytom B Clin Cytom 78:211–230
Wang SA, Pozdnyakova O, Jorgensen JL, Medeiros LJ, Stachurski D, Anderson M et al (2009) Detection of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes and related bone marrow diseases, with emphasis on diagnostic pitfalls and caveats. Haematologica 94:29–36
Scheinberg P, Marte M, Nunez O, Young NS (2010) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones in severe aplastic anemia patients treated with horse anti-thymocyte globulin plus cyclosporine. Haematologica 95:1075–1080
Young NS (2009) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and myelodysplastic sydromes: clonal expansion of PIG-A-mutant hematopoietic cells in bone marrow failure. Haematologica 94(1):3–7
Brodsky RA (2017) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, Heslop HE, Anastasi J, Abutalib SA et al (eds) Hematology: basic principles and practice, 7th edn. Elsevier, Philadelphia, p 417
Chopra A, Pati H, Mahapatra M, Mishra P, Seth T, Kumar S et al (2012) Flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndrome: analysis of diagnostic utility using maturation pattern-based and quantitative approaches. Ann Hematol 91(9):1351–1362
Shah NM, Prajapati SG, Adesara RP, Patel AP (2009) An analysis of 30 cases of myelodysplastic syndrome. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 52(2):206–209
Vundinti BR, Kerketta L, Jijina F, Ghosh K (2009) Cytogenetic study of myelodysplastic syndrome from India. Indian J Med Res 130(2):155–159
Aul C, Gattermann N, Schneider W (1992) Age-related incidence and other epidemiological aspects of myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 82(2):358–367
Chatterjee T, Dixit A, Mohapatra M, Tyagi S, Gupta PK, Mishra P et al (2004) Clinical, haematological and histomorphological profile of adult myelodysplastic syndrome. Study of 96 cases in a single institute. Eur J Haematol 73(2):93–97
Raza A, Ravandi F, Rastogi A, Bubis J, Lim SH, Weitz I, Castro-Malaspina H, Galili N, Jawde RA, Illingworth A (2014) A prospective multicenter study of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells in patients with bone marrow failure. Cytom B Clin Cytom 86:175–182
Agarwal R, Chapple P, Brown M, Szer J, Juneja S (2015) Analysis of abnormal clones by the fluorescent aerolysin method in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria and other marrow disorders. Int J Lab Hematol 37:14–21
Wang H, Chuhjo T, Yasue S, Omine M, Nakao S (2002) Clinical significance of a minor population of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria-type cells in bone marrow failure syndrome. Blood 100:3897–3902
Vundinti BR, Kerketta L, Jijina F, Ghosh K (2009) Cytogenetic study of myelodysplastic syndrome from India. Indian J Med Res 130(2):155–159
Chaubey R, Sazawal S, Dada R, Mahapatra M, Saxena R (2011) Cytogenetic profile of Indian patients with de novo myelodysplastic syndromes. Indian J Med Res 134:452–457
Ogata K (2008) Diagnostic flow cytometry for low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes. Hematol Oncol 26(4):193–198
Pozdnyakova O, Miron PM, Tang G, Walter O, Raza A, Woda B et al (2008) Cytogenetic abnormalities in a series of 1029 patients with primary myelodysplastic syndromes: a report from the US with a focus on some undefined single chromosomal abnormalities. Cancer 113(12):3331–3340
Haase D, Germing U, Schanz J, Pfeilstocker M, Nosslinger T, Hildebrandt B et al (2007) New insights into the prognostic impact of the karyotype in MDS and correlation with subtypes: evidence from a core dataset of 2124 patients. Blood 110(13):4385–4395
Shih A, Chin-Yee IH, Hedley B, Keeney M, Wells RA, Sutherland DR, Hsia CC (2011) Screening patients with myelodysplastic syndrome and aplastic anemia for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones: a retrospective study. Blood 118(21):3426
Illingworth A, Marinov I, Sutherland DR, Wagner-Ballon O, DelVecchio L (2018) ICCS/ESCCA consensus guidelines to detect GPI-deficient cells in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) and related disorders part 3—data analysis, reporting and case studies. Cytom Part B 94B:49–66
Sutherland DR, Keeney M, Illingworth A (2012) Practical guidelines for the high sensitivity detection and monitoring of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones by flow cytometry. Cytom B Clin Cytom 82(4):195–208
Dunn DE, Tanawattanacharoen P, Boccuni P et al (1999) Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells in patients with bone marrow failure syndromes. Ann Intern Med 131:401–408
Rocha JMC, Silva ML, Souza MEL, Murao M, Araújo SSDS, Santos SME (2014) Detection of PNH cells by flow cytometry, using multiparameter analysis. J Bras Pathol Med Lab 50:105–114
Rocha JMC, Silva ML, Souza MEL, Murao M, Araújo SSDS, Santos SME (2014) Detection of PNH cells by flow cytometry, using multiparameter analysis. J Bras Patol Med Lab 50:105–114
Gupta SK, Pati HP, Tejomurtula AP, Seth T (2010) PNH clone assessment by flow cytometry and its clinical correlation in PNH and aplastic anemia. J Hematopathol 3(4):137–143
Rahman K, Gupta R, Yadav G, Husein N, Singh MK, Nityanand S (2017) Fluorescent aerolysin (FLAER)-based paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) screening: a single center experience from India. Int J Lab Hematol 39(3):261–271
Donohue RE, Marcogliese AN, Sasa GS, Elghetany MT, Redkar AA, Bertuch AA, Curry CV (2018) Standardized high-sensitivity flow cytometry testing for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria in children with acquired bone marrow failure disorders: a single center us study. Cytom Part B 94:699–704
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Sir Ganga Ram Hospital for providing infrastructure to conduct the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naim, F., Saraf, A., Dass, J. et al. A Prospective, Cross Sectional Study of PNH Clone in MDS Patients Using High Sensitivity Flowcytometry: A Single Center Experience. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 36, 519–525 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-019-01219-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-019-01219-1