Abstract
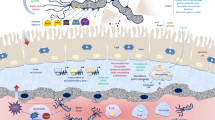
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) is a specific subset of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) strains that are characterized by their ability to cause bloody diarrhea (hemorrhagic colitis) and potentially life-threatening, extraintestinal complications such as hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), which is associated with acute renal failure., contributing to severe clinical outcomes. The Shiga toxins (Stxs), produced by EHEC, are primary virulence factors. These potent cytotoxins are composed of one enzymatically active A subunit (StxA) and five receptor-binding B subunits (StxB). Although the toxins are primarily associated with cytotoxic effects, they also elicit other pathogenic consequences due to their induction of a number of biological processes, including apoptosis through ER-stress, pro-inflammatory responses, autophagy, and post-translational modification (PTM). Moreover, several studies have reported the association between Stxs and extracellular vesicles (EVs), including microvesicles and exosomes, demonstrating that Stx-containing EVs secreted by intoxicated macrophages are taken up by recipient cells, such as toxin-sensitive renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. This mechanism likely contributes to the spreading of Stxs within the host, and may exacerbate gastrointestinal illnesses and kidney dysfunction. In this review, we summarize recent findings relating to the host responses, in different types of cells in vitro and in animal models, mediated by Stxs-containing exosomes. Due to their unique properties, EVs have been explored as therapeutic agents, drug delivery systems, and diagnostic tools. Thus, potential therapeutic applications of EVs in EHEC Stxs-mediated pathogenesis are also briefly reviewed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuña, S. M., Floeter-Winter, L. M., & Muxel, S. M. (2020). microRNAs: Biological regulators in pathogen-host interactions. Cells, 9, 113.
Adams, N. L., Byrne, L., Smith, G. A., Elson, R., Harris, J. P., Salmon, R., Smith, R., O’Brien, S. J., Adak, G. K., & Jenkins, C. (2016). Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157, England and Wales, 1983–2012. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 22, 590–597.
Arvidsson, I., Ståhl, A. L., Hedström, M. M., Kristoffersson, A. C., Rylander, C., Westman, J. S., Storry, J. R., Olsson, M. L., & Karpman, D. (2015). Shiga toxin-induced complement-mediated hemolysis and release of complement-coated red blood cell-derived microvesicles in hemolytic uremic syndrome. The Journal of Immunology, 194, 2309–2318.
Atay, S., Gercel-Taylor, C., & Taylor, D. D. (2011). Human trophoblast-derived exosomal fibronectin induces pro-inflammatory IL-1β production by macrophages. American Journal of Reproductive Immunology, 66, 259–269.
Bahmani, L., & Ullah, M. (2022). Different sourced extracellular vesicles and their potential applications in clinical treatments. Cells, 11, 1989.
Bai, X., Fu, S., Zhang, J., Fan, R., Xu, Y., Sun, H., He, X., Xu, J., & Xiong, Y. (2018). Identification and pathogenomic analysis of an Escherichia coli strain producing a novel shiga toxin 2 subtype. Scientific Reports, 8, 6756.
Bebelman, M. P., Smit, M. J., Pegtel, D. M., & Baglio, S. R. (2018). Biogenesis and function of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 188, 1–11.
Behrens, F., Holle, J., Kuebler, W. M., & Simmons, S. (2020). Extracellular vesicles as regulators of kidney function and disease. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental, 8, 22.
Biadglegne, F., Rademacher, P., De Sulbaran, Y. G. J., König, B., Rodloff, A. C., Zedler, U., Dorhoi, A., & Sack, U. (2021). Exosomes in serum–free cultures of THP–1 macrophages infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Molecular Medicine Reports, 24, 815.
Bitzan, M., Richardson, S., Huang, C., Boyd, B., Petric, M., & Karmali, M. A. (1994). Evidence that verotoxins (shiga-like toxins) from Escherichia coli bind to p blood group antigens of human erythrocytes in vitro. Infection and Immunity, 62, 3337–3347.
Borges, F. T., Reis, L. A., & Schor, N. (2013). Extracellular vesicles: Structure, function, and potential clinical uses in renal diseases. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 46, 824–830.
Boss, I. W., & Renne, R. (2011). Viral miRNAs and immune evasion. BBA Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 1809, 708–714.
Cai, H., Reinisch, K., & Ferro-Novick, S. (2007). Coats, tethers, rabs, and SNAREs work together to mediate the intracellular destination of a transport vesicle. Developmental Cell, 12, 671–682.
Cao, Q., Huang, C., Chen, X. M., & Pollock, C. A. (2022). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in chronic kidney disease. Frontiers in Medicine, 9, 816656.
Carnero, E., Sutherland, J. D., & Fortes, P. (2011). Adenovirus and miRNAs. BBA Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 1809, 660–667.
