Abstract
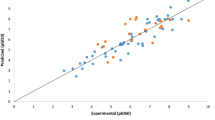
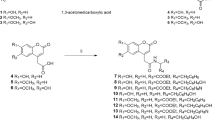
To predict a new materials of superior melanogenesis inhibitory activities (MIA), the comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) models on MIA of alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzoates and N-alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzamides analogues against mouse melanoma cell were derived and discussed quantitatively. The optimized CoMFA model II from the field fit alignment demonstrated better predictability of molecular structure with the non-cross validated conventional coefficient (r2 nev.=0.984) and cross-validated coefficient (r2 cv. or q=0.706) than that from atom based fit alignment. Also, the relative contribution of the optimized CoMFA model II showed the steric (63.8%), electrostatic (18.4%), and hydrophobic (ClogP) field (17.8%), respectively. The results indicated that the esters (alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzoates) are more active inhibitors than the amides (N-alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzamides). Furthermore, the optimized CoMFA model II is proven to be a useful approach to design a highly active melanogenesis inhibitor molecules, and enables to predict R1=n-dodecy and R2=n-heptyloxy substituted compound of alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzoates as the most active compounds (Pred. pI50=5.87).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akamatsu, M., Current state and perspectives of 3D-QSAR, Curr. Topics Med. Chem., 2, 1381–1394 (2002).
Allinger, N. L., Chen, K., and Lii, J. H. An Improved Force Field (MM4) for Saturated Hydrocarbons. J. Comput. Chem., 17, 642–668 (1996).
Casanola-Martin, G. M., Marrero-Ponce, Y., Khan, M. T. H., Ather, A., Khan, K. M., Torrens, F., and Rptondo, R., Dragon method for finding novel tyrosinease inhibitors: Biosilico identification and experimental in vitro assays. Eur. J. Med. Chem., 42, 1370–1381 (2007).
Cho, S. J., Roh, J. S., Sun, W. S., Kim, S. H., and Park, K. D., N-benzylamides: A new class of potent tyrosine inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 16, 2682–2684 (2006).
Clark, M., Cramer III, R. D., Jones, D. M., Patterson, D. E., and Simerroth, P. E., Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 2. toward its use with 3D-structural database. Tetrahedron Comput. Methodol. 3, 47–59 (1990).
Cramer, III R. D., Patterson, D. E., and Bunce, J. D., Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 110, 5959–5967 (1988).
Dooley, T. P., Gadwood, R. C., Kilgore, K., and Thomasco, L. M., Development of an in vitro primary screen for skin depigmentation and antimelanoma agents, Skin Pharm., 7, 188–200 (1994).
Ha, Y. M., Chung, S. W., Song, S., Lee, H., Suh, H., and Chung, H. Y., 4-(6-hydroxy-2-naphthyl)-1,3-bezendiol: A potent, new tyrosinase inhibitor. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 39, 1711–1715 (2007).
Islam, M. N., Song, Y., and Iskander, M. N., Investigation of structural requirements of anticancer activity at the paclitaxel/tubulin binding site using CoMFA and CoMSIA, J. Mol. Graphics and Modelling., 21, 263–272 (2003).
Kellogg, G. E., Semus, S. F., and Abraham, D. J., HINT: A new method of empirical hydrophobic field calculation for CoMFA. J. Comp.-Aided Mol. Design., 5, 545–552 (1991).
Kerr, R., Parallel helix bundles and ion channels: Molecular modeling via simulated annealing and restrained molecular dynamics. Biophys. J., 67, 1501–1515 (1994).
Kim, D. S., Kim, S. Y., Moon, S. J., Chung, J. H., Kim, K. H., Cho, K. H., and Park, K. C., Cerimide inhibits cell proliferation through Akt/PKB inactivation and decreases melanin synthesis in Mel-Ab cells. Pigment Cell Res., 14(2), 110–115, (2001).
Kovatcheva, A., Buchbauer, G., Golbraikh, A., and Wolschann, P., QSAR Modeling of α-Campholenic Derivatives with Sandalwood Odor. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 43, 259–266 (2003).
