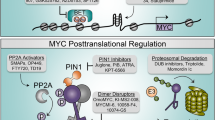
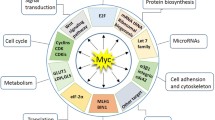
Abstract
The Myc transcription factor family affects the expression of a large group of genes that play an important role during tumourigenesis. Therefore, deregulated expression of the MYC gene family is a hallmark of multiple human tumours. An indirect reduction of Myc-protein levels due to interference with protein-stabilizing mechanisms could be a promising therapeutic approach targeting Myc-dependent tumours.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Sheiness D, Fanshier L, Bishop JM (1978) Identification of nucleotide sequences which may encode the oncogenic capacity of avian retrovirus MC29. J Virol 28:600–610
Dang CV (2012) MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 149:22–35
Soucek L, Whitfield JR, Sodir NM et al. (2013) Inhibition of Myc family proteins eradicates KRas-driven lung cancer in mice. Genes Dev 27:504–513
Popov N, Wanzel M, Madiredjo M et al. (2007) The ubiquitin-specific protease USP28 is required for MYC stability. Nat Cell Biol 9:765–774
Chauhan D, Tian Z, Nicholson B et al. (2012) A small molecule inhibitor of ubiquitin-specific protease-7 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells and overcomes bortezomib resistance. Cancer Cell 22:345–358
Otto T, Horn S, Brockmann M et al. (2009) Stabilization of N-Myc is a critical function of Aurora A in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell 15:67–78
Brockmann M, Poon E, Berry T et al. (2013) Small molecule inhibitors of aurora-a induce proteasomal degradation of N-myc in childhood neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell 24:75–89
Fraile JM, Quesada V, Rodríguez D et al. (2012) Deubiquitinases in cancer: new functions and therapeutic options. Oncogene 31:2373–2378
Kaelin WG Jr. (2005) The concept of synthetic lethality in the context of anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 5:689–698
Mendes-Pereira AM, Martin SA, Brough R et al. (2009) Synthetic lethal targeting of PTEN mutant cells with PARP inhibitors. EMBO Mol Med 1:315–322
Liu L, Ulbrich J, Müller J et al. (2012) Deregulated MYC expression induces dependence upon AMPK-related kinase 5. Nature 483:608–612
Sloane DA, Trikic MZ, Chu ML et al. (2010) Drug-resistant aurora A mutants for cellular target validation of the small molecule kinase inhibitors MLN8054 and MLN8237. ACS Chem Biol 5:563–576
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Anne Carstensen Jahrgang 1986. 2005–2010 Studium der Molekularen Biomedizin an der Universität Bonn. Seit 2010 Promotionsstudentin bei Prof. Dr. M. Eilers, Universität Würzburg.
Markus Brockmann 2001–2007 Biochemiestudium an der Universität Bielefeld und University of Notre Dame, South Bend, IN, USA. 2007–2013 Promotion an den Universitäten Marburg und Würzburg. Seit 2013 Postdoc am Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, Niederlande.
Martin Eilers Jahrgang 1960. 1978–1984 Chemie- und Biochemiestudium an den Universitäten Münster, Tübingen, Edinburgh, UK. 1988 Promotion am Biozentrum der Universität Basel, Schweiz, bei Prof. Dr. G. Schatz. 1988–1990 Postdoc an der University of California, San Francisco, USA bei Dr. M. Bishop. 1991–1996 Forschungsgruppen — leiter am Zentrum für Molekulare Biologie der Universität Heidelberg. 1997–2008 Professor für Molekularbiologie (C4), Universität Marburg. Seit 2008 Professor für Biochemie und Molekularbiologie, Universität Würzburg.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carstensen, A., Brockmann, M. & Eilers, M. Myc — Proteinstabilität als Angriffsziel für zielgerichtete Therapien. Biospektrum 19, 726–729 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-013-0382-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-013-0382-1