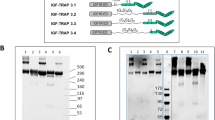
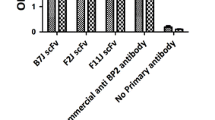
Abstract
Owing to the extraordinary potency in inhibiting protein translation that could eventually lead to apoptosis of tumor cells, ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) such as gelonin have been considered attractive drug candidates for cancer therapy. However, due to several critical obstacles (e.g., severe toxicity issues caused by a lack of selectivity in their mode of action and the low cytotoxicity via poor cellular uptake, etc.), clinical application of RIPs is yet far from being accomplished. To overcome these challenges, in the present study, we engineered gelonin fusion proteins with anti-insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) affibody (“IAFF”) via the genetic recombinant method and the SpyCatcher/SpyTag-mediated conjugation method. To this end, recombinant gelonin-anti-IGF-1R affibody (rGel-IAFF), gelonin-SpyCatcher (Gel-SpyCatcher) and SpyTag-IAFF fusion proteins were produced from the E. coli expression system, and gelonin-IAFF conjugate was synthesized by mixing Gel-SpyCatcher and SpyTag-IAFF. After preparation of both rGel-IAFF and Gel-IAFF conjugate, their components’ functionality was characterized in vitro. Our assay results confirmed that, while both Gel-IAFF and Gel-SpyCatcher retained equipotent N-glycosidase activity to that of gelonin, IAFF was able to selectively bind to IGF-1R overexpressed U87 MG brain cancer cells over low expression LNCaP cells. The results of cellular analyses showed that rGel-IAFF and Gel-IAFF conjugate both exhibited a greater cell uptake in the U87 MG cells than gelonin, but not in the LNCaP cells, yielding a significantly augmented cytotoxicity only in the U87 MG cells. Remarkably, rGel-IAFF and Gel-IAFF conjugate displayed 22- and 5.6-fold lower IC50 values (avg. IC50: 180 and 720 nM, respectively) than gelonin (avg. IC50: 4000 nM) in the U87 MG cells. Overall, the results of the present research demonstrated that fusion of gelonin with IAFF could provide an effective way to enhance the anti-tumor activity, while reducing the associated toxicity of gelonin.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen TM (2002) Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2:750–763
Atkinson SF, Bettinger T, Seymour LW, Behr JP, Ward CM (2001) Conjugation of folate via gelonin carbohydrate residues retains ribosomal-inactivating properties of the toxin and permits targeting to folate receptor positive cells. J Biol Chem 276:27930–27935
Bashyal S, Noh G, Keum T, Choi YW, Lee S (2016) Cell penetrating peptides as an innovative approach for drug delivery; then, present and the future. J Pharm Investig 46:205–220
Bertrand N, Wu J, Xu X, Kamaly N, Farokhzad OC (2014) Cancer nanotechnology: the impact of passive and active targeting in the era of modern cancer biology. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 66:2–25
Chong LD (2017) Brain cancer therapy. Science 355:258
Domeradzka NE, Werten MW, Wolf FA, de Vries R (2016) Protein cross-linking tools for the construction of nanomaterials. Curr Opin Biotechnol 39:61–67
Frejd FY, Kim KT (2017) Affibody molecules as engineered protein drugs. Exp Mol Med 49:e306
Ham SH, Min KA, Shin MC (2017) Molecular tumor targeting of gelonin by fusion with F3 peptide. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38:897–906
Huang X, Peng X, Wang Y, Wang Y, Shin DM, El-Sayed MA, Nie S (2010) A reexamination of active and passive tumor targeting by using rod-shaped gold nanocrystals and covalently conjugated peptide ligands. ACS Nano 4:5887–5896
Kim CH, Lee SG, Kang MJ, Lee S, Choi YW (2017a) Surface modification of lipid-based nanocarriers for cancer cell-specific drug targeting. J Pharm Investig 47:203–227
Kim MC, Lin MM, Sohn Y, Kim JJ, Kang BS, Kim DK (2017b) Polyethyleneimine-associated polycaprolactone-Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a gene delivery vector. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 105:145–154
Lee TY, Park YS, Garcia GA, Sunahara RK, Woods JH, Yang VC (2012) Cell permeable cocaine esterases constructed by chemical conjugation and genetic recombination. Mol Pharm 9:1361–1373
Lee JH, Sahu A, Jang C, Tae G (2015) The effect of ligand density on in vivo tumor targeting of nanographene oxide. J Control Release 209:219–228
Li L, Fierer JO, Rapoport TA, Howarth M (2014) Structural analysis and optimization of the covalent association between SpyCatcher and a peptide Tag. J Mol Biol 426:309–317
Luo HC, Li N, Yan L, Mai KJ, Sun K, Wang W, Lao GJ, Yang C, Zhang LM, Ren M (2017) Comparison of the cellular transport mechanism of cationic, star-shaped polymers and liposomes in HaCat cells. Int J Nanomedicine 12:1085–1096
Malik A, Sutantyo ML, Hapsari I, Sinurat AV, Purwati EM, Jufri M, Suryadi H (2016) Simultaneous identification and verification of gelatin type in capsule shells by electrophoresis and polymerase chain reaction. J Pharm Investig 46:475–485
