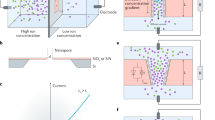
Abstract
Water evaporation-induced electricity generation is a promising technology for renewable energy harvesting. However, the output power of some reported two-dimensional (2D) nanofluidic films is still restricted by the relatively weak water–solid interactions within the tortuous nanochannels. To further enhance the comprehension and utilization of water–solid interactions, it is of utmost importance to conduct an in-depth investigation and propose a regulatory concept encompassing ion transport. Herein, we propose tortuosity regulation of 2D nanofluidic titanium oxide (Ti0.87O2) films to optimize the ion transport within the interlayer nanochannel for enhanced efficiency in water evaporation-induced electricity generation for the first time. The significance of tortuosity in ion transport is elucidated by designing three 2D nanofluidic films with different tortuosity. Tortuosity analysis and in situ Raman measurement demonstrate that low tortuosity can facilitate the formation of efficient pathways for hydrated proton transport and promote water–solid interactions. Consequently, devices fabricated with the optimized 2D nanofluidic films exhibited a significantly enhanced output power density of approximately 204.01 µW·cm−2, far exceeding those prepared by the high-tortuosity 2D nanofluidic films. This work highlights the significance of the construction of low tortuosity channels for 2D nanofluidic films with excellent performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang, Y. X.; Cheng, H. H.; Yang, C.; Yao, H. Z.; Li, C.; Qu, L. T. All-region-applicable, continuous power supply of graphene oxide composite. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1848–1856.
Liang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z. H.; Deng, Y. X.; Xiao, Y. K.; Cheng, H. H.; Zhang, P. P.; Huang, Y. X.; Shao, H. B.; Qu, L. T. Electric power generation via asymmetric moisturizing of graphene oxide for flexible, printable and portable electronics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1730–1735.
Aji, A. S.; Nishi, R.; Ago, H.; Ohno, Y. High output voltage generation of over 5 V from liquid motion on single-layer MoS2. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104370.
Zhong, H. K.; Xia, J.; Wang, F. C.; Chen, H. S.; Wu, H. G.; Lin, S. S. Gaaphene–piezoelectric material heterostructure for harvesting energy from water flow. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604226.
Liu, C.; Ye, C. C.; Wu, Y. Y.; Liu, Y. F.; Liu, Z. H.; Chen, Z. T.; Ma, R. Z.; Sakai, N.; Xue, L.; Sun, J. W. et al. Atomic-scale engineering of cation vacancies in two-dimensional unilamellar metal oxide nanosheets for electricity generation from water evaporation. Nano Energy 2023, 110, 108348.
Cai, M.; Wei, Y. X.; Li, Y. K.; Li, X.; Wang, S. B.; Shao, G. S.; Zhang, P. 2D semiconductor nanosheets for solar photocatalysis. EcoEnergy 2023, 1, 248–295
Chen, Y. X.; Lu, C. Graphitic carbon nitride nanomaterials for highperformance supercapacitors. Carbon Neutralizat. 2023, 2, 585–602.
Sun, Z. Y.; Wen, X.; Wang, L. M.; Ji, D. X.; Qin, X. H.; Yu, J. Y.; Ramakrishna, S. Emerging design principles, materials, and applications for moisture-enabled electric generation. eScience 2022, 2, 32–46.
Shen, D. Z.; Duley, W. W.; Peng, P.; Xiao, M.; Feng, J. Y.; Liu, L.; Zou, G. S.; Zhou, Y. N. Moisture-enabled electricity generation: From physics and materials to self-powered applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003722.
Zhang, S. Y.; Chu, W. C.; Li, L. X.; Guo, W. L. Voltage distribution in porous carbon black films induced by water evaporation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 8959–8964.
Sun, Z. Z.; Han, C. L.; Gao, S. W.; Li, Z. X.; Jing, M. X.; Yu, H. P.; Wang, Z. K. Achieving efficient power generation by designing bioinspired and multi-layered interfacial evaporator. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5077.
