Abstract
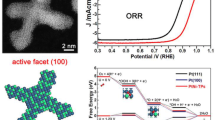
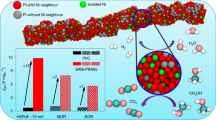
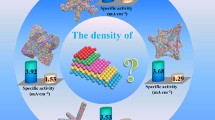
The control of the size, composition, and shape of platinum nanocrystals has attracted much attention recently, mostly due to their unique properties and related catalytic functionalities. However, the realization of platinum nanocrystals with controlled exposed facets and dimensionality remains a significant challenge. Herein, we show an efficient synthetic strategy to selectively prepare highly controllable platinum nanocrystals with distinct dimensionalities from onedimensional nanowires to zero-dimensional octahedra. Although the synthesis of platinum nanowires has been reported multiple times, the synthetic approach reported herein is much more novel and robust and ultimately results in high yields of high-quality platinum nanowires. Such dimensionality tuning on {111} facet dominated platinum nanocrystals allows us to firstly investigate the effect of the number of edges/corners on the electrocatalytic properties. Our results show that the synthesized platinum nanocrystals exhibit very interesting dimensionality-dependent electrocatalytic activity towards both the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and methanol oxidation reaction (MOR), in which one-dimensional platinum nanowires with minimized edges/corners show enhanced electrocatalytic activities with respect to zero-dimensional platinum octahedra. Our dimensionality tuning also provides Pt nanowires with superior durability for the oxygen reduction reaction with negligible activity decay over the course of 30,000 potential sweeps. The present work highlights that the {111} facet bound platinum nanowires with minimized edges/corners are indeed promising candidates as electrocatalysts with excellent activity and superior durability.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, X. L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Dai, X. P.; Gao, J. S.; Li, X. Y.; Zhang, P. F.; Wang, H. H.; Yu, N. F. et al. Synthesis of Pt-Ni alloy nanocrystals with high-index facets and enhanced electrocatalytic properties. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 126, 12730–12735.
Wu, J. B.; Yang, H. Platinum-based oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1848–1857.
You, H. J.; Zhang, F. L.; Liu, Z.; Fang, J. X. Free-standing Pt–Au hollow nanourchins with enhanced activity and stability for catalytic methanol oxidation. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2829–2835.
Xia, B. Y.; Ng, W. T.; Wu, H. B.; Wang, X.; Lou, X. W. Self-supported interconnected Pt nanoassemblies as highly stable electrocatalysts for low-temperature fuel cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 124, 7325–7328.
Wu, J. B.; Gross, A.; Yang, H. Shape and compositioncontrolled platinum alloy nanocrystals using carbon monoxide as reducing agent. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 798–802.
Tian, N.; Zhou, Z. Y.; Sun, S. G.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. L. Synthesis of tetrahexahedral platinum nanocrystals with high-index facets and high electro-oxidation activity. Science 2007, 316, 732–735.
Huang, X. Q.; Zhao, Z. P.; Fan, J. M.; Tan, Y. M.; Zheng, N. F. Amine-assisted synthesis of concave polyhedral platinum nanocrystals having {411} high-index facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4718–4721.
Lacroix, L. M.; Gatel, C.; Arenal, R.; Garcia, C.; Lachaize, S.; Blon, T.; Warot-Fonrose, B.; Snoeck, E.; Chaudret, B.; Viau, G. Tuning complex shapes in platinum nanoparticles: From cubic dendrites to fivefold stars. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4690–4694.
Cui, C. H.; Gan, L.; Heggen, M.; Rudi, S.; Strasser, P. Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 765–771.
Wu, Y. E.; Wang, D. S.; Niu, Z. Q.; Chen, P. C.; Zhou, G.; Li, Y. D. A strategy for designing a concave Pt–Ni alloy through controllable chemical etching. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12524–12528.
Zhu, C. Z.; Guo, S. J.; Dong, S. J. PdM (M = Pt, Au) bimetallic alloy nanowires with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for electro-oxidation of small molecules. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2326–2331.
Guo, S. J.; Zhang, S.; Su, D.; Sun, S. H. Seed-mediated synthesis of core/shell FePtM/FePt (M = Pd, Au) nanowires and their electrocatalysis for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13879–13884.
Zhang, S.; Hao, Y. Z.; Su, D.; Doan-Nguyen, V. V. T.; Wu, Y. T.; Li, J.; Sun, S. H.; Murray, C. B. Monodisperse core/ shell Ni/FePt nanoparticles and their conversion to Ni/Pt to catalyze oxygen reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15921–15924.
Sneed, B. T.; Young, A. P.; Jalalpoor, D.; Golden, M. C.; Mao, S. J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tsung, C. K. Shaped Pd–Ni–Pt core-sandwich-shell nanoparticles: Influence of Ni sandwich layers on catalytic electrooxidations. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7239–7250.
Maksimuk, S.; Yang, S. C.; Peng, Z. M.; Yang, H. Synthesis and characterization of ordered intermetallic PtPb nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8684–8685.
Ma, L.; Wang, C. M.; Xia, B. Y.; Mao, K. K.; He, J. W.; Wu, X. J.; Xiong, Y. J.; Lou, X. W. Platinum multicubes prepared by Ni2+-mediated shape evolution exhibit high electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 127, 5758–5763.
