Abstract
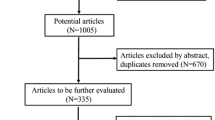
Palmar hyperhidrosis (PH) refers to excessive sweating that affects patients’ quality of life, resulting in social and work impairment and emotional distress. Thoracic sympathectomy (TS) is the best surgery option for palmar hyperhidrosis; however, there was no agreement for the choice of optimal surgery level. The aim of this study was to systematically compare postoperative effect between thoracoscopic T3 and T4 thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis and to help clinical decision. Studies comparing T3 versus T4 thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis were searched overall the database and a meta-analysis was performed. After searching, 12 articles were selected and a total of 1192 patients with palmar hyperhidrosis, of whom 567 patients underwent T3 thoracic sympathectomy and 625 patients underwent T4 thoracic sympathectomy. After analysis, we found that T4 thoracic sympathectomy had fewer side effects than T3 thoracic sympathectomy, so T4 may be the optimal level for thoracic sympathectomy in palmar hyperhidrosis patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
McConaghy JR, Fosselman D (2018) Hyperhidrosis: management options. Am Fam Physician 97(11):729–734
Fujimoto T, Kawahara K, Yokozeki H (2013) Epidemiological study and considerations of primary focal hyperhidrosis in Japan: from questionnaire analysis. J Dermatol 40(11):886–890. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.12258
Lai FC, Tu YR, Li YP, Li X, Lin M, Chen JF, Lin JB (2015) Nation wide epidemiological survey of primary palmar hyperhidrosis in the People’s Republic of China. Clin Auton Res 25(2):105–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-014-0259-5
Ribeiro Santos Morard M, Betanho Martins R, Lopes Ribeiro AC, Guimaraes Rocha Lima P, Dos Santos CB, Junior J (2019) Primary hyperhidrosis prevalence and characteristics among medical students in Rio de Janeiro. PLoS One 14(9):e0220664. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220664
Dogru MV, Sezen CB, Girgin O, Cansever L, Kocaturk CI, Metin M, Dincer SI (2020) Is there any relationship between quality of life and the level of sympathectomy in primary palmar hyperhidrosis? Single-center experience. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 68(3):273–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11748-019-01210-7
Gregoriou S, Sidiropoulou P, Kontochristopoulos G, Rigopoulos D (2019) Management strategies of palmar hyperhidrosis: challenges and solutions. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 12:733–744. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S210973
Bagheri R, Sharifian Attar A, Haghi SZ, Salehi M, Moradpoor R (2016) Thoracoscopic sympathicotomy in the treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 24(7):687–691. https://doi.org/10.1177/0218492316657729
Yazbek G, Wolosker N, Kauffman P, de Campos JRM, Puech-Leao P, Jateneii FB (2009) Twenty months of evolution following sympathectomy on patients with palmar hyperhidrosis: sympathectomy at the T3 level is better than at the T2 level. Clinics 64(8):743–749. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1807-59322009000800006
Moya J, Ramos R, Morera R, Villalonga R, Perna V, Macia I, Ferrer G (2006) Thoracic sympathicolysis for primary hyperhidrosis: a review of 918 procedures. Surg Endosc 20(4):598–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-005-0557-z
Gossot D, Kabiri H, Caliandro R, Debrosse D, Girard P, Grunenwald D (2001) Early complications of thoracic endoscopic sympathectomy: a prospective study of 940 procedures. Ann Thorac Surg 71(4):1116–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-4975(01)02422-5
Walles T, Somuncuoglu G, Steger V, Veit S, Friedel G (2009) Long-term efficiency of endoscopic thoracic sympathicotomy: survey 10 years after surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 8(1):54–57. https://doi.org/10.1510/icvts.2008.185314
Abd Ellatif ME, Hadidi AE, Musa AM, Askar W, Abbas A, Negm A, Moatamed A, Dawoud I (2014) Optimal level of sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis: T3 versus T4 in a retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg 12(8):778–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.05.039
Huang L, Jiang H, Wei D, Xue Q, Ding Q, Hu R (2019) A comparative study of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for the treatment of hand sweating. J Thorac Dis 11(8):3336–3340. https://doi.org/10.21037/jtd.2019.08.18
