Abstract
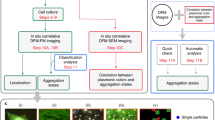
Structure, especially to track and monitor the phagocytosis process of nanoparticles by cells. Herein, we prepared a MoO2 hollow nanosphere with a strong surface plasmon resonance effect in the visible light region, which exhibited an excellent surface enhanced Raman scattering effect. When the 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA) molecules are modified, it can be efficiently used as Raman probe molecules to perform clear three-dimensional cell imaging. No matter when the nanoparticles are located inside the cell, outside the cell or partly inside the cell, they all can be clearly presented by this enhanced Raman probe molecule. These results provide a rapid and accurate method for three-dimensional imaging of cells, especially for tracking the phagocytosis of nanoparticles.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wegner, K. D.; Hildebrandt, N. Quantum dots: Bright and versatile in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4792–4834.
Bruchez, M. Jr.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss S.; Alivisatos, A. P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016.
Hötzer, B.; Medintz, I. L.; Hildebrandt, N. Fluorescence in nanobiotechnology: Sophisticated fluorophores for novel applications. Small 2012, 8, 2297–2326.
Morgner, F.; Geißler, D.; Stufler, S.; Butlin, N. G.; Löhmannsröben, H. G.; Hildebrandt, N. A quantum-dot-based molecular ruler for multiplexed optical analysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7570–7574.
Wegner, K. D.; Morgner, F.; Oh, E.; Goswami, R.; Susumu, K.; Stewart, M. H.; Medintz, I. L.; Hildebrandt, N. Three-dimensional solution-phase förster resonance energy transfer analysis of nanomolar quantum dot bioconjugates with subnanometer resolution. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4299–4312.
Li, C. Y.; Chen, G. C.; Zhang, Y. J.; Wu, F.; Wang, Q. B. Advanced fluorescence imaging technology in the near-infrared-II window for biomedical applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 14789–14804.
Yezhelyev, M. V.; Qi, L. F.; O’Regan, R. M.; Nie, S. M.; Gao, X. H. Proton-sponge coated quantum dots for siRNA delivery and intracellular imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9006–9012.
Anderson, N.; Anger, P.; Hartschuh, A.; Novotny, L. Subsurface Raman imaging with nanoscale resolution. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 744–749.
Song, Z. L.; Chen, Z.; Bian, X.; Zhou, L. Y.; Ding, D.; Liang, H.; Zou, Y. X.; Wang, S. S.; Chen, L.; Yang, C. et al. Alkyne-functionalized superstable graphitic silver nanoparticles for Raman imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13558–13561.
Wang, X.; Liu, G. K.; Xu, M. X.; Ren, B.; Tian, Z. Q. Development of weak signal recognition and an extraction algorithm for Raman imaging. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12909–12916.
Yamakoshi, H.; Dodo, K.; Palonpon, A.; Ando, J.; Fujita, K.; Kawata, S.; Sodeoka, M. Alkyne-tag Raman imaging for visualization of mobile small molecules in live cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20681–20689.
He, Z.; Han, Z. H.; Kizer, M.; Linhardt, R. J.; Wang, X.; Sinyukov, A. M.; Wang, J. Z.; Deckert, V.; Sokolov, A. V.; Hu, J. et al. Tip-enhanced Raman imaging of single-stranded DNA with single base resolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 753–757.
Palonpon, A. F.; Ando, J.; Yamakoshi, H.; Dodo, K.; Sodeoka, M.; Kawata, S.; Fujita, K. Raman and SERS microscopy for molecular imaging of live cells. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 677–692.
Lal, S.; Grady, N. K.; Kundu, J.; Levin, C. S.; Lassiter, J. B.; Halas, N. J. Tailoring plasmonic substrates for surface enhanced spectroscopies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 898–911.
Hong, G. S.; Diao, S.; Antaris, A. L.; Dai, H. J. Carbon nanomaterials for biological imaging and nanomedicinal therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10816–10906.
Smith, B. R.; Gambhir, S. S. Nanomaterials for in vivo imaging. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 901–986.
Zong, C.; Xu, M. X.; Xu, L. J.; Wei, T.; Ma, X.; Zheng, X. S.; Hu, R.; Ren, B. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for bioanalysis: Reliability and challenges. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4946–4980.
Kong, L. B.; Navas-Moreno, M.; Chan, J. W. Fast confocal Raman imaging using a 2-D multifocal array for parallel hyperspectral detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1281–1285.
Jokerst, J. V.; Cole, A. J.; Van de Sompel, D.; Gambhir, S. S. Gold nanorods for ovarian cancer detection with photoacoustic imaging and resection guidance via Raman imaging in living mice. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 10366–10377.
