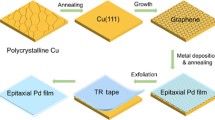
Abstract
The chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of graphene on Cu substrates enables the fabrication of large-area monolayer graphene on desired substrates. However, during the transfer of the synthesized graphene, topographic defects are unavoidably formed along the Cu grain boundaries, degrading the electrical properties of graphene and increasing the device-to-device variability. Here, we introduce a method of hot-pressing as a surface pre-treatment to improve the thermal stability of Cu thin film for the suppression of grain boundary grooving. The flattened Cu thin film maintains its smooth surface even after the subsequent high temperature CVD process necessary for graphene growth, and the formation of graphene without wrinkles is realized. Graphene field effect transistors (FETs) fabricated using the graphene synthesized on hot-pressed Cu thin film exhibit superior field effect mobility and significantly reduced device-to-device variation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, K; Cao, P.; Heath, J. R. Scanning tunneling microscopy characterization of the electrical properties of wrinkles in exfoliated graphene monolayers. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4446–4451.
Ahmad, M.; Han, S. A.; Tien, D. H.; Jung, J.; Seo, Y. Local conductance measurement of graphene layer using conductive atomic force microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 054307.
Franklin, A. D.; Han, S.-J.; Bol, A. A.; Haensch, W. Effects of nanoscale contacts to graphene. IEEE Elec. Dev. Lett. 2011, 32, 1035–1037.
Yan, L.; Punckt, C.; Aksay, I. A.; Mertin, W.; Bacher, G. Local voltage drop in a single functionalized graphene sheet characterized by Kelvin probe force microscopy. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3543–3549.
Zhu, W.; Low, T.; Perebeinos, V.; Bol, A. A.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, H.; Tersoff, J.; Avouris, P. Structure and electronic transport in graphene wrinkles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3431–3436.
Guo, Y.; Guo, W. Electronic and field emission properties of wrinkled graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 117, 692–696.
Lee, J.-K.; Yamazaki, S.; Yun, H.; Park, J.; Kennedy, G. P.; Kim, G.-T.; Pietzsch, O.; Wiesendanger, R.; Lee, S.; Hong, S.; et al. Modification of electrical properties of graphene by substrate-induced nanomodulation. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 3494–3500.
Wang, C.; Lan L.; Tan, H. The physics of wrinkling in graphene membranes under local tension. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 2764–2773.
Clark, K. W.; Zhang, X.-G.; Vlassiouk, I. V.; He, G.; Feenstra, R. M.; Li, A.-P. Spatially resolved mapping of electrical conductivity across individual domain (grain) boundaries in graphene. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7956–7966.
Lanza, M.; Wang, Y.; Bayerl, A.; Gao, T.; Porti, M.; Nafria, M.; Liang, H.; Jing, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Tuning graphene morphology by substrate towards wrinkle-free devices: Experiment and simulation. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 104301.
Mun, J. H.; Cho, B. J. Synthesis of monolayer graphene having a negligible amount of wrinkles by stress relaxation. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2496–2499.
Yan, H.; Chu, Z.-D.; Yan, W.; Liu, M.; Meng, L.; Yang, M.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Dou, R.-F.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Superlattice Dirac points and space-dependent Fermi velocity in a corrugated graphene monolayer. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 075405.
Chae, S. J.; Güneş, F.; Kim, K. K.; Kim, E. S.; Han, G. H.; Kim, S. M.; Shin, H. J.; Yoon, S. M.; Choi, J. Y.; Park, M. H.; et al. Synthesis of large-area graphene layers on Poly-nickel substrate by chemical vapor deposition: Wrinkle formation. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2328–2333.
Liu, N.; Pan, Z.; Fu, L.; Zhnag, C.; Dai, B.; Liu, Z. The origin of wrinkles on transferred graphene. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 996–1004.
Luo, Z.; Lu, Y.; Singer, D. W.; Berck, M. E.; Somers, L. A.; Goldsmith, B. R.; Johnson, A. C. Effect of substrate roughness and feedstock concentration on growth of wafer-scale graphene at atmospheric pressure. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1441–1447.
Chen, Z.; Ren, W.; Gao, L.; Liu, B.; Pei, S.; Cheng, H.-M. Three-dimensional flexible and conductive interconnected graphene networks grown by chemical vapour deposition. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 424–428.
Zhang, Y.; Gao, T.; Xie, S.; Dai, B.; Fu, L.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z. Different growth behaviors of ambient pressure chemical vapor deposition graphene on Ni (111) and Ni films: A scanning tunneling microscopy study. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 402–411.
Surwade, S. P.; Li, Z.; Liu, H. Thermal oxidation and unwrinkling of chemical vapor deposition-grown graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 20600–20606.
Krell, A. Improved hardness and hierarchic influences on wear in submicron sintered alumina. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 209, 156–163.
Onishi, T.; Yoshikawa, T. Application of high-pressure annealing process to dual damascene copper interconnections. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 1605–1614.
Shin, D. H.; Park, J.-J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, K.-T. Constrained groove pressing and its application to grain refinement of aluminum. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 328, 98–103.
Genin, F.; Mullins, W.; Wynblatt, P. The effect of stress on grain boundary grooving. Acta Metall. Mater. 1993, 41, 3541–3547.
Volkert, C.; Lingk, C. Effect of compression on grain growth in Al films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 3677–3679.
Ferrari, A.; Meyer, J.; Scardaci, V.; Casiraghi, C.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F.; Piscanec, S.; Jiang, D.; Novoselov, K.; Roth, S.; et al. Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 187401.
Graf, D.; Molitor, F.; Ensslin, K.; Stampfer, C.; Jungen, A.; Hierold, C.; Wirtz, L. Spatially resolved Raman spectroscopy of single-and few-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 238–242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mun, J.H., Oh, J.G., Bong, J.H. et al. Wrinkle-free graphene with spatially uniform electrical properties grown on hot-pressed copper. Nano Res. 8, 1075–1080 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0585-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0585-x