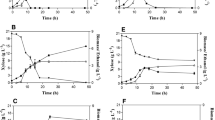
Abstract
Pediococcus acidilactici DQ2, an isolate from corn stover hydrolysate, has been reported to produce more than 100 g/L lactic acid from corn stover hydrolysate. To determine if the outstanding performance is strain-specific or species-specific, three Pediococcus strains, two strains of P. acidilactici (DQ2 and DSM 20284) and one strain of P. pentosaceus (ATCC 25745), were compared for lactic acid production from glucose in the presence of inhibitors often found in lignocellulosic hydrolysates. P. acidilactici DQ2 showed the best results among the three strains tested, suggesting that the excellent performance of DQ2 is a unique feature of this specific strain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dworkin, M. (2006) The Genera Pediococcus and Tetragenococcus. pp. 229–266. In: W. H. Holzapfel, C. M. A. P. Franz, and W. Ludwig (eds.). The Prokaryotes. Springer, US Press, NY, USA.
Pederson, C. S. (1949) The Genus Pediococcus. Bacteriol. Rev. 13: 225–232.
Nampoothiri, K. M., N. R. Nair, and R. P. John (2010) An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 8493–8501.
Ryu, H. W., Y. M. Kim, and Y. J. Wee (2012) Influence of operating parameters on concentration and purification of L-lactic acid using electrodialysis. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 17: 1261–1269.
Hwang, H. J., S. Y. Lee, S. M. Kim, and S. B. Lee (2011) Fermentation of seaweed sugars by Lactobacillus species and the potential of seaweed as a biomass feedstock. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 16: 1231–1239.
Yoon, H. H. (1997) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of cellulose for lactic acid production. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2: 101–104.
Shigenobu, M., A. Tomohiro, I. Noriaki, D. Lies, B. F. Jin, H. B. Cui, and O. Mitsuyasu (2004) Production of L-lactic acid from corncob. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 97: 153–157.
Hassan, K. S., B. M. Ana, G. K. Richard, and J. S. Richard (2001) Lactic acid production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of alfalfa fiber. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 92: 518–523.
Ronald, H. W. M., R. R. Bakker, M. L. A. Jansen, D. Visser, E. Jong, G. Eggink, and R. A. Weusthui (2008) Lactic acid production from lime-treated wheat straw by Bacillus coagulans: Neutralization of acid by fed-batch addition of alkaline substrate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 78: 751–758.
Zhao, K., Q. Qiao, D. Chu, H. Gu, T. H. Dao, J. Zhang, and J. Bao (2012) Simultaneous saccharification and high titer lactic acid fermentation of corn stover using a newly isolated lactic acid bacterium Pediococcus acidilactici DQ2. Bioresour. Technol. 135: 481–489.
Tanasupawat, S., S. Okada, M. Kozaki, and K. Komogata (1993) Characterization of Pediococcus pentosaceus and Pediococcus acidilactici strains and replacement of the type strain of P. acidilactici with the proposed neotype DSM 20284. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43: 860–863.
De Man, J. C., M. Rogosa, and M. E. Sharpe (1960) A medium for the cultivation of Lactobcilli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 23: 130–135.
Raj, S. M., C. Rathnasingh, J. E. Jo, and S. Park (2008) Production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid from glycerol by a novel recombinant Escherichia coli BL21 strain. Proc. Biochem. 43: 1440–1446.
Almeida, J. R. M., T. Modig, A. Petersson, B. Hahn-Hagerdal, G. Liden, and M. F. Gorwa-Grauslund (2007) Increased tolerance and conversion of inhibitors in lignocellulosic hydrolysates by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 82: 340–349.
Zhang, J., Z. N. Zhu, X. F. Wang, N. Wang, W. Wang, and J. Bao (2010) Biodetoxification of toxins generated from lignocellulose pretreatment using a newly isolated fungus Amorphotheca resinae ZN1 and the consequent ethanol fermentation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 3: 26.
Almeida, J. R. M., M. Bertilsson, M. F. Gorwa-Grauslund, S. Gorsich, and G. Lidén (2009) Metabolic effects of furaldehydes and impacts on biotechnological processes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 82: 625–638.
Zaldivar, J. and L. O. Ingram (1999) Effect of organic acids on the growth and fermentation of ethanologenic Escherichia coli LY01. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 66: 203–210.
Klinke, H. B., B. K. Ahring, A. S. Schmidt, and A. B. Thomsen (2002) Characterization of degradation products from alkaline wet oxidation of wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 82: 15–26.
Palmqvist, E. and B. Hahn-Hägerdal (2000) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. II. Inhibitors and mechanisms of inhibition. Bioresour. Technol. 74: 25–33.
Mills, T. Y., N. R. Sandoval, and R. T. Gill (2009) Cellulosic hydrolysate toxicity and tolerance mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2: 26.
Zhang, J., X. Wang, D. Chu, Y. He, and J. Bao (2011) Dry pretreatment of lignocelluloses with extremely low steam and water usage for bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 4480–4488.
Almeida, J. R. M., T. Modig, A. Petersson, B. Hähn-Hägerdal, G. Lidén, and M. F. Gorwa-Grauslund (2007) Increased tolerance and conversion of inhibitors in lignocellulosic hydrolysates by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 82: 340–349.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Ashok, S., Seol, E. et al. Comparison of three Pediococcus strains for lactic acid production from glucose in the presence of inhibitors generated by acid hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol Bioproc E 18, 1192–1200 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0360-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0360-y