Huang, Y. M.; Swarup, V. P.; Bishnoi, S. W. Rapid Raman imaging of stable, functionalized nanoshells in mammalian cell cultures. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2914–2920.
Kang, J. W.; Nguyen, F. T.; Lue, N.; Dasari, R. R.; Heller, D. A. Measuring uptake dynamics of multiple identifiable carbon nanotube species via high-speed confocal Raman imaging of live cells. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6170–6174.
Zhang, W.; Dong, Z. Q.; Zhu, L.; Hou, Y. Z.; Qiu, Y. P. Direct observation of the release of nanoplastics from commercially recycled plastics with correlative Raman imaging and scanning electron microscopy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7920–7926.
Bocklitz, T. W.; Crecelius, A. C.; Matthäus, C.; Tarcea, N.; von Eggeling, F.; Schmitt, M.; Schubert, U. S.; Popp, J. Deeper understanding of biological tissue: Quantitative correlation of MALDITOF and Raman imaging. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10829–10834.
Clemente, I.; Aznar, M.; Nerín, C. Raman imaging spectroscopy as a tool to investigate the cell damage on Aspergillus ochraceus caused by an antimicrobial packaging containing benzyl isothiocyanate. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4772–4779.
Ishigaki, M.; Meksiarun, P.; Kitahama, Y.; Zhang, L. L.; Hashimoto, H.; Genkawa, T.; Ozaki, Y. Unveiling the aggregation of lycopene in vitro and in vivo: UV-Vis, resonance Raman, and Raman imaging studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 8046–8057.
Pozzi, E. A.; Sonntag, M. D.; Jiang, N.; Klingsporn, J. M.; Hersam, M. C.; Van Duyne, R. P. Tip-enhanced Raman imaging: An emergent tool for probing biology at the nanoscale. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 885–888.
Ertsgaard, C. T.; Wittenberg, N. J.; Klemme, D. J.; Barik, A.; Shih, W. C.; Oh, S. H. Integrated nanogap platform for sub-volt dielectrophoretic trapping and real-time Raman imaging of biological nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5946–5953.
Karanja, C. W.; Hong, W. L.; Younis, W.; Eldesouky, H. E.; Seleem, M. N.; Cheng, J. X. Stimulated Raman imaging reveals aberrant lipogenesis as a metabolic marker for azole-resistant Candida albicans. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9822–9829.
Toda, S.; Yanagita, N.; Jokar, E.; Diau, E. W. G.; Shigeto, S. Inter- and intragrain inhomogeneity in 2D perovskite thin films revealed by relative grain orientation imaging using low-frequency polarized Raman microspectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 3871–3876.
Arzumanyan, G. M.; Doroshkevich, N. V.; Mamatkulov, K. Z.; Shashkov, S. N.; Zinovev, E. V.; Vlasov, A. V.; Round, E. S.; Gordeliy, V. I. Highly sensitive coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering imaging of protein crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13457–13460.
Liu, H. L.; Yang, Z. L.; Meng, L. Y.; Sun, Y. D.; Wang, J.; Yang, L. B.; Liu, J. H.; Tian, Z. Q. Three-dimensional and time-ordered surface-enhanced Raman scattering hotspot matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5332–5341.
Zhang, Y. Q.; Gu, Y. Q.; He, J.; Thackray, B. D.; Ye, J. Ultrabright gap-enhanced Raman tags for high-speed bioimaging. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3905.
Wang, X.; Huang, S. C.; Hu, S.; Yan, S.; Ren, B. Fundamental understanding and applications of plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2020, 2, 253–271.
Harmsen, S.; Wall, M. A.; Huang, R. M.; Kircher, M. F. Cancer imaging using surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 1400–1414.
Zhang, Q. Q.; Li, X. S.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, H.; Yi, W. C.; Liu, J. Y.; Han, J.; Xi, G. C. A metallic molybdenum dioxide with high stability for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14903.
Liu, W.; Li, X. S.; Li, W. T.; Zhang, Q. Q.; Bai, H.; Li, J. F.; Xi, G. C. Highly stable molybdenum dioxide nanoparticles with strong Plasmon resonance are promising in photothermal cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 163, 43–54.
Zhu, Y. P.; El-Demellawi, J. K.; Yin, J.; Lopatin, S.; Lei, Y. J.; Liu, Z. X.; Miao, X. H.; Mohammed, O. F.; Alshareef, H. N. Unprecedented surface Plasmon modes in monoclinic MoO2 nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1908392.
Acknowledgements
This work received financial support from the Science Foundation of Chinese Academy of Inspection and Quarantine (No. 2017JK045) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2017YFF0210003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Li, W., Li, Y. et al. Determine the position of nanoparticles in cells by using surface-enhanced Raman three-dimensional imaging. Nano Res. 14, 3402–3406 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3726-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3726-z