Chang, W. H., Cerione, R. A., & Antonyak, M. A. (2021). Extracellular vesicles and their roles in Cancer Progression. In M. Robles-Flores (Ed.), Cancer Cell Signaling. Methods in Molecular Biology (p. 143). US: Humana.
Chen, L., Yao, X., Yao, H., Ji, Q., Ding, G., & Liu, X. (2020). Exosomal mir-103-3p from LPS-activated THP-1 macrophage contributes to the activation of hepatic stellate cells. The FASEB Journal, 34, 5178–5192.
Chen, J., Tan, Q., Yang, Z., & Jin, Y. (2022). Engineered extracellular vesicles: Potentials in cancer combination therapy. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 20, 132.
Cherla, R. P., Lee, S. Y., Mees, P. L., & Tesh, V. L. (2006). Shiga toxin 1-induced cytokine production is mediated by map kinase pathways and translation initiation factor eIF4E in the macrophage-like THP-1 cell line. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 79, 397–407.
Ching, J. C. Y., Jones, N. L., Ceponis, P. J., Karmali, M. A., & Sherman, P. M. (2002). Escherichia coli shiga-like toxins induce apoptosis and cleavage of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase via in vitro activation of caspases. Infection and Immunity, 70, 4669–4677.
Chinnappan, M., Srivastava, A., Amreddy, N., Razaq, M., Pareek, V., Ahmed, R., Mehta, M., Peterson, J. E., Munshi, A., & Ramesh, R. (2020). Exosomes as drug delivery vehicle and contributor of resistance to anticancer drugs. Cancer Letters, 486, 18–28.
Christianson, H. C., Svensson, K. J., van Kuppevelt, T. H., Li, J. P., & Belting, M. (2013). Cancer cell exosomes depend on cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans for their internalization and functional activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110, 17380–17385.
Clancy, J., & D’Souza-Schorey, C. (2018). Extracellular vesicles in cancer: Purpose and promise. Cancer Journal, 24, 65–69.
Condrat, C. E., Thompson, D. C., Barbu, M. G., Bugnar, O. L., Boboc, A., Cretoiu, D., Suciu, N., Cretoiu, S. M., & Voinea, S. C. (2020). miRNAs as biomarkers in disease: Latest findings regarding their role in diagnosis and prognosis. Cells, 9, 276.
Delrue, C., De Bruyne, S., Speeckaert, R., & Speeckaert, M. M. (2023). Urinary extracellular vesicles in chronic kidney disease: From bench to bedside? Diagnostics, 13, 443.
Doyle, L. M., & Wang, M. Z. (2019). Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells, 8, 727.
DuPont, H. L. (2007). The growing threat of foodborne bacterial enteropathogens of animal origin. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 45, 1353–1361.
Elsharkasy, O. M., Nordin, J. Z., Hagey, D. W., de Jong, O. G., Schiffelers, R. M., Andaloussi, S. E., & Vader, P. (2020). Extracellular vesicles as drug delivery systems: Why and how? Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 159, 332–343.
Endo, Y., Tsurugi, K., Yutsudo, T., Takeda, Y., Ogasawara, T., & Igarashi, K. (1988). Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. European Journal of Biochemistry, 171, 45–50.
Erdbrügger, U., Blijdorp, C. J., Bijnsdorp, I. V., Borràs, F. E., Burger, D., Bussolati, B., Byrd, J. B., Clayton, A., Dear, J. W., Falcón-Pérez, J. M., et al. (2021). Urinary extracellular vesicles: A position paper by the urine task force of the international society for extracellular vesicles. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 10, e12093.
Erickson, M. C., & Doyle, M. P. (2007). Food as a vehicle for transmission of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Journal of Food Protection, 70, 2426–2449.
Escrevente, C., Keller, S., Altevogt, P., & Costa, J. (2011). Interaction and uptake of exosomes by ovarian cancer cells. Bmc Cancer, 11, 108.
FAO/WHO STEC Expert Group. (2019). Hazard identification and characterization: Criteria for categorizing shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli on a risk basis. Journal of Food Protection, 82, 7–21.
Feng, D., Zhao, W. L., Ye, Y. Y., Bai, X. C., Liu, R. Q., Chang, L. F., Zhou, Q., & Sui, S. F. (2010). Cellular internalization of exosomes occurs through phagocytosis. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark), 11, 675–687.
Fitzner, D., Schnaars, M., van Rossum, D., Krishnamoorthy, G., Dibaj, P., Bakhti, M., Regen, T., Hanisch, U. K., & Simons, M. (2011). Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. Journal of Cell Science, 124, 447–458.