Xu, Y. Z.; Xu, J. L.; Zhang, J. Y.; Li, X. X.; Fu, B. W.; Song, C. Y.; Shang, W.; Tao, P.; Deng, T. All-in-one polymer sponge composite 3D evaporators for simultaneous high-flux solar-thermal desalination and electricity generation. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106882.
Shao, C. X.; Ji, B. X.; Xu, T.; Gao, J.; Gao, X.; Xiao, Y. K.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, N.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. T. Large-scale production of flexible, high-voltage hydroelectric films based on solid oxides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 30927–30935.
Fang, S. M.; Li, J. D.; Xu, Y.; Shen, C.; Guo, W. L. Evaporating potential. Joule 2022, 6, 690–701.
Xue, G. B.; Xu, Y.; Ding, T. P.; Li, J.; Yin, J.; Fei, W. W.; Cao, Y. Z.; Yu, J.; Yuan, L. Y.; Gong, L. et al. Water-evaporation-induced electricity with nanostructured carbon materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 317–321.
Zhang, G.; Duan, Z.; Qi, X.; Xu, Y. T.; Li, L.; Ma, W. G.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C. H.; Yao, W. Harvesting environment energy from water-evaporation over free-standing graphene oxide sponges. Carbon 2019, 148, 1–8.
Ma, Q. L.; He, Q. Y.; Yin, P. F.; Cheng, H. F.; Cui, X. Y.; Yun, Q. B.; Zhang, H. Rational design of MOF-based hybrid nanomaterials for directly harvesting electric energy from water evaporation. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003720.
Yoon, S. G.; Jin, H. D.; Lee, W. H.; Han, J.; Cho, Y. H.; Kim, Y. S. Evaporative electrical energy generation via diffusion-driven ion-electron-coupled transport in semiconducting nanoporous channel. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105522.
Sun, J. C.; Li, P. D.; Qu, J. Y.; Lu, X.; Xie, Y. Q.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Gang, M.; Feng, Q. J.; Liang, H. W. et al. Electricity generation from a Ni-Al layered double hydroxide-based flexible generator driven by natural water evaporation. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 269–278.
Tian, J. L.; Zang, Y. H.; Sun, J. C.; Qu, J. Y.; Gao, F.; Liang, G. Y. Surface charge density-dependent performance of Ni-Al layered double hydroxide-based flexible self-powered generators driven by natural water evaporation. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104502.
Yoon, S. G.; Yang, Y.; Yoo, J.; Jin, H. D.; Lee, W. H.; Park, J.; Kim, Y. S. Natural evaporation-driven ionovoltaic electricity generation. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2019, 1, 1746–1751.
Wang, X.; Yuan, G.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, J. J.; Yang, C. Y.; Hu, S. Composite laminar membranes for electricity generation from water evaporation. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 307–311.
Liu, K.; Yang, P. H.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Ding, T. P.; Xue, G. B.; Chen, Q.; Feng, G.; Zhou, J. Induced potential in porous carbon films through water vapor absorption. Angew Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8003–8007.
Ai, X. Y.; Li, Y. H.; Li, Y. W.; Gao, T. T.; Zhou, K. G. Recent progress on the smart membranes based on two-dimensional materials. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2832–2844.
Li, Z. Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, D. K.; Wan, X. Y.; Wang, X. B.; Fang, Z.; Peng, X. S. Polyaniline-coated MOFs nanorod arrays for efficient evaporation-driven electricity generation and solar steam desalination. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2021, 8, 2004552.
Wei, D.; Yang, F. Y.; Jiang, Z. H.; Wang, Z. L. Flexible iontronics based on 2D nanofluidic material. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4965.
Zhang, Z. K.; Shen, W. H.; Lin, L. X.; Wang, M.; Li, N.; Zheng, Z. F.; Liu, F.; Cao, L. X. Vertically transported graphene oxide for highperformance osmotic energy conversion. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2020, 7, 2000286.
Guo, Q.; Chen, N.; Qu, L. T. Two-dimensional materials of group-IVA boosting the development of energy storage and conversion. Carbon Energy 2020, 2, 54–71.
