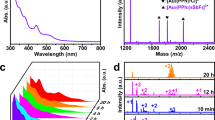
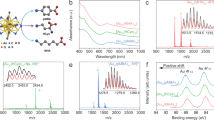
Abstract
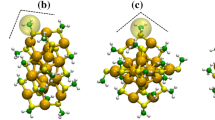
The structure determination of metal nanoclusters protected by ligands is critical in understanding their physical and chemical properties, yet it remains elusive how the metal core and ligand of metal clusters cooperatively contribute to the observed performances. Here, with the successful synthesis of Au44TBPA22Cl2 cluster (TBPA = 4-tert-butylphenylacetylene), the structural isomer of previously reported Au44L28 clusters (L denoted as ligand) is filled, thereby providing an opportunity to explore the property evolution rules imparted by different metal core structures or different surface ligands. Time-resolved transient absorption spectroscopy reveals that the difference in the core structure between Au44TBPA22Cl2 and Au44L28 can bring nearly 360 times variation of excited-state lifetime, while only 3–24 times differences in excited-state lifetimes of the three Au44L28 nanoclusters with identical metal core but different ligands are observed, which is due to much stronger impact of the metal core than the surface ligands in the electronic energy bands of the clusters. In addition, the Au44 clusters protected by alkyne ligands are shown to be highly effective toward the electrochemical oxidation of ethanol, compared to the Au44 clusters capped by thiolates, which is ascribed to smaller charge transfer impedance of the former clusters. We anticipate that the study will enhance the process in controlling the nanomaterial properties by precisely tailoring metal core or surface patterns.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin, R. C.; Zeng, C. J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y. X. Atomically precise colloidal metal nanoclusters and nanoparticles: Fundamentals and opportunities. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10346–10413.
Kang, X.; Li, Y. W.; Zhu, M. Z.; Jin, R. C. Atomically precise alloy nanoclusters: Syntheses, structures, and properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6443–6514.
Jin, R. C.; Li, G.; Sharma, S.; Li, Y. W.; Du, X. S. Toward active-site tailoring in heterogeneous catalysis by atomically precise metal nanoclusters with crystallographic structures. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 567–648.
Guan, Z. J.; Li, J. J.; Hu, F.; Wang, Q. M. Structural engineering toward gold nanocluster catalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 20212, 61, e202209725.
Kang, X.; Zhu, M. Z. Tailoring the photoluminescence of atomically precise nanoclusters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2422–2457.
Zhang, Y. F.; Zhang, J. J.; Li, Z. W.; Qin, Z. X.; Sharma, S.; Li, G. Atomically precise copper dopants in metal clusters boost up stability, fluorescence, and photocatalytic activity. Commun. Chem. 2023, 6, 24.
Qin, Z. X.; Hu, S.; Han, W. H.; Li, Z. W.; Xu, W. W.; Zhang, J. J.; Li, G. Tailoring optical and photocatalytic properties by single-Agatom exchange in Au13Ag12(PPh3)10Cl8 nanoclusters. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 2971–2976.
Jadzinsky, P. D.; Calero, G.; Ackerson, C. J.; Bushnell, D. A.; Kornberg, R. D. Structure of a thiol monolayer-protected gold nanoparticle at 1.1 Å resolution. Science 2007, 318, 430–433.
Nakashima, T.; Tanibe, R.; Yoshida, H.; Ehara, M.; Kuzuhara, M.; Kawai, T. Self-regulated pathway-dependent chirality control of silver nanoclusters. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208273.
Huang, J. H.; Wang, Z. Y.; Zang, S. Q.; Mak, T. C. W. Spontaneous resolution of chiral multi-thiolate-protected Ag30 nanoclusters. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1971–1976.
Sun, Y. N.; Liu, X.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, M. Y. Active-site tailoring of gold cluster catalysts for electrochemical CO2 reduction. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 11551–11560.