Fraser, M. E., Chernaia, M. M., Kozlov, Y. V., & James, M. N. (1994). Crystal structure of the holotoxin from Shigella dysenteriae at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature Structural Biology, 1, 59–64.
Fraser, M. E., Fujinaga, M., Cherney, M. M., Melton-Celsa, A. R., Twiddy, E. M., O’Brien, A. D., & James, M. N. (2004). Structure of shiga toxin type 2 (Stx2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 27511–27517.
Friesema, I. H. M., Kuiling, S., Igloi, Z., & Franz, E. (2021). Optimization of notification criteria for shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli surveillance, the netherlands. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 27, 258–261.
Gai, X., Tang, B., Liu, F., Wu, Y., Wang, F., Jing, Y., Huang, F., Jin, D., Wang, L., & Zhang, H. (2019). mTOR/miR-145-regulated exosomal GOLM1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma through augmented GSK-3β/MMPs. Journal of Genetics and Genomics, 46, 235–245.
Géminard, C., De Gassart, A., Blanc, L., & Vidal, M. (2004). Degradation of AP2 during reticulocyte maturation enhances binding of Hsc70 and Alix to a common site on TfR for sorting into exosomes. Traffic (Copenhagen, Denmark), 5, 181–193.
Gomes, T. A., Elias, W. P., Scaletsky, I. C. A., Guth, B. E. C., Rodrigues, J. F., Piazza, R. M. F., Ferreira, L. C. S., & Martinez, M. B. (2016). Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 47, 3–30.
Grange, C., & Bussolati, B. (2022). Extracellular vesicles in kidney disease. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 18, 499–513.
Guay, C. (2019). Lymphocyte-derived exosomal microRNAs promote pancreatic β cell death and may contribute to type 1 diabetes development. Cell Metabolism, 29, 348–361.
Guessous, F., Marcinkiewicz, M., Polanowska-Grabowska, R., Keepers, T. R., Obrig, T., & Gear, A. R. (2005). Shiga toxin 2 and lipopolysaccharide cause monocytic THP-1 cells to release factors which activate platelet function. Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 94, 1019–1027.
Hao, S., Bai, O., Li, F., Yuan, J., Laferte, S., & Xiang, J. (2007). Mature dendritic cells pulsed with exosomes stimulate efficient cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses and antitumour immunity. Immunology, 120, 90–102.
Havelaar, A. H., Kirk, M. D., Torgerson, P. R., Gibb, H. J., Hald, T., Lake, R. J., Praet, N., Bellinger, D. C., de Silva, N. R., Gargouri, N., et al. (2015). World Health Organization global estimates and regional comparisons of the burden of foodborne disease in 2010. PLoS Medicine, 12, e1001923.
Hazrati, A., Soudi, S., Malekpour, K., Mahmoudi, M., Rahimi, A., Hashemi, S. M., & Varma, R. S. (2022). Immune cells-derived exosomes function as a double-edged sword: Role in disease progression and their therapeutic applications. Biomarker Research, 10, 30.
He, X., Quiñones, B., Loo, M. T., Loos, S., Scavia, G., Brigotti, M., Levtchenko, E., & Monnens, L. (2015). Serum shiga toxin 2 values in patients during acute phase of diarrhoea-associated haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Acta Paediatrica, 104, e564–e568.
Hehnly, H., Sheff, D., & Stamnes, M. (2006). Shiga toxin facilitates its retrograde transport by modifying microtubule dynamics. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 17, 4379–4389.
Henkel, J. S., Baldwin, M. R., & Barbieri, J. T. (2010). Toxins from bacteria. In A. Luch (Ed.), Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology. Experientia Supplementum (pp. 1–29). Basel: Birkhäuser.
Herrmann, I. K., Wood, M. J. A., & Fuhrmann, G. (2021). Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nature Nanotechnology, 16, 748–759.
Hessvik, N. P., & Llorente, A. (2018). Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 75, 193–208.
Hugel, B., Martínez, M. C., Kunzelmann, C., & Freyssinet, J. M. (2005). Membrane microparticles: Two sides of the coin. Physiology, 20, 22–27.
Hum, C., Loiselle, J., Ahmed, N., Shaw, T. A., Toudic, C., & Pezacki, J. P. (2021). MicroRNA mimics or inhibitors as antiviral therapeutic approaches against COVID-19. Drugs, 81, 517–531.
Hussen, B. M., Hidayat, H. J., Salihi, A., Sabir, D. K., Taheri, M., & Ghafouri-Fard, S. (2021). MicroRNA: A signature for cancer progression. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 138, 111528.
Inal, J. M., Ansa-Addo, E. A., Stratton, D., Kholia, S., Antwi-Baffour, S. S., Jorfi, S., & Lange, S. (2012). Microvesicles in health and disease. Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis, 60, 107–121.