Min KA, He H, Yang VC, Shin MC (2016) Construction and characterization of gelonin and saporin plasmids for toxic gene-based cancer therapy. Arch Pharm Res 39:677–686
Olson JJ, Nayak L, Ormond DR, Wen PY, Kalkanis SN, Committee ACJG (2014) The role of cytotoxic chemotherapy in the management of progressive glioblastoma: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 118:501–555
Reddington SC, Howarth M (2015) Secrets of a covalent interaction for biomaterials and biotechnology: SpyTag and SpyCatcher. Curr Opin Chem Biol 29:94–99
Reiss K, Wang JY, Romano G, Furnari FB, Cavenee WK, Morrione A, Tu X, Baserga R (2000) IGF-I receptor signaling in a prostatic cancer cell line with a PTEN mutation. Oncogene 19:2687–2694
Rock K, McArdle O, Forde P, Dunne M, Fitzpatrick D, O’Neill B, Faul C (2012) A clinical review of treatment outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme–the validation in a non-trial population of the results of a randomised Phase III clinical trial: has a more radical approach improved survival? Br J Radiol 85:e729–e733
Sathornsumetee S, Reardon DA, Desjardins A, Quinn JA, Vredenburgh JJ, Rich JN (2007) Molecularly targeted therapy for malignant glioma. Cancer 110:13–24
Schardt JS, Oubaid JM, Williams SC, Howard JL, Aloimonos CM, Bookstaver ML, Lamichhane TN, Sokic S, Liyasova MS, O’Neill M, Andresson T, Hussain A, Lipkowitz S, Jay SM (2017) Engineered multivalency enhances affibody-based HER3 inhibition and downregulation in cancer cells. Mol Pharm 14:1047–1056
Schrot J, Weng A, Melzig MF (2015) Ribosome-inactivating and related proteins. Toxins (Basel) 7:1556–1615
Shin MC, Zhang J, David AE, Trommer WE, Kwon YM, Min KA, Kim JH, Yang VC (2013) Chemically and biologically synthesized CPP-modified gelonin for enhanced anti-tumor activity. J Control Release 172:169–178
Shin MC, Zhao J, Zhang J, Huang Y, He H, Wang M, Min KA, Yang VC (2015) Recombinant TAT-gelonin fusion toxin: synthesis and characterization of heparin/protamine-regulated cell transduction. J Biomed Mater Res A 103:409–419
Shin MC, Min KA, Cheong H, Moon C, Huang Y, He H, Yang VC (2016) Preparation and characterization of gelonin-melittin fusion biotoxin for synergistically enhanced anti-tumor activity. Pharm Res 33:2218–2228
Shin MC, Min KA, Cheong H, Moon C, Huang Y, He H, Yang VC (2017) Tandem-multimeric F3-gelonin fusion toxins for enhanced anti-cancer activity for prostate cancer treatment. Int J Pharm 524:101–110
Singh P, Alex JM, Bast F (2014) Insulin receptor (IR) and insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF-1R) signaling systems: novel treatment strategies for cancer. Med Oncol 31:805
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Son JH, Hwang EC, Kim J (2016) Systematic analyses of the ultraviolet radiation resistance-associated gene product (UVRAG) protein interactome by tandem affinity purification. Arch Pharm Res 39:370–379
Srinivasarao M, Galliford CV, Low PS (2015) Principles in the design of ligand-targeted cancer therapeutics and imaging agents. Nat Rev Drug Discov 14:203–219
Stirpe F (2013) Ribosome-inactivating proteins: from toxins to useful proteins. Toxicon 67:12–16
Stirpe F, Olsnes S, Pihl A (1980) Gelonin, a new inhibitor of protein synthesis, nontoxic to intact cells. Isolation, characterization, and preparation of cytotoxic complexes with concanavalin A. J Biol Chem 255:6947–6953
Su X, Cheng K, Liu Y, Hu X, Meng S, Cheng Z (2015) PET imaging of insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor expression with a 64Cu-labeled Affibody molecule. Amino Acids 47:1409–1419
Sudo K, Niikura K, Iwaki K, Kohyama S, Fujiwara K, Doi N (2017) Human-derived fusogenic peptides for the intracellular delivery of proteins. J Control Release 255:1–11
Tolmachev V, Orlova A, Nilsson FY, Feldwisch J, Wennborg A, Abrahmsen L (2007) Affibody molecules: potential for in vivo imaging of molecular targets for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 7:555–568
Ul Ain Q, Lee JH, Woo YS, Kim YH (2016) Effects of protein transduction domain (PTD) selection and position for improved intracellular delivery of PTD-Hsp27 fusion protein formulations. Arch Pharm Res 39:1266–1274
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the grants from Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2015R1C1A1A02036781 and NRF-2017R1C1B5015491). This study was also supported by the Inje University Research Fund, Republic of Korea (Grant #: 20160539). We thank Dr. Wolfgang E. Trommer (University of Kaiserslautern, Germany) for the gelonin expression vector (pET28a-Gel).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ham, S., Min, K.A., Yang, J.W. et al. Fusion of gelonin and anti-insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) affibody for enhanced brain cancer therapy. Arch. Pharm. Res. 40, 1094–1104 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0953-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-017-0953-7