Liu, Z. H.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z. T.; Huang, H. L.; Liu, Y. F.; Xue, L.; Sun, J. W.; Wang, X.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, J. W. Recent advances in two-dimensional materials for hydrovoltaic energy technology. Exploration 2023, 3, 20220061.
Tjaden, B.; Brett, D. J. L.; Shearing, P. R. Tortuosity in electrochemical devices: A review of calculation approaches. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 63, 47–67.
Sobieski, W. Numerical Investigations of tortuosity in randomly generated pore structures. Math. Comput. Simul. 2019, 166, 1–20.
Qin, D. T.; Liu, Z. Y.; Bai, H. W.; Sun, D. D. Three-dimensional architecture constructed from a graphene oxide nanosheet-polymer composite for high-flux forward osmosis membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 12183–12192.
Da Silva, M. T. Q. S.; Do Rocio Cardoso, M.; Veronese, C. M. P.; Mazer, W. Tortuosity: A brief review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 58, 1344–1349.
Weiss, M.; Ruess, R.; Kasnatscheew, J.; Levartovsky, Y.; Levy, N. R.; Minnmann, P.; Stolz, L.; Waldmann, T.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M.; Aurbach, D. et al. Fast charging of lithium-ion batteries: A review of materials aspects. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101126.
Kuang, Y. D.; Chen, C. J.; Kirsch, D.; Hu, L. B. Thick electrode batteries: Principles, opportunities, and challenges. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901457.
Ebner, M.; Geldmacher, F.; Marone, F.; Stampanoni, M.; Wood, V. X-ray tomography of porous, transition metal oxide based lithium ion battery electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2013, 3, 845–850.
Xue, X. Z.; Lin, D.; Li, Y. Low tortuosity 3D-printed structures enhance reaction kinetics in electrochemical energy storage and electrocatalysis. Small Structures 2022, 3, 2200159.
Huang, H. L.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z. Y.; Wu, Y. Y.; Liu, Y. F.; Fan, J. B.; Zhang, G.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, J. W. Functional inorganic additives in composite solid-state electrolytes for flexible lithium metal batteries. Adv. Powder Mater. 2024, 3, 100141.
Ebner, M.; Wood, V. Tool for tortuosity estimation in lithium ion battery porous electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A3064–A3070.
Li, L. S.; Erb, R. M.; Wang, J. J.; Wang, J.; Chiang, Y. M. Fabrication of low-tortuosity ultrahigh-area-capacity battery electrodes through magnetic alignment of emulsion-based slurries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802472.
Zhou, Y. B.; Chen, C. J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D. P.; Xu, L. S.; Dai, J. Q.; Liou, S. C.; Wang, Y. L.; Li, C.; Xie, H. et al. Decoupling ionic and electronic pathways in low-dimensional hybrid conductors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17830–17837.
Qin, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, G.; Portehault, D.; Garvey, C. J.; Gogotsi, Y.; Lei, W. W.; Chen, Y. High and stable ionic conductivity in 2D nanofluidic ion channels between boron nitride layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6314–6320.
Yu, L.; Gao, T. T.; Mi, R. Y.; Huang, J.; Kong, W. Q.; Liu, D. P.; Liang, Z. Q.; Ye, D. D.; Chen, C. J. 3D-printed mechanically strong and extreme environment adaptable boron nitride/cellulose nanofluidic macrofibers. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 7609–7617
Xiong, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X. Y.; Liu, Y. F.; Wu, Y. Y.; Wang, S. J.; Safaei, J.; Sun, B.; Ma, R. Z.; Liu, Z. W. et al. Atomic-scale regulation of anionic and cationic migration in alkali metal batteries. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4184.
Cai, T. L.; Lan, L. Y.; Peng, B.; Zhang, C.; Dai, S. F.; Zhang, C.; Ping, J. F.; Ying, Y. B. Bilayer wood membrane with aligned ion nanochannels for spontaneous moist-electric generation. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 6476–6483.