Iordanov, M. S., Pribnow, D., Magun, J. L., Dinh, T. H., Pearson, J. A., Chen, S. L., & Magun, B. E. (1997). Ribotoxic stress response: Activation of the stress-activated protein kinase JNK1 by inhibitors of the peptidyl transferase reaction and by sequence-specific RNA damage to the alpha-sarcin/ricin loop in the 28S rRNA. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 17, 3373–3381.
Iranifar, E., Seresht, B. M., Momeni, F., Fadaei, E., Mehr, M. H., Ebrahimi, Z., Rahmati, M., Kharazinejad, E., & Mirzaei, H. (2019). Exosomes and microRNAs: New potential therapeutic candidates in Alzheimer disease therapy. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234, 2296–2305.
Jeon, J. S., Kim, E., Bae, Y. U., Yang, W. M., Lee, H., Kim, H., Noh, H., Han, D. C., Ryu, S., & Kwon, S. H. (2020). MicroRNA in extracellular vesicles released by damaged podocytes promote apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells. Cells, 9, 1409.
Jeppesen, D. K., Fenix, A. M., Franklin, J. L., Higginbotham, J. N., Zhang, Q., Zimmerman, L. J., Liebler, D. C., Ping, J., Liu, Q., Evans, R., et al. (2019). Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell, 177, 428–445.
Jerse, A. E., Yu, J., Tall, B. D., & Kaper, J. B. (1990). A genetic locus of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli necessary for the production of attaching and effacing lesions on tissue culture cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 87, 7839–7843.
Johansson, K., Willysson, A., Kristoffersson, A. C., Tontanahal, A., Gillet, D., Ståhl, A. L., & Karpman, D. (2020). Shiga toxin-bearing microvesicles exert a cytotoxic effect on recipient cells only when the cells express the toxin receptor. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 10, 212.
Joseph, A., Cointe, A., Mariani Kurkdjian, P., Rafat, C., & Hertig, A. (2020). Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: A narrative review. Toxins, 12, 67.
Karpman, D., Papadopoulou, D., Nilsson, K., Sjögren, A. C., Mikaelsson, C., & Lethagen, S. (2001). Platelet activation by Shiga toxin and circulatory factors as a pathogenetic mechanism in the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood, 97, 3100–3108.
Kim, I., Xu, W., & Reed, J. C. (2008). Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 7, 1013–1030.
Kim, J., Yao, F., Xiao, Z., Sun, Y., & Ma, L. (2018). MicroRNAs and metastasis: Small RNAs play big roles. Cancer and Metastasis Reviews, 37, 5–15.
Kim, J. S., Lee, M. S., & Kim, J. H. (2020). Recent updates on outbreaks of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and its potential reservoirs. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 10, 273.
Kodali, M., Castro, O. W., Kim, D. K., Thomas, A., Shuai, B., Attaluri, S., Upadhya, R., Gitai, D., Madhu, L. N., Prockop, D. J., et al. (2019). Intranasally administered human MSC-derived extracellular vesicles pervasively incorporate into neurons and microglia in both intact and status epilepticus injured forebrain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21, 181.
Krause, M., Samoylenko, A., & Vainio, S. J. (2015). Exosomes as renal inductive signals in health and disease, and their application as diagnostic markers and therapeutic agents. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 3, 65.
Lacher, D. W., Gangiredla, J., Patel, I., Elkins, C. A., & Feng, P. C. H. (2016). Use of the Escherichia coli identification microarray for characterizing the health risks of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from foods. Journal of Food Protection, 79, 1656–1662.
Lagatie, O., Tritsmans, L., & Stuyver, L. J. (2013). The miRNA world of polyomaviruses. Virology Journal, 10, 268.
Landskroner-Eiger, S., Moneke, I., & Sessa, W. C. (2013). miRNAs as modulators of angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, 3, a006643.
Lee, M. S., & Tesh, V. L. (2019). Roles of Shiga toxins in immunopathology. Toxins, 11, 212.
Lee, M. S., Cherla, R. P., Leyva-Illades, D., & Tesh, V. L. (2009). Bcl-2 regulates the onset of shiga toxin 1-induced apoptosis in THP-1 cells. Infection and Immunity, 77, 5233–5244.
Lee, M. S., Koo, S., Jeong, D. G., & Tesh, V. L. (2016). Shiga toxins as multi-functional proteins: Induction of host cellular stress responses, role in pathogenesis and therapeutic applications. Toxins, 8, 77.
Lee, K. S., Lee, J., Lee, P., Kim, C. U., Kim, D. J., Jeong, Y. J., Park, Y. J., Tesh, V. L., & Lee, M. S. (2020). Exosomes released from Shiga toxin 2a-treated human macrophages modulate inflammatory responses and induce cell death in toxin receptor expressing human cells. Cell Microbiology, 22, e13249.
