Summary
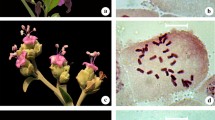
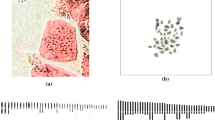
The karyotypes of Crotalaria juncea L., C. sagittalis L. (sect. Calycinae Wight & Arn.), C. mollicula Kunth and C. pumila Ortega (sect. Crotalariae Baker) were obtained by a surface-spreading and air-drying method (splash). All species have chromosome numbers based on x = 8 (2n = 16, 32). Chromosomes are metacentric (m) or submetacentric (sm), with one pair of satellite-chromosomes per complement. Although similar, the karyotypes are not particularly uniform, supporting the view that inter-specific differences of karyotypes can be used in species characterisation. There is sufficient evidence to show that large structural chromosome changes and hybridisation are significant in the diversification of this genus, particularly in the New World.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almada, R. D., Daviña, J. R. & Seijo J. G. (2006). Karyotype analysis and chromosome evolution in southernmost South American species of Crotalaria (Leguminosae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 150: 329 – 341.
Arellano, J. (1986). Etnobotánica de leguminosas: notas sobre algunas de las especies utilizadas en la alimentación en México. Anales Inst. Biol. Univ. Nac. Autón. Mexico, Bot. 57: 123 – 142
Atchison, E. (1950). Studies in the Leguminosae. V. Cytological observations on Crotalaria. J. Elisha Mitchell Sci. Soc. 66: 70 – 75.
Boulter, D., Derbyshire, E., Frahm-Leliveld, J. A. & Polhill, R. M. (1970). Observations on the cytology and seed proteins of various African species of Crotalaria L. (Leguminosae). New Phytol. 69: 117 – 131.
Chennaveeraiah, M. S. & Patil, B. C. (1973). Chromosome number and karyotype study in eight species of Crotalaria. Cytologia 38: 73 – 79.
Cotias de Oliveira, A. L. P. & Aguiar-Perecin, M. L. R. (1999). Karyotype evolution in the genus Crotalaria (Leguminosae). Cytologia 64: 165 – 174.
D’Ovidio, R. & Marchi, P. (1990). DNA content, karyotype structure analysis and karyotype symmetry in Ranunculus L. (Ranunculaceae). Italian species belonging to sections Flammula (Webb) Benson and Micranthus (Ovcz) Nyarady. Caryologia 43: 99 – 115.
Datta, R. M. & Choudhury, P. C. (1966). Karyotype in Crotalaria. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 93: 241 – 243.
Fernández, A. (1977). Números cromosómicos en Angiospermas. Hickenia 15: 83 – 86.
Flores, A. S., Corrêa, A. M., Forni-Martins, E. R. & Tozzi, A. M. G. A. (2006). Chromosome numbers in Brazilian species of Crotalaria (Leguminosae, Papilionoideae) and their taxonomic significance. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 151: 271 – 277.
Gómez-Sosa, E. (2000). Las especies argentinas de Crotalaria (Leguminosae-Crotalarieae): novedades, descripciones y claves. Gayana Botánica 57: 67 – 87.
Gupta, R. & Gupta, P. K. (1978). Karyotypic studies in the genus Crotalaria Linn. Cytologia 43: 357 – 369.
Kundu, A. K. & Sharma, A. K. (1985). Chromosome characteristics and DNA content in Mentha Linn. The Nucleus 28: 89 – 96.
Le Roux, M. M., Van Wick, B-E., Boatwright, J. S. & Tilney, P. M. (2011). The systematic significance of morphological and anatomical variation in fruits of Crotalaria and related genera of tribe Crotalarieae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 165: 84 – 106.
Levan, A., Fredga, K. & Sandberg, A. A. (1964). Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosome. Hereditas 52: 201 – 219.
Magoon, M. L., Koppar, M. N., Ramanna, M. S. & Shina, A. K. (1963). Cytomorphological studies in genus Crotalaria. La Cellule 63: 375 – 396.
Mangotra, R. & Koul, A. K. (1991). Polyploidy in genus Crotalaria. Cytologia 56: 293 – 296.
Navashin, M. S. (1928). Amphiplastie – eine neue karyologische Erscheinung. Proc. Int. Conf. Genet. 5: 1148 – 1152.
Palomino, G. & Vázquez, R. (1991). Cytogenetic studies in Mexican populations of species of Crotalaria L. (Leguminosae-Papilionoideae). Cytologