Abstract
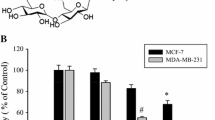
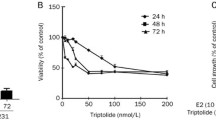
Estrogen receptor (ER)-α is an important therapeutic target in the clinical treatment of breast cancer. A potential down-regulator of ER-α, diosgenyl α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-[β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1→4)]-α-l-arabinopyranoside is a newly synthesized diosgenyl saponin named compound 22. This study evaluated the in vitro mechanism of compound 22 as an anticancer agent for breast cancer. Our results indicated that compound 22 selectively inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in ER-positive MCF-7 cells, compared with ER-negative MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A cells. Western blot analysis showed that compound 22 decreased the expression of procaspase-3, procaspase-8, and survivin; and increased the expression of Fas ligand and cleaved PARP1 in MCF-7 cells, indicating that compound 22-induced apoptosis was mediated by the extrinsic pathway. This apoptosis was associated with the suppression of ER-α protein and mRNA expression and the inhibition of ER-DNA binding to the estrogen responsive element. Moreover, ER-α mediated gene expression such as c-Myc and cyclin D1 was reduced, and the activation of p38 and ERK 1/2 was significantly decreased after treatment with compound 22 in MCF-7 cells. Taken together, these results demonstrate that compound 22 down-regulates ER-α expression and induces apoptosis through the extrinsic pathway, suggesting that compound 22 may be effective in the treatment of ER-positive breast cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosini, G., C. Adida, and D.C. Altieri. 1997. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nature Medicine 3: 917–921.
Chen, Z., T.B. Gibson, F. Robinson, L. Silvestro, G. Pearson, B. Xu, A. Wright, C. Vanderbilt, and M.H. Cobb. 2001. MAP kinases. Chemical Reviews 101: 2449–2476.
Chen, Y., E.A. Alvarez, D. Azzam, S.A. Wander, N. Guggisberg, M. Jorda, Z. Ju, B.T. Hennessy, and J.M. Slingerland. 2011. Combined Src and ER blockade impairs human breast cancer proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 128: 69–78.
Chun, J., R.J. Choi, S. Khan, D.S. Lee, Y.C. Kim, Y.J. Nam, D.U. Lee, and Y.S. Kim. 2012. Alantolactone suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by down-regulating NF-κB, MAPK and AP-1 via the MyD88 signaling pathway in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. International Immunopharmacology 14: 375–383.
Chun, J., E.J. Joo, M. Kang, and Y.S. Kim. 2013. Platycodin D induces anoikis and caspase-mediated apoptosis via p38 MAPK in AGS human gastric cancer cells. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 114: 456–470.
Clemons, M., S. Danson, and A. Howell. 2002. Tamoxifen (“Nolvadex”): A review. Cancer Treatment Reviews 28: 165–180.
Gadducci, A., S. Cosio, and A.R. Genazzani. 2004. Use of estrogen antagonists and aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer and hormonally sensitive tumors of the uterine body. Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs 5: 1031–1044.
Hahm, E.R., J. Lee, Y. Huang, and S.V. Singh. 2011. Withaferin a suppresses estrogen receptor-α expression in human breast cancer cells. Molecular Carcinogenesis 50: 614–624.
Kaskiw, M.J., M.L. Tassotto, J. Th’ng, and Z.H. Jiang. 2008. Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of diosgenyl saponin analogues. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 16: 3209–3217.
Kurokawa, H., A.E. Lenferink, J.F. Simpson, P.I. Pisacane, M.X. Sliwkowski, J.T. Forbes, and C.L. Arteaga. 2000. Inhibition of HER2/neu (erbB-2) and mitogen-activated protein kinases enhances tamoxifen action against HER2-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Research 60: 5887–5894.
Liang, Y., C. Yan, and N.F. Schor. 2001. Apoptosis in the absence of caspase 3. Oncogene 20: 6570–6578.