LeJeune, J. T., Besser, T. E., Merrill, N. L., Rice, D. H., & Hancock, D. D. (2001). Livestock drinking water microbiology and the factors influencing the quality of drinking water offered to cattle. Journal of Dairy Science, 84, 1856–1862.
Li, X., & Yang, L. (2022). Urinary exosomes: Emerging therapy delivery tools and biomarkers for urinary system diseases. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 150, 113055.
Li, C., Zhou, T., Chen, J., Li, R., Chen, H., Luo, S., Chen, D., Cai, C., & Li, W. (2022). The role of exosomal miRNAs in cancer. Journal of Translational Medicine, 20, 6.
Lin, Y., Zhang, C., Xiang, P., Shen, J., Sun, W., & Yu, H. (2020). Exosomes derived from HeLa cells break down vascular integrity by triggering endoplasmic reticulum stress in endothelial cells. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 9, 1722385.
Ling, H., Boodhoo, A., Hazes, B., Cummings, M. D., Armstrong, G. D., Brunton, J. L., & Read, R. J. (1998). Structure of the Shiga-like toxin I B-pentamer complexed with an analogue of its receptor Gb3. Biochemistry, 37, 1777–1788.
Locking, M. E., Pollock, K. G., Allison, L. J., Rae, L., Hanson, M. F., & Cowden, J. M. (2011). Escherichia coli O157 infection and secondary spread, scotland, 1999–2008. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 17, 524–527.
Lorenzen, J. M., Menne, J., Schmidt, B. M., Schmidt, M., Martino, F., Dietrich, R., Samiri, S., Worthmann, H., Heeren, M., Weissenborn, K., et al. (2012). Circulating microRNAs in patients with shiga-toxin-producing E. coli O104:H4 induced hemolytic uremic syndrome. Plos One, 7, e47215.
Ma, Y., Dong, S., Li, X., Kim, B. Y. S., Yang, Z., & Jiang, W. (2020). Extracellular vesicles: An emerging nanoplatform for cancer therapy. Frontiers In Oncology, 10, 606906.
Machiels, J. P., Lambrecht, M., Hanin, F. X., Duprez, T., Gregoire, V., Schmitz, S., & Hamoir, M. (2014). Advances in the management of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. F1000Prime Reports, 6, 44.
Mack, M., Kleinschmidt, A., Brühl, H., Klier, C., Nelson, P. J., Cihak, J., Plachý, J., Stangassinger, M., Erfle, V., & Schlöndorff, D. (2000). Transfer of the chemokine receptor CCR5 between cells by membrane-derived microparticles: A mechanism for cellular human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection. Nature Medicine, 6, 769–775.
Manzano-Román, R., & Siles-Lucas, M. (2012). MicroRNAs in parasitic diseases: Potential for diagnosis and targeting. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, 186, 81–86.
Marshall, K. E., Hexemer, A., Seelman, S. L., Fatica, M. K., Blessington, T., Hajmeer, M., Kisselburgh, H., Atkinson, R., Hill, K., Sharma, D., et al. (2020). Lessons learned from a decade of investigations of shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli outbreaks linked to leafy greens, United States and Canada. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 26, 2319–2328.
Mathieu, M., Martin-Jaular, L., Lavieu, G., & Théry, C. (2019). Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nature Cell Biology, 21, 9–17.
Matsuzaka, Y., & Yashiro, R. (2022). Extracellular vesicles as novel drug-delivery systems through intracellular communications. Membranes, 12, 550.
Melton-Celsa, A. R. (2014). Shiga toxin (stx) classification, structure, and function. Microbiology Spectrum, 2, EHEC–0024.
Miguel, V., Cui, J. Y., Daimiel, L., Espinosa-Díez, C., Fernández-Hernando, C., Kavanagh, T. J., & Lamas, S. (2018). The role of microRNAs in environmental risk factors, noise-induced hearing loss, and mental stress. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 28, 773–796.
Montecalvo, A., Larregina, A. T., Shufesky, W. J., Stolz, D. B., Sullivan, M. L. G., Karlsson, J. M., Baty, C. J., Gibson, G. A., Erdos, G., Wang, Z., et al. (2012). Mechanism of transfer of functional microRNAs between mouse dendritic cells via exosomes. Blood, 119, 756–766.
Morelli, A. E., Larregina, A. T., Shufesky, W. J., Sullivan, M. L. G., Stolz, D. B., Papworth, G. D., Zahorchak, A. F., Logar, A. J., Wang, Z., Watkins, S. C., et al. (2004). Endocytosis, intracellular sorting, and processing of exosomes by dendritic cells. Blood, 104, 3257–3266.
Morita, E., Sandrin, V., Chung, H. Y., Morham, S. G., Gygi, S. P., Rodesch, C. K., & Sundquist, W. I. (2007). Human ESCRT and ALIX proteins interact with proteins of the midbody and function in cytokinesis. The EMBO Journal, 26, 4215–4227.
Mosquera-Heredia, M. I., Morales, L. C., Vidal, O. M., Barceló, E., Silvera-Redondo, C., Vélez, J. I., & Garavito-Galofre, P. (2021). Exosomes: Potential disease biomarkers and new therapeutic targets. Biomedicines, 9, 1061.
Munkonda, M. N., Akbari, S., Landry, C., Sun, S., Xiao, F., Turner, M., Holterman, C. E., Nasrallah, R., Hébert, R. L., Kennedy, C. R. J., et al. (2018). Podocyte-derived microparticles promote proximal tubule fibrotic signaling via p38 MAPK and CD36. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 7, 1432206.
Muthu, S., Bapat, A., Jain, R., Jeyaraman, N., & Jeyaraman, M. (2021). Exosomal therapy-a new frontier in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Investigation, 8, 7.
Ng, T. B., Wong, J. H., & Wang, H. (2010). Recent progress in research on ribosome inactivating proteins. Current Protein & Peptide Science, 11, 37–53.
O’Brien, J., Hayder, H., Zayed, Y., & Peng, C. (2018). Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 9, 402.
Obregon, C., Rothen-Rutishauser, B., Gerber, P., Gehr, P., & Nicod, L. P. (2009). Active uptake of dendritic cell-derived exovesicles by epithelial cells induces the release of inflammatory mediators through a TNF-α-mediated pathway. The American Journal of Pathology, 175, 696–705.
Obrig, T. G., & Karpman, D. (2012). Shiga toxin pathogenesis: Kidney complications and renal failure. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, 357, 105–136.
Pan, Q., Ramakrishnaiah, V., Henry, S., Fouraschen, S., de Ruiter, P. E., Kwekkeboom, J., Tilanus, H. W., Janssen, H. L., & van der Laan, L. J. (2012). Hepatic cell-to-cell transmission of small silencing RNA can extend the therapeutic reach of RNA interference (RNAi). Gut, 61, 1330–1339.
Park, J. Y., Jeong, Y. J., Park, S. K., Yoon, S. J., Choi, S., Jeong, D. G., Chung, S. W., Lee, B. J., Kim, J. H., Tesh, V. L., et al. (2017). Shiga toxins induce apoptosis and er stress in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Toxins, 9, 319.
Peng, L., Liu, H., Ruan, H., Tepp, W. H., Stoothoff, W. H., Brown, R. H., Johnson, E. A., Yao, W. D., Zhang, S. C., & Dong, M. (2013). Cytotoxicity of botulinum neurotoxins reveals a direct role of syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 in neuron survival. Nature Communications, 4, 1472.
Phillips, A. D., Navabpour, S., Hicks, S., Dougan, G., Wallis, T., & Frankel, G. (2000). Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 target peyer’s patches in humans and cause attaching/effacing lesions in both human and bovine intestine. Gut, 47, 377–381.
Piedade, D., & Azevedo-Pereira, J. M. (2016). The role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis of herpesvirus infection. Viruses, 8, 156.
Raposo, G., & Stoorvogel, W. (2013). Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. Journal of Cell Biology, 200, 373–383.
Rosso, D. A., Rosato, M., Gómez, F. D., Álvarez, R. S., Shiromizu, C. M., Keitelman, I. A., Ibarra, C., Amaral, M. M., & Jancic, C. C. (2021). Human glomerular endothelial cells treated with shiga toxin type 2 activate γδ T lymphocytes. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 11, 765941.
Rubin, O., Canellini, G., Delobel, J., Lion, N., & Tissot, J. D. (2012). Red blood cell microparticles: Clinical relevance. Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy, 39, 342–347.
Scheutz, F., Teel, L. D., Beutin, L., Piérard, D., Buvens, G., Karch, H., Mellmann, A., Caprioli, A., Tozzoli, R., Morabito, S., et al. (2012). Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing STX nomenclature. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 50, 2951–2963.
Schorey, J. S., Cheng, Y., Singh, P. P., & Smith, V. L. (2015). Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles in host-pathogen interactions. EMBO Reports, 16, 24–43.
Shetty, A. K., & Upadhya, R. (2021). Extracellular vesicles in health and disease. Aging and Disease, 12, 1358–1362.
Shi, M., Liu, C., Cook, T. J., Bullock, K. M., Zhao, Y., Ginghina, C., Li, Y., Aro, P., Dator, R., He, C., et al. (2014). Plasma exosomal α-synuclein is likely CNS-derived and increased in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathologica, 128, 639–650.