Wang, L. Z.; Sasaki, T. Titanium oxide nanosheets: Graphene analogues with versatile functionalities. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9455–9486.
Sasaki, T.; Watanabe, M.; Hashizume, H.; Yamada, H.; Nakazawa, H. Macromolecule-like aspects for a colloidal suspension of an exfoliated titanate. Pairwise association of nanosheets and dynamic reassembling process initiated from it. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8329–8335.
Li, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, Q.; Banis, M. N.; Sun, X. L.; Sham, T. K. Tracking the effect of sodium insertion/extraction in amorphous and anatase TiO2 nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 11773–11782.
Ata-ur-Rehman; Ali, G.; Abbas, S. M.; Iftikhar, M.; Zahid, M.; Yaseen, S.; Saleem, S.; Haider, S.; Arshad, M.; Badshah, A. Axial expansion of Ni-doped TiO2 nanorods grown on carbon nanotubes for favourable lithium-ion intercalation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122021.
Yadav, A. K.; Haque, S. M.; De, R.; Ahmed, M. A.; Srihari, V.; Gupta, M.; Phase, D. M.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jha, S. N.; Bhattacharyya, D. Local structure investigation of Mn- and Co-doped TiO2 thin films by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 11012–11024.
El Koura, Z.; Rossi, G.; Calizzi, M.; Amidani, L.; Pasquini, L.; Miotello, A.; Boscherini, F. XANES study of vanadium and nitrogen dopants in photocatalytic TiO2 thin films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 221–231.
Peng, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y. F.; Liu, C.; Huang, H. L.; Fan, J. B.; Xiong, P.; Zhu, J. W. Strain engineering of two-dimensional materials for energy storage and conversion applications. Chem. Synth. 2023, 3, 47.
Ju, Z. Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J. Y.; King, S. T.; Chang, C. C.; Yan, S.; Xue, Y.; Takeuchi, K. J.; Marschilok, A. C.; Wang, L. et al. Tortuosity engineering for improved charge storage kinetics in high-areal-capacity battery electrodes. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 6700–6708.
Wang, K. Q.; Xu, W. H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Li, J. F.; Zhang, H. L.; Li, J. J.; Wang, Z. K. Bio-inspired water-driven electricity generators: From fundamental mechanisms to practical applications. Nano Res. Energy 2023, 2, e9120042.
Dao, V. D.; Vu, N. H.; Thi Dang, H. L.; Yun, S. N. Recent advances and challenges for water evaporation-induced electricity toward applications. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105979.
Zhang, Z. H.; Li, X. M.; Yin, J.; Xu, Y.; Fei, W. W.; Xue, M. M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J. X.; Guo, W. L. Emerging hydrovoltaic technology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1109–1119.
Wu, M.; Peng, M. W.; Liang, Z. Q.; Liu, Y. L.; Zhao, B.; Li, D.; Wang, Y. W.; Zhang, J. C.; Sun, Y. H.; Jiang, L. Printed honeycomb-structured reduced graphene oxide film for efficient and continuous evaporation-driven electricity generation from salt solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 26989–26997.
García-García, R.; García, R. E. Microstructural effects on the average properties in porous battery electrodes. J. Power Sources 2016, 309, 11–19.
Ebner, M.; Chung, D. W.; García, R. E.; Wood, V. Tortuosity anisotropy in lithium-ion battery electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301278.
Li, S.; Fan, Z. D.; Wu, G. Q.; Shao, Y. Y.; Xia, Z.; Wei, C. H.; Shen, F.; Tong, X. L.; Yu, J. C.; Chen, K. et al. Assembly of nanofluidic MXene fibers with enhanced ionic transport and capacitive charge storage by flake orientation. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7821–7832.
Wang, Y.; Lian, T. T.; Tarakina, N. V.; Yuan, J. Y.; Antonietti, M. Lamellar carbon nitride membrane for enhanced ion sieving and water desalination. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7339.