Seong, H.; Efremov, V.; Park, G.; Kim, H.; Yoo, J. S.; Lee, D. Atomically precise gold nanoclusters as model catalysts for identifying active sites for electroreduction of CO2. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14563–14570.
Li, R. Z.; Wang, D. S. Understanding the structure-performance relationship of active sites at atomic scale. Nano Res. 2022, 75, 6888–6923.
Zhou, M.; Zeng, C. J.; Chen, Y. X.; Zhao, S.; Sfeir, M. Y.; Zhu, M. Z.; Jin, R. C. Evolution from the plasmon to exciton state in ligand-protected atomically precise gold nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13240.
Zhang, Y. Y.; Tang, A. C.; Cai, X.; Xu, J. Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y. Manipulating the organic-inorganic interface of atomically precise Au36(SR)24 catalysts for CO oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 3003–3006.
Liu, J. W.; Feng, L.; Su, H. F.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Q. Q.; Wang, X. P.; Tung, C. H.; Sun, D.; Zheng, L. S. Anisotropic assembly of Ag52 and Ag76 nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1600–1603.
Hossain, S.; Niihori, Y.; Nair, L. V.; Kumar, B.; Kurashige, W.; Negishi, Y. Alloy clusters: Precise synthesis and mixing effects. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3114–3124.
Guan, Z. J.; Zeng, J. L.; Yuan, S. F.; Hu, F.; Lin, Y. M.; Wang, Q. M. Au57Ag53(C=CPh)40Br12: A large nanocluster with C1 symmetry. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5703–5707.
Zheng, X. B.; Li, B. B.; Wang, Q. S.; Wang, D. S.; Li, Y. D. Emerging low-nuclearity supported metal catalysts with atomic level precision for efficient heterogeneous catalysis. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 7806–7839.
Zheng, Y. K.; Wu, J. B.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. M. Gold nanoclusters for theranostic applications. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2021, 431, 213689.
Ma, X. S.; Tang, Y.; Ma, G. Y.; Qin, L. B.; Tang, Z. H. Controllable synthesis and formation mechanism study of homoleptic alkynyl-protected Au nanoclusters: Recent advances, grand challenges, and great opportunities. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 602–614.
Han, S.; Zhang, Z. C.; Li, S. P.; Qi, L. M.; Xu, G. B. Chemiluminescence and electrochemiluminescence applications of metal nanoclusters. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 794–801.
Liu, X.; Xu, W. W.; Huang, X. Y.; Wang, E. D.; Cai, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, C. F.; Gao, Y. et al. De novo design of Au36(SR)24 nanoclusters. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3349.
Higaki, T.; Liu, C.; Zeng, C. J.; Jin, R. X.; Chen, Y. X.; Rosi, N. L.; Jin, R. C. Controlling the atomic structure of Au30 nanoclusters by a ligand-based strategy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6694–6697.
Zheng, K.; Zhang, J. W.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z. M.; Li, G. Motif-mediated Au25(SPh)5(PPh3)10X2 nanorods with conjugated electron delocalization. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 501–507.
Zhang, S. S.; Liu, R. C.; Zhang, X. C.; Feng, L.; Xue, Q. W.; Gao, Z. Y.; Tung, C. H.; Sun, D. Core engineering of paired core-shell silver nanoclusters. Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 2118–2124.
Li, Y. W.; Chen, Y. X.; House, S. D.; Zhao, S.; Wahab, Z.; Yang, J. C.; Jin, R. C. Interface engineering of gold nanoclusters for CO oxidation catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 29425–29434.
Wan, X. K.; Wang, J. Q.; Nan, Z. A.; Wang, Q. M. Ligand effects in catalysis by atomically precise gold nanoclusters. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701823.
Wang, Y.; Wan, X. K.; Ren, L. T.; Su, H. F.; Li, G.; Malola, S.; Lin, S. C.; Tang, Z. C.; Häkkinen, H.; Teo, B. K. et al. Atomically precise alkynyl-protected metal nanoclusters as a model catalyst: Observation of promoting effect of surface ligands on catalysis by metal nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3278–3281.