Shi, M., Kovac, A., Korff, A., Cook, T. J., Ginghina, C., Bullock, K. M., Yang, L., Stewart, T., Zheng, D., Aro, P., et al. (2016). CNS tau efflux via exosomes is likely increased in Parkinson’s disease but not in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 12, 1125–1131.
Smith, W. E., Kane, A. V., Campbell, S. T., Acheson, D. W., Cochran, B. H., & Thorpe, C. M. (2003). Shiga toxin 1 triggers a ribotoxic stress response leading to p38 and JNK activation and induction of apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Infection and Immunity, 71, 1497–1504.
Soccio, P., Moriondo, G., Lacedonia, D., Tondo, P., Quarato, C. M. I., Barbaro, F., M. P., and, & Scioscia, G. (2022). Evs-miRNA: The new molecular markers for chronic respiratory diseases. Life, 12, 1544.
Ståhl, A. L., Sartz, L., Nelsson, A., Békássy, Z. D., & Karpman, D. (2009). Shiga toxin and lipopolysaccharide induce platelet-leukocyte aggregates and tissue factor release, a thrombotic mechanism in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Plos One, 4, e6990.
Ståhl, A. L., Sartz, L., & Karpman, D. (2011). Complement activation on platelet-leukocyte complexes and microparticles in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood, 117, 5503–5513.
Ståhl, A. L., Arvidsson, I., Johansson, K. E., Chromek, M., Rebetz, J., Loos, S., Kristoffersson, A. C., Békássy, Z. D., Mörgelin, M., & Karpman, D. (2015). A novel mechanism of bacterial toxin transfer within host blood cell-derived microvesicles. PLoS Pathogens, 11, e1004619.
Ståhl, A. L., Johansson, K., Mossberg, M., Kahn, R., & Karpman, D. (2019). Exosomes and microvesicles in normal physiology, pathophysiology, and renal diseases. Pediatric Nephrology, 34, 11–30.
Stein, P. E., Boodhoo, A., Tyrrell, G. J., Brunton, J. L., & Read, R. J. (1992). Crystal structure of the cell-binding B oligomer of verotoxin-1 from E. coli. Nature, 355, 748–750.
Suh, J. H., Joo, H. S., Hong, E. B., Lee, H. J., & Lee, J. M. (2021). Therapeutic application of exosomes in inflammatory diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 1144.
Svensson, K. J., Christianson, H. C., Wittrup, A., Bourseau-Guilmain, E., Lindqvist, E., Svensson, L. M., Mörgelin, M., & Belting, M. (2013). Exosome uptake depends on ERK1/2-heat shock protein 27 signaling and lipid raft-mediated endocytosis negatively regulated by caveolin-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288, 17713–17724.
Tack, D. M., Kisselburgh, H. M., Richardson, L. C., Geissler, A., Griffin, P. M., Payne, D. C., & Gleason, B. L. (2021). Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli outbreaks in the United States, 2010–2017. Microorganisms, 9, 1529.
Tauro, B. J., Greening, D. W., Mathias, R. A., Ji, H., Mathivanan, S., Scott, A. M., & Simpson, R. J. (2012). Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods, 56, 293–304.
Te Loo, D. M. W. M., Hinsbergh, V. W. M. V., Heuvel, L. P. W. J. V. D., & Monnens, L. A. H. (2001). Detection of verocytotoxin bound to circulating polymorphonuclear leukocytes of patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 12, 800–806.
Temchura, V. V., Tenbusch, M., Nchinda, G., Nabi, G., Tippler, B., Zelenyuk, M., Wildner, O., Überla, K., & Kuate, S. (2008). Enhancement of immunostimulatory properties of exosomal vaccines by incorporation of fusion-competent G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Vaccine, 26, 3662–3672.
Théry, C., Boussac, M., Véron, P., Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P., Raposo, G., Garin, J., & Amigorena, S. (2001). Proteomic analysis of dendritic cell-derived exosomes: A secreted subcellular compartment distinct from apoptotic vesicles. The Journal of Immunology, 166, 7309–7318.
Tian, T., Zhu, Y. L., Hu, F. H., Wang, Y. Y., Huang, N. P., & Xiao, Z. D. (2013). Dynamics of exosome internalization and trafficking. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 228, 1487–1495.
Tian, Y., Cheng, C., Wei, Y., Yang, F., & Li, G. (2022). The role of exosomes in inflammatory diseases and tumor-related inflammation. Cells, 11, 1005.
Tomasetti, M., Lee, W., Santarelli, L., & Neuzil, J. (2017). Exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer metabolism: Possible implications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Experimental & Molecular Medicine, 49, e285.