Chi, J. G.; Liu, C. R.; Che, L. F.; Li, D. J.; Fan, K.; Li, Q.; Yang, W. H.; Dong, L. X.; Wang, G. F.; Wang, Z. L. Harvesting water-evaporation-induced electricity based on liquid–solid triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2022, 9, e2201586.
Hu, Q. C.; Ma, Y. J.; Ren, G. P.; Zhang, B. T.; Zhou, S. G. Water evaporation-induced electricity with Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm8047.
Hällström, L.; Koskinen, T.; Tossi, C.; Juntunen, T.; Tittonen, I. Multiphysics simulation explaining the behaviour of evaporation-driven nanoporous generators. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 256, 115382.
Rehman, M. M. U.; Nagayama, G. Contribution of solid–liquid–vapor interface to droplet evaporation. Colloid Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 656, 130419.
Li, S.; Zhang, Q. Ionic gelatin thermoelectric generators. Joule 2020, 4, 1628–1629.
Li, L. H.; Feng, S. J.; Bai, Y. Y.; Yang, X. Q.; Liu, M. Y.; Hao, M. M.; Wang, S. Q.; Wu, Y.; Sun, F. Q.; Liu, Z. et al. Enhancing hydrovoltaic power generation through heat conduction effects. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1043.
Sun, Z. N.; Zhang, W. L.; Guo, J. C.; Song, J. N.; Deng, X. Is heat really beneficial to water evaporation-driven electricity. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 12370–12375.
Shao, B. B.; Wu, Y. F.; Song, Z. H.; Yang, H. W.; Chen, X.; Zou, Y. T.; Zang, J. Q.; Yang, F.; Song, T.; Wang, Y. S. et al. Freestanding silicon nanowires mesh for efficient electricity generation from evaporation-induced water capillary flow. Nano Energy 2022, 94, 106917.
Xu, T.; Ding, X. T.; Shao, C. X.; Song, L.; Lin, T. Y.; Gao, X.; Xue, J. L.; Zhang, Z. P.; Qu, L. T. Electric power generation through the direct interaction of pristine graphene–oxide with water molecules. Small 2018, 14, 1704473.
Wang, Y. H.; Zheng, S. S.; Yang, W. M.; Zhou, R. Y.; He, Q. F.; Radjenovic, P.; Dong, J. C.; Li, S. N.; Zheng, J. X.; Yang, Z. L. et al. In situ Raman spectroscopy reveals the structure and dissociation of interfacial water. Nature 2021, 600, 81–85
Hu, Q. C.; Ouyang, S. L.; Li, J.; Cao, Z. Raman spectroscopic investigation on pure D2O/H2O from 303 to 573 K: Interpretation and implications for water structure. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2017, 48, 610–617.
Gao, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, G.; Li, C. X.; Hu, L. Vibrational features of confined water in nanoporous TiO2 by Raman spectra. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 026801.
Kang, Y. C.; Zhang, F.; Li, H. Z.; Wei, W. R.; Dong, H. T.; Chen, H.; Sang, Y. H.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. H. Modulating the electrolyte inner solvation structure via low polarity co-solvent for low-temperature aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Energy Environ. Mater., in press, https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12707.
Wang, Z. Y.; Huang, Y. C.; Zhang, T. S.; Xu, K. Q.; Liu, X. L.; Zhang, A. R.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Dai, J. W.; Jiang, Z. N. et al. Unipolar solution flow in calcium-organic frameworks for seawater-evaporation-induced electricity generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 1690–1700.
Li, J.; Liu, K.; Ding, T. P.; Yang, P. H.; Duan, J. J.; Zhou, J. Surface functional modification boosts the output of an evaporation-driven water flow nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 797–802.
Shen, H. J.; Shen, X.; Wu, Z. H. Simulating the isotropic Raman spectra of O–H stretching mode in liquid H2O based on a machine learning potential: The influence of vibrational couplings. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 28180–28188.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22179062, 52125202, and U2004209), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK2023010081), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 30922010303).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Liu, C., Ni, A. et al. Tortuosity regulation of two-dimensional nanofluidic films for water evaporation-induced electricity generation. Nano Res. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6642-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6642-1