Longa, S. D., The dinuclear copper site structure of agaricus bisporus tyrosinase in solution probed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy, J. Biol. Chem., 271(35), 21025–21030 (1996).
Liu, J., Yi, W., Wan, Y., Ma, L., and Song, H.,1-(1-arylethylidene) thiosemicarbazide derivatives: A new class of tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 16, 1096–1102 (2008).
Lu, D., Willard, D., Patel, I. R., Kadwell, S., Overton, L., Kost, T., Luther, M., Chen, W., Woychik, R. P., and Wilkison, W. O., Agouti protein is an antagonist of the melanocytestimulating- hormone receptor. Nature., 371, 799–802 (1994).
Marshall, G. R., Barry, C. D., Bosshard, H. E., Dammkoehler, R. A., and Dunn, D. A., In Computer assisted Drug Design (Olsen, E. C. and Christoffersen, R. E. Eds.). ACS Washington D.C., p. 205, (1979).
Masuda, M., Tejima, T., Suzuki, T., and Imokawa, G., Skin Lighteners, Cosmetic & Oiletries., 111(10), 65–77 (1996).
Morimura, K., Yamazaki, C., Hattori, Y., Makabe, H., Kamo, T., and Hirota, M. A tyrosine inhibitor, Daedalin A, from mycelial culture of Daedalea dickinisii. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 71, 2837–2840 (2007).
Murthy, V. S. and Kulkarni, V. M., 3D-QSAR CoMFA and CoMSIA on Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 10, 2267–2282 (2002).
Parvez, S., Kang, M., Chung, H-S., and Bae, H., Naturally occurring tyrosinase inhibitors: Mechanism and applications in skin health, cosmetics and agriculture industries. Phytother. Res., 805–816 (2007).
Purcell, W. P. and Singer, J. A., A brief review and table of semiempirical parameters used in the Huckel molecular orbital method. J. Chem. Eng. Data., 122, 235–246 (1967).
Purushottamachar, P. and Kulkarni, V. M., 3D-QSAR of N-Myristoyl transferase Inhibiting Antifungal Agents by CoMFA and CoMSIA Methods. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 11,3487–3497 (2003).
Raichurkar, A. V. and Kulkarni, V. M., Understanding the antitumor activity of novel hydroxysemicarbazide derivatives as ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors using CoMFA and CoMSIA, J. Med. Chem., 46, 4419–4417 (2003).
Sato, K., Takahashi, H., Iraha, R., and Toriyama, M., Down-regulation of tyrosinase expression by acetylsalicylic acid in murine B16 melanoma. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 33–37 (2008).
Sung, N. D., Jung, H. S., and Kim, S. J., Holographic quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis on the melano-genesis inhibitory activities of alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzene and N-alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzene derivatives. J. Soc. Cosmet. Scientists Korea, 30(4), 491–497 (2004).
Sung, N. D., Jung, H. S., and Kim, S. J., Holographic quantitative structure- activity relationships on the skin sensitization of alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzene and N-alkyl- 3,4- dihydroxybenzene derivatives. J. Soc. Cosmet. Scientists Korea, 31(1), 91–96 (2005).
Tripos Inc., Sybyl Molecular Modeling and QSAR Software on CD-Rom, (Ver. 8.0) Theory and Manual., St. Louis, (2008).
Takara, K., Iwasaki, H., Ujihara, K., and Wada, K., Human tyrosinase inhibitor in Rum distillate wastewater. J. Oleo Sci., 57, 191–196 (2008).
Ullah, F., Hussain, H., Hussain, J., Bukhari, I. A., Khan, B. M. T. H., Choudhary, M. I., Gilani, A. H., and Ahmad, V. U., Tyrosinase inhibitory pentacyclic triterpenes and analgestic and spasmolytic activities of methanol extracts Rhododendron collettianum. Phytother. Res., 21, 1076–1081 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SJ., Myung, PK. & Sung, ND. CoMFA on the melanogenesis inhibitory activity of alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzoate, N-alkyl-3,4-dihydroxybenzamide analogues, and prediction of higher active compounds. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 1540–1546 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-2148-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-2148-4