Liu, M.J., Z. Wang, Y. Ju, J.B. Zhou, Y. Wang, and R.N. Wong. 2004. The mitotic-arresting and apoptosis-inducing effects of diosgenyl saponins on human leukemia cell lines. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 27: 1059–1065.
Lukas, J., J. Bartkova, and J. Bartek. 1996. Convergence of mitogenic signalling cascades from diverse classes of receptors at the cyclin D-cyclin-dependent kinase-pRb-controlled G1 checkpoint. Molecular and Cellular Biology 16: 6917–6925.
Man, S., W. Gao, Y. Zhang, L. Huang, and C. Liu. 2010. Chemical study and medical application of saponins as anti-cancer agents. Fitoterapia 81: 703–714.
Man, S., W. Gao, Y. Yan, Z. Liu, and C. Liu. 2011. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases related to metastasis by diosgenyl and pennogenyl saponins. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 137: 1221–1227.
Moghadam, S.J., A.M. Hanks, and K. Keyomarsi. 2011. Breaking the cycle: An insight into the role of ERα in eukaryotic cell cycles. Journal of carcinogenesis 10: 25.
Morgan, L., R.I. Nicholson, and S. Hiscox. 2008. SRC as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Endocrine, Metabolic and Immune Disorders: Drug Targets 8: 273–278.
Pettersson, K., K. Grandien, G.G. Kuiper, and J.A. Gustafsson. 1997. Mouse estrogen receptor β forms estrogen response element-binding heterodimers with estrogen receptor α. Molecular Endocrinology 11: 1486–1496.
Sayeed, A., S.D. Konduri, W. Liu, S. Bansal, F. Li, and G.M. Das. 2007. Estrogen receptor α inhibits p53-mediated transcriptional repression: Implications for the regulation of apoptosis. Cancer Research 67: 7746–7755.
Schmitt, F., Nguyen, P.H., Gupta, N., Mayer, D., Eph receptor B4 is a regulator of estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, (2013).
Sommer, S., and S.A. Fuqua. 2001. Estrogen receptor and breast cancer. Seminars in Cancer Biology 11: 339–352.
Srinivasan, S., S. Koduru, R. Kumar, G. Venguswamy, N. Kyprianou, and C. Damodaran. 2009. Diosgenin targets Akt-mediated prosurvival signaling in human breast cancer cells. International Journal of Cancer 125: 961–967.
Thompson, E.B. 1998. The many roles of c-Myc in apoptosis. Annual Review of Physiology 60: 575–600.
Vincken, J.P., L. Heng, A. de Groot, and H. Gruppen. 2007. Saponins, classification and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 68: 275–297.
Wang, L.S., Y.W. Huang, S. Liu, P. Yan, and Y.C. Lin. 2008. Conjugated linoleic acid induces apoptosis through estrogen receptor α in human breast tissue. BMC Cancer 8: 208.
Wang, B., J. Chun, Y. Liu, L. Han, Y.S. Wang, E.J. Joo, Y.S. Kim, and M.S. Cheng. 2012. Synthesis of novel diosgenyl saponin analogues and apoptosis-inducing activity on A549 human lung adenocarcinoma. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry 10: 8822–8834.
Wong, C.W., C. McNally, E. Nickbarg, B.S. Komm, and B.J. Cheskis. 2002. Estrogen receptor-interacting protein that modulates its nongenomic activity-crosstalk with Src/Erk phosphorylation cascade. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99: 14783–14788.
Zhang, Z., B. Maier, R.J. Santen, and R.X. Song. 2002. Membrane association of estrogen receptor alpha mediates estrogen effect on MAPK activation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 294: 926–933.
Zivadinovic, D., and C.S. Watson. 2005. Membrane estrogen receptor-α levels predict estrogen-induced ERK1/2 activation in MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Research 7: R130–R144.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korean Government (MEST) (MRC No. 2009-93146).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jaemoo Chun and Lina Han have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chun, J., Han, L., Xu, M.Y. et al. The induction of apoptosis by a newly synthesized diosgenyl saponin through the suppression of estrogen receptor-α in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 1477–1486 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0279-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0279-z