Abstract
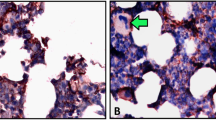
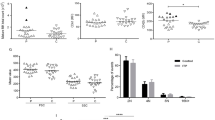
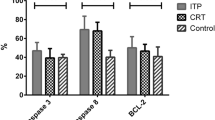
To investigate the contribution and mechanism of eosinophil granulocytes and NK cells-mediated cytotoxicity to the pathogenesis of ITP. Mononuclear cells and platelets were prepared from the bone marrow of 16 ITP patients and 10 healthy controls. Separately, eosinophil granulocytes and NK cells were selected with magnetic microbeads. As the target cells, the autologous platelets were cultured with eosinophil granulocytes and NK cells respectively for 6 h and then stained with annexin V. Ratio of platelets expressing annexin V was determined by flow cytometry. The fraction of NK cells expressing perforin, granzyme B, FasL and TNF were determined by flow cytometry. Human eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) level in the bone marrow was determined by ECP ELISA kit. The annexin V positive platelet ratio of the ITP group was significantly higher than that of the control group; the expression rates of granzyme B, perforin, FasL on NK cells of the ITP group were significantly higher than those of the control group. Expression of human ECP in bone marrow of immune thrombocytopenia patients was higher than that of healthy controls. NK cells and eosinophil granulocytes are activated in ITP and might be involved in the pathogenesis of ITP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang F, Chu X, Wang L, Zhu Y, Li L, Ma D, Peng J, Hou M (2006) cell-mediated lysis of autologous platelets in chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur J Haematol 76(5):427–431
Olsson B, Andersson PO, Jacobsson S, Carlsson L, Wadenvik H (2005) Disturbed apoptosis of T-cells in patients with active idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Haemost 93(1):139–144
Heyns Adu P, Badenhorst PN, Lotter MG, Pieters H, Wessels P, Kotze HF (1986) Platelet turnover and kinetics in immune thrombocytopenic purpura: results with autologous 3In-labeled platelets and homologous 51Cr-labeled platelets differ. Blood 67(1):86–92
Chin NS, Koong PL (1990) A study of 31 patients with easy bruising from University Hospital, Kuala Lumpur. Med J Malays 45(4):325–328
Laosombat V, Wongchanchailert M, Sattayasevana B, Kietthubthew S, Wiriyasateinkul A (2001) Acquired platelet dysfunction with eosinophilia in children in the south of Thailand. Platelets 12(1):5–14
Lucas GN, Seneviratne TR (1996) A case of acquired platelet dysfunction with eosinophilia. Ceylon Med J 41(3):122
Maziero AM, Lorenzetti R, Donato JL, Lilla S, De Nucci G (2013) Inhibition of human platelet aggregation by eosinophils. Life Sci 93(9–11):416–422
Cao JY, Wang H (2004) Role of Fas-FasL in insulitis in nonobese diabetic mouse. Chin Med J (Engl) 117(4):615–617
Podack ER, Lowrey DM, Lichtenheld M, Olsen KJ, Aebischer T, Binder D, Rupp F, Hengartner H (1988) Structure, function and expression of murine and human perforin 1 (P1). Immunol Rev 103:203–211
Shi L, Mai S, Israels S, Browne K, Trapani JA, Greenberg AH (1997) Granzyme B (GraB) autonomously crosses the cell membrane and perforin initiates apoptosis and GraB nuclear localization. J Exp Med 185(5):855–866
Rasp G, Thomas PA, Bujia J (1994) Eosinophil inflammation of the nasal mucosa in allergic and allergic and non-allergic rhinitis measured by eosinophil cationic protein levels in native nasal fluid and serum. Clin Exp Allergy 24(12):1151–1156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Wang Shuguo declares that he has no conflict of interest. Liu Fenghai declares that he has no conflict of interest. Zhao Hongguo declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of The Affiliated Qingdao Municipal Hospital of Qingdao University and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Liu, F. & Zhao, H. Eosinophil Granulocyte and NK Cell-Mediated Platelet Destruction in Immune Thrombocytopenia. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 34, 121–124 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0830-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-017-0830-z