Tontanahal, A., Arvidsson, I., & Karpman, D. (2021). Annexin induces cellular uptake of extracellular vesicles and delays disease in Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection. Microorganisms, 9, 1143.
Trobaugh, D. W., & Klimstra, W. B. (2017). MicroRNA regulation of RNA virus replication and pathogenesis. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 23, 80–93.
Van Niel, G., Porto-Carreiro, I., Simoes, S., & Raposo, G. (2006). Exosomes: A common pathway for a specialized function. The Journal of Biochemistry, 140, 13–21.
Varrone, E., Carnicelli, D., & Brigotti, M. (2021). Extracellular vesicles and renal endothelial cells: A fatal attraction in hemolytic uremic syndrome. The American Journal of Pathology, 191, 795–804.
Vella, L. J., Sharples, R. A., Nisbet, R. M., Cappai, R., & Hill, A. F. (2008). The role of exosomes in the processing of proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases. European Biophysics Journal, 37, 323–332.
Vogel, A. D., Upadhya, R., & Shetty, A. K. (2018). Neural stem cell derived extracellular vesicles: Attributes and prospects for treating neurodegenerative disorders. EBioMedicine, 38, 273–282.
Wang, L., & Zhang, L. (2020). Circulating exosomal miRNA as diagnostic biomarkers of neurodegenerative diseases. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 13, 53.
Wang, J., Wu, F., Liu, C., Dai, W., Teng, Y., Su, W., Kong, W., Gao, F., Cai, L., Hou, A., et al. (2019). Exosomes released from rabies virus-infected cells may be involved in the infection process. Virologica Sinica, 34, 59–65.
Wang, X., Zhou, Y., Gao, Q., Ping, D., Wang, Y., Wu, W., Lin, X., Fang, Y., Zhang, J., & Shao, A. (2020). The role of exosomal microRNAs and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 17, 3232869.
Wani, S., Man Law, I. K., & Pothoulakis, C. (2020). Role and mechanisms of exosomal miRNAs in IBD pathophysiology. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 319, G646–G654.
Watanabe-Takahashi, M., Yamasaki, S., Murata, M., Kano, F., Motoyama, J., Yamate, J., Omi, J., Sato, W., Ukai, H., Shimasaki, K., et al. (2018). Exosome-associated Shiga toxin 2 is released from cells and causes severe toxicity in mice. Scientific Reports, 8, 10776.
Willysson, A., Ståhl, A. L., Gillet, D., Barbier, J., Cintrat, J. C., Chambon, V., Billet, A., Johannes, L., & Karpman, D. (2020). Shiga toxin uptake and sequestration in extracellular vesicles is mediated by its B-subunit. Toxins, 12, 449.
Yaker, L., Kamel, S., Ausseil, J., & Boullier, A. (2020). Effects of chronic kidney disease and uremic toxins on extracellular vesicle biology. Toxins, 12, 811.
Yáñez-Mo, M., Siljander, P. R., Andreu, Z., Zavec, A. B., Borràs, F. E., Buzas, E. I., Buzas, K., Casal, E., Cappello, F., Carvalho, J., et al. (2015). Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 4, 27066.
Zaborowski, M. P., Balaj, L., Breakefield, X. O., & Lai, C. P. (2015). Extracellular vesicles: Composition, biological relevance, and methods of study. Bioscience, 65, 783–797.
Zech, D., Rana, S., Büchler, M. W., & Zöller, M. (2012). Tumor-exosomes and leukocyte activation: An ambivalent crosstalk. Cell Communication and Signaling, 10, 37.
Zheng, D., Huo, M., Li, B., Wang, W., Piao, H., Wang, Y., Zhu, Z., Li, D., Wang, T., & Liu, K. (2020). The role of exosomes and exosomal microRNA in cardiovascular disease. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 8, 616161.
Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Gong, H., Luo, S., & Cui, Y. (2021). The role of exosomes and their applications in cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 12204.
Zumbrun, S. D., Hanson, L., Sinclair, J. F., Freedy, J., Melton-Celsa, A. R., Rodriguez-Canales, J., Hanson, J. C., & O’Brien, A. D. (2010). Human intestinal tissue and cultured colonic cells contain globotriaosylceramide synthase mRNA and the alternate shiga toxin receptor globotetraosylceramide. Infection and Immunity, 78, 4488–4499.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the KRIBB Research Initiative Program (KGM9942314, KGM5322321) and by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: HI23C0041) and also by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2018M3A9H4077992, 2022R1A2C1003699, 2022M3H9A1084279).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to repeat.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KS., Park, JY., Jeong, YJ. et al. The Fatal Role of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli Shiga Toxin-associated Extracellular Vesicles in Host Cells. J Microbiol. 61, 715–727 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-023-00066-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-023-00066-0