Lee SS, Lee YU, Lee JH, Lee JC (2017) Comparison of the long-term results of R3 and R4 sympathicotomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 50(3):197–201. https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.3.197
Kavakli K, Caylak H, Isik H, Sapmaz E, Yucel O, Yucel O (2012) Comparative outcomes of T3 and T4 sympathicotomy for patients with palmar hyperhidrosis. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 12:S28–S29
Ishy A, de Campos JR, Wolosker N, Kauffman P, Tedde ML, Chiavoni CR, Jatene FB (2011) Objective evaluation of patients with palmar hyperhidrosis submitted to two levels of sympathectomy: T3 and T4. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 12(4):545–548. https://doi.org/10.1510/icvts.2010.252015
Kim WO, Kil HK, Yoon KB, Yoon DM, Lee JS (2010) Influence of T3 or T4 sympathicotomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Am J Surg 199(2):166–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.12.024
Liu Y, Yang J, Liu J, Yang F, Jiang G, Li J, Huang Y, Wang J (2009) Surgical treatment of primary palmar hyperhidrosis: a prospective randomized study comparing T3 and T4 sympathicotomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 35(3):398–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.10.048
Mahdy T, Youssef T, Elmonem HA, Omar W, Elateef AA (2008) T4 sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: looking for the right operation. Surgery 143(6):784–789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2008.01.007
Noh DS, Park CK, Kum DY, Kim JB (2008) The effect of thoracoscopic sympathicotomy at the 4th rib (R4) for treating palmar hyperhidrosis. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 41:343–346
Wolosker N, Yazbek G, Ishy A, de Campos JR, Kauffman P, Puech-Leao P (2008) Is sympathectomy at T4 level better than at T3 level for treating palmar hyperhidrosis? J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 18(1):102–106. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2007.0030
Yang J, Tan JJ, Ye GL, Gu WQ, Wang J, Liu YG (2007) T3/T4 thoracic sympathictomy and compensatory sweating in treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis. Chin Med J 120(18):1574–1577
Chang YT, Li HP, Lee JY, Lin PJ, Lin CC, Kao EL, Chou SH, Huang MF (2007) Treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis: T(4) level compared with T(3) and T(2). Ann Surg 246(2):330–336. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3180caa466
Goh PMY, Cheah WK, De Costa M, Sim EKW (2000) Needlescopic thoracic sympathectomy: treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 70(1):240–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-4975(00)01489-2
Lee DY, Yoon YH, Shin HK, Kim HK, Hong YJ (2000) Needle thoracic sympathectomy for essential hyperhidrosis: intermediate-term follow-up. Ann Thorac Surg 69(1):251–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-4975(99)01191-1
Turhan K, Cakan A, Cagirici U (2011) Preserving T2 in thoracic sympathicotomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: less tissue trauma, same effectiveness. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 59(6):353–356. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1250646
Cheng A, Johnsen H, Chang MY (2015) Patient satisfaction after thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: do method and level matter? Perm J 19(4):29–31. https://doi.org/10.7812/TPP/15-040
Chang YT, Li HP, Lee JY, Lin PJ, Lin CC, Kao EL, Chou SH, Huang MF (2007) Treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis: T4 level compared with T3 and T2. Ann Surg 246(2):330–336. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e3180caa466
Lin CC, Telaranta T (2001) Lin-Telaranta classification: the importance of different procedures for different indications in sympathetic surgery. Ann Chir Gynaecol 90(3):161–166
Dewey TM, Herbert MA, Hill SL, Prince SL, Mack MJ (2006) One-year follow-up after thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis: outcomes and consequences. Ann Thorac Surg 81(4):1227–1233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.11.006
Wolosker N, Yazbek G, Ishy A, De Campos JRM, Kauffman P, Puech-Leão P (2008) Is sympathectomy at T4 level better than at T3 level for treating palmar hyperhidrosis? J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech 18(1):102–106. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2007.0030
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Xu, Z. & Li, H. The Best Thoracic Sympathectomy Level for Palmar Hyperhidrosis: a Meta-analysis. Indian J Surg 83, 828–834 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-020-02512-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-020-02512-4