Abstract
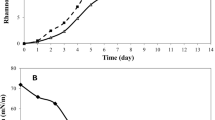
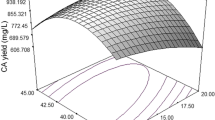
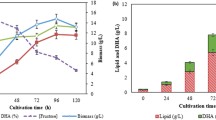
Rhamsan gum is a type of water-soluble exopolysaccharide produced by species of Sphingomonas bacteria. The optimal fermentation medium for rhamsan gum production by Sphingomonas sp. CGMCC 6833 was explored definition. Single-factor experiments indicate that glucose, soybean meal, K2HPO4 and MnSO4 compose the optimal medium along with and initial pH 7.5. To discover ideal cultural conditions for rhamsan gum production in a shake flask culture, response surface methodology was employed, from which the following optimal ratio was derived: 5.38 g/L soybean meal, 5.71 g/L K2HPO4 and 0.32 g/L MnSO4. Under ideal fermentation rhamsan gum yield reached 19.58 g/L ± 1.23 g/L, 42.09% higher than that of the initial medium (13.78 g/L ± 1.38 g/L). Optimizing the fermentation medium results in enhanced rhamsan gum production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, F.L., Best, G.H., and Linfroth, T.A. 1991. Welan gum in cement compositions. US Patent 5004506.
Arockiasamy, S. and Banik, R.M. 2008. Optimization of gellan gum production by Sphingomonas paucimobilis ATCC 31461 with nonionic surfactants using central composite design. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 105, 204–210.
Bajaj, I.B., Saudagar, P.S., Singhal, R.S., and Pandey, A. 2006. Statistical approach to optimization of fermentative production of gellan gum from Sphingomonas paucimobilis ATCC 31461. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 102, 150–156.
Bajaj, I. and Singhal, R. 2007. Gellan gum for reducing oil uptake in sev, a legume based product during deep-fat frying. Food Chem. 104, 1472–1477.
Banik, R.M., Kanari, B., and Upadhyay, S.N. 2000. Exopolysaccharide of the gellan family: prospects and potential. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 16, 407–414.
Coviello, T., Dentini, M., Rambone, G., Desideri, P., Carafa, M., Murtas, E., Riccieria, F.M., and Alhaiquea, F. 1998. A novel cocrosslinked polysaccharide: Studies for a controlled delivery matrix. J. Control. Release 55, 57–66.
Dennis, H.H., Thomas, O.M., and Paul, S. 1991. Oil reservoir permeability profile control with crosslinked welan gum biopolymers. US Patent 4981520.
Epstein, W. 2003. The roles and regulation of potassium in bacteria. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 75, 293–320.
Freitas, F., Alves, V.D., Pais, J., Costa, N., Oliveira, C., Mafra, L., Hilliou, L., Oliveira, R., and Reis, M.A.M. 2009. Characterization of an extracellular polysaccharide produced by a Pseudomonas strain grown on glycerol. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 859–865.
Hagiwara, A., Imai, N., Doi, Y., Sano, M., Tamano, S., Omoto, T., Asai, I., Yasuhara, K., and Hayashi, S.M. 2010. Ninety-day oral toxicity study of rhamsan gum, a natural food thickener produced from Sphingomonas ATCC 31961, in Crl:CD(SD)IGS rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 35, 493–501.
Jafarzade, M., Yahya, N.A., Shayesteh, F., Usup, G., and Ahmad, A. 2013. Influence of culture conditions and medium composition on the production of antibacterial compounds by marine Serratia sp. WPRA3. 2013. J. Microbiol. 51, 373–379.
Jerry, A.P., Suzanna, M.S., and Harold, R.H. 1983. Heteropolysac-charide S-194. US Patent 4401760.
Jin, H., Lee, N.K., Shin, M.K., Kim, S.K., Kaplan, D.L., and Lee, J.W. 2003. Production of gellan gum by Sphingomonas paucimobilis NK2000 with soybean pomace. Biochem. Eng. J. 16, 357–360.
Kang, K.S. and Pettitt, D.J. 1993. Xanthan, Gellan, Welan, and Rhamsan, pp. 341–397, In BeMiller, J.N. and Whistler, R.L. (eds.), Industrial Gums: Polysaccharides and Their Derivatives, Academic Press Inc, San Diego, USA.
Li, H., Xu, H., Xu, H., Li, S., and Ouyang, P.K. 2010. Biosynthetic pathway of sugar nucleotides essential for welan gum production in Alcaligenes sp. CGMCC2428. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 86, 295–303.
Li, H., Xu, H., Xu, H., Li, S., Ying, H.J., and Ouyang, P.K. 2011. Enhanced welan gum production using a two-stage agitation speed control strategy in Alcaligenes sp. CGMCC2428. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 34, 95–102.
Lobas, D., Schumpe, S., and Deckwer, W.D. 1992. The production of gellan polysaccharide with Sphingomonas paucimobilis E2 (DSM 6314). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37, 411–415.
Monot, F. and Quinn, F.X. 1996. Method and medium for producing gellan in the presence of manganese. WO 96/41890.
Morrison, N.A., Clark, R.C., Chen, Y.L., Talashek, T., and Sworn, G. 1999. Gelatin alternatives for the food industry. Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci. 114, 127–131.
Paula, M.D., Goissis, G., and Martins, V.C.A. 2007. Rheological behavior of anionic collagen injectable gels in the presence of rhamsan for plastic surgery applications. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. M. 18, 1683–1690.
Plank, J. 2004. Applications of biopolymers and other biotechnological products in building materials. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 66, 1–9.
Pollock, T.J. 2002. Sphingan group of exopolysaccharides (EPS), vol. 5, pp. 239–258 in Biopolymers, In Vandamme, E.J., DeBaets, S., and Steinbuchel, A. (eds.), Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany.
Seo, M.J., Kim, M.J., Lee, H.H., Kim, S.R., Kang, B.W., Park, J.U., Rhu, E.J., Choi, Y.H., and Jeong, Y.K. 2010. Initial acidic pH is critical for mycelial cultures and functional exopolysaccharide production of an edible mushroom, Laetiporus sulphureus var. miniatus JM 27. J. Microbiol. 48, 881–884.
Utter, M.F. and Werkman, C.H. 1942. Effect of metal ions on the reaction of phosphopyuvate by Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 146, 289–300.
Vercaemer, C.J., Davies, S.N., Pafitis, D.G., Maintland, G.C., and Poyet, J.P. 1997. Selective zonal isolation of oil wells. US Patent 5697441.
Xu, H., Jiang, M., Li, H., Lu, D.Q., and Ouyang, P.K. 2005. Efficient production of poly(γ-glutamic acid) by newly isolated Bacillus subtilis NX-2. Proc. Biochem. 40, 519–523.
Xu, H., Xu, X.Y., Dong, S.H., Li, S., and Liang, J.F. 2012. A kind of Sphingomonas sp. and its application in the production of rhamsan gum. China Patent 201210504461.3.
Yoon, S., Hong, E., Kim, S., Lee, P., Kim, M., Yang, H., and Ryu, Y. 2012. Optimization of culture medium for enhanced production of exopolysaccharide from Aureobasidium pullulans. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 35, 167–192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, XY., Dong, SH., Li, S. et al. Statistical experimental design optimization of rhamsan gum production by Sphingomonas sp. CGMCC 6833. J Microbiol. 53, 272–278 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-3662-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-3662-2