Abstract
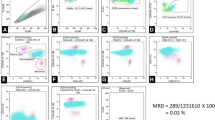
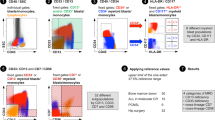
Minimal residual disease is currently the most powerful prognostic indicator in Precursor B lymphoblastic leukemia. Multiparameter flow cytometry is the most commonly used modality. Seventy three B ALL cases and 15 normal marrows were evaluated for expression patterns of leukemia markers (CD38, CD58, CD73) in all 73 cases and CD66c, CD86 and CD123 in 23 cases. CD73 was aberrantly expressed in 90.41% cases and CD86 in 60.87% B ALL cases. Thus addition of these markers in MRD panels can increase the sensitivity of the assay.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campana D, Coustan-Smith E (1999) Detection of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia by flow cytometry. Cytometry 38:139–152
Coustan-Smith E, Sancho J, Behm FG, Hancock ML, Razzouk BI, Ribeiro RC et al (2002) Prognostic importance of measuring early clearance of leukemic cells by flow cytometry in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 100(1):52–58
Borowitz MJ, Pullen DJ, Shuster JJ, Viswanatha D, Montogomery K, Willman CL et al (2003) Minimal residual disease in childhood precursor B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: relation to other risk factors. A Children’s Oncology Group Study. Leukemia 17:1566–1572
Bruggemann M, Raff T, Kneba M (2012) Has MRD monitoring superseded other prognostic factors in adult ALL? Blood 120(23):4470–4481
Coustan Smith E, Song G, Clark C, Key L, Liu P, Mehrpooya M et al (2011) New markers for minimal residual disease detection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 117(23):6267–6276
Cave H, van der Werff ten Bosch J, Suciu S, Guidal C, Waterkeyn C, Otten J et al (1998) Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer—Childhood Leukemia Cooperative Group. N Engl J Med 339(9):591–598
Coustan-Smith E, Behm FG, Sanchez J, Boyett JM, Hancock ML, Raimondi SC et al (1998) Immunological detection of minimal residual disease in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 351(9102):550–554
van Dongen JJ, Seriu T, Panzer-Grumayer ER, Biondi A, Pongers-Willemse MJ, Corral L et al (1998) Prognostic value of minimal residual disease in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in childhood. Lancet 352:1731–1738
Dhédin N, Huynh A, Maury S, Tabrizi R, Beldjord K, Asnafi V et al (2015) Role of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with Ph-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 125(16):2486–2496
Wang W, Gao L, Li Y, Li ZL, Gong M, Huang FZ et al (2016) The application of CD73 in minimal residual disease monitoring using flow cytometry in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 57(5):1174–1181. doi:10.3109/10428194.2015.1070153
Patkar N, Abu Alex A, Bargavi B (2012) Standardizing minimal residual disease by flow cytometry for precursor B lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a developing country. Cytom B Clin Cytom 82B:252–258
Tembhare PR, Ghogale S, Ghatwai N, Badrinath Y, Kunder N, Patkar NV et al (2016) Evaluation of new markers for minimal residual disease monitoring in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia: CD73 and CD86 are the most relevant new markers to increase the efficacy of MRD 2016; 00B: 000–000. Cytom B Clin Cytom. doi:10.1002/cyto.b.21486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Approval from Institute board for conducting the study was taken.
Human and Animal Rights
No animals were included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, S., Mehta, A., Kapoor, G. et al. Evaluating New Markers for Minimal Residual Disease Analysis by Flow Cytometry in Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 34, 48–53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0845-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0845-5