Komanicky, V.; Menzel, A.; You, H. Investigation of oxygen reduction reaction kinetics at (111)-(100) nanofaceted platinum surfaces in acidic media. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 23550–23557.
Stamenkovic, V. R.; Fowler, B.; Mun, B. S.; Wang, G. F.; Ross, P. N.; Lucas, C. A.; Markovic, N. M. Improved oxygen reduction activity on Pt3Ni(111) via increased surface site availability. Science 2007, 315, 493–497.
Cui, C. H.; Li, H. H.; Liu, X. J.; Gao, M. R.; Yu, S. H. Surface composition and lattice ordering-controlled activity and durability of CuPt electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 916–924.
Cui, C. H.; Gan, L.; Li, H. H.; Yu, S. H.; Heggen, M.; Strasser, P. Octahedral PtNi nanoparticle catalysts: Exceptional oxygen reduction activity by tuning the alloy particle surface composition. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5885–5889.
Xia, B. Y.; Wu, H. B.; Yan, Y.; Lou, X. W.; Wang, X. Ultrathin and ultralong single-crystal platinum nanowire assemblies with highly stable electrocatalytic activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9480–9485.
Rana, M.; Chhetri, M.; Loukya, B.; Patil, P. K.; Datta, R.; Gautam, U. K. High-yield synthesis of sub-10 nm Pt nanotetrahedra with bare <111> facets for efficient electrocatalytic applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4998–5005.
Xia, Y. N.; Xiong, Y. J.; Lim, B.; Skrabalak, S. E. Shapecontrolled synthesis of metal nanocrystals: Simple chemistry meets complex physics? Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 60–103.
Ringe, E.; Van Duyne, R. P.; Marks, L. D. Kinetic and thermodynamic modified wulff constructions for twinned nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 15859–15870.
Zhou, W.; Wu, J. B.; Yang, H. Highly uniform platinum icosahedra made by hot injection-assisted GRAILS method. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2870–2874.
Marković, N. M.; Schmidt, T. J.; Stamenković, V.; Ross, P. N. Oxygen reduction reaction on Pt and Pt bimetallic surfaces: A selective review. Fuel Cells 2001, 1, 105–116.
He, C. Z.; Desai, S.; Brown, G.; Bollepalli, S. PEM fuel cell catalysts: Cost, performance, and durability. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2005, 14, 41–44.
Shao, Y. Y.; Yin, G. P.; Gao, Y. Z. Understanding and approaches for the durability issues of Pt-based catalysts for PEM fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 558–566.
Xia, Y. N.; Yang, P. D.; Sun, Y. G.; Wu, Y. Y.; Mayers, B.; Gates, B.; Yin, Y. D.; Kim, F.; Yan, H. Q. One-dimensional nanostructures: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 353–389.
Tao, A. R.; Habas, S.; Yang, P. D. Shape control of colloidal metal nanocrystals. Small 2008, 4, 310–325.
Koenigsmann, C.; Santulli, A. C.; Gong, K. P.; Vukmirovic, M. B.; Zhou, W. P.; Sutter, E.; Wong, S. S.; Adzic, R. R. Enhanced electrocatalytic performance of processed, ultrathin, supported Pd–Pt core–shell nanowire catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9783–9795.
Guo, S. J.; Li, D. G.; Zhu, H. Y.; Zhang, S.; Markovic, N. M.; Stamenkovic, V. R.; Sun, S. H. FePt and CoPt nanowires as efficient catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3465–3468.
Guo, S. J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X. L.; Sun, S. H. Synthesis of ultrathin FePtPd nanowires and their use as catalysts for methanol oxidation reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15354–15357.
Zhu, H. Y.; Zhang, S.; Guo, S. J.; Su, D.; Sun, S. H. Synthetic control of FePtM nanorods (M = Cu, Ni) to enhance the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7130–7133.
Clavilier, J. The role of anion on the electrochemical behaviour of a {111} platinum surface; an unusual splitting of the voltammogram in the hydrogen region. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1980, 107, 211–216.
Song, Y. J.; Garcia, R. M.; Dorin, R. M.; Wang, H. R.; Qiu, Y.; Coker, E. N.; Steen, W. A.; Miller, J. E.; Shelnutt, J. A. Synthesis of platinum nanowire networks using a soft template. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3650–3655.
Li, C. L.; Jiang, B.; Miyamoto, N.; Kim, J. H.; Malgras, V.; Yamauchi, Y. Surfactant-directed synthesis of mesoporous Pd films with perpendicular mesochannels as efficient electrocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11558–11561.
Huang, X. Q.; Zheng, N. F. One-pot, high-yield synthesis of 5-fold twinned Pd nanowires and nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4602–4603.
Technical plan—Fuel cells. In Muti-year Research, Development, and Demonstration Plan [Online]; U. S. Department of Energy, 2012, pp 3.4-1–3.4-58. (http://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/mypp/pdfs/fuel_cells.pdf) (accessed Jun 6, 2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, L., Feng, Y., Yao, J. et al. Facet and dimensionality control of Pt nanostructures for efficient oxygen reduction and methanol oxidation electrocatalysts. Nano Res. 9, 2811–2821 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1170-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1170-2