Zeng, C. J.; Chen, Y. X.; Iida, K.; Nobusada, K.; Kirschbaum, K.; Lambright, K. J.; Jin, R. C. Gold quantum boxes: On the periodicities and the quantum confinement in the Au28, Au36, Au44, and Au52 magic series. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3950–3953.
Liu, X.; Yao, G.; Cheng, X. L.; Xu, J. Y.; Cai, X.; Hu, W. G.; Xu, W. W.; Zhang, C. F.; Zhu, Y. Cd-driven surface reconstruction and photodynamics in gold nanoclusters. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3290–3294.
Tang, S. S.; Xu, J. Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y. Ag doped Au44 nanoclusters for electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 to CO. Chem. Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202201262.
Zhou, M.; Higaki, T.; Hu, G. X.; Sfeir, M. Y.; Chen, Y. X.; Jiang, D. E.; Jin, R. C. Three-orders-of-magnitude variation of carrier lifetimes with crystal phase of gold nanoclusters. Science 2019, 364, 279–282.
Zhou, M.; Higaki, T.; Li, Y. W.; Zeng, C. J.; Li, Q.; Sfeir, M. Y.; Jin, R. C. Three-stage evolution from nonscalable to scalable optical properties of thiolate-protected gold nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 19754–19764.
Kwak, K.; Thanthirige, V. D.; Pyo, K.; Lee, D.; Ramakrishna, G. Energy gap law for exciton dynamics in gold cluster molecules. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 4898–4905.
Bai, S. X.; Xu, Y.; Cao, K. L.; Huang, X. Q. Selective ethanol oxidation reaction at the Rh–SnO2 interface. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005767.
Chen, D. P.; Yuan, L.; Li, M. J.; Han, W. J.; Liu, X. D.; Liu, X. C.; Wang, C. Y. Pd monolayer on the 3D-hollow-porous Au microsphere as an advanced electrocatalyst for the ethanol oxidation reaction. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 5087–5098.
Zheng, J. H.; Li, G.; Zhang, J. M.; Cheng, N. Y.; Ji, L. F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. L.; Zhang, B. W.; Jiang, Y. X.; Sun, S. G. General strategy for evaluating the d-band center shift and ethanol oxidation reaction pathway towards Pt-based electrocatalysts. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 279–288.
Behravesh, E.; Melander, M. M.; Wärnå, J.; Salmi, T.; Honkala, K.; Murzin, D. Y. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethanol on gold: Combination of kinetic experiments and computation approach to unravel the reaction mechanism. J. Catal. 2021, 394, 193–205.
Zhang, Y. Y.; Wang, J. G.; Yu, X. F.; Baer, D. R.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, L. Q.; Wang, F. Y.; Zhu, Z. H. Potential-dynamic surface chemistry controls the electrocatalytic processes of ethanol oxidation on gold surfaces. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 215–221.
Lei, Z.; Wan, X. K.; Yuan, S. F.; Guan, Z. J.; Wang, Q. M. Alkynyl approach toward the protection of metal nanoclusters. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2465–2474.
Tang, Q.; Jiang, D. E. Insights into the PhC≡C/Au interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 10804–10810.
Huang, L.; Zhang, X. P.; Wang, Q. Q.; Han, Y. J.; Fang, Y. X.; Dong, S. J. Shape-control of Pt-Ru nanocrystals: Tuning surface structure for enhanced electrocatalytic methanol oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1142–1147.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 22125202, 22273095, and 22101128), Programs for high-level entrepreneurial and innovative talents introduction of Jiangsu Province, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. YSBR-007), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2022M721551).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, T., Kong, J., Tang, S. et al. The modification toward excited-state dynamics and catalytic activity by isomeric Au44 clusters. Nano Res. 16, 11383–11388 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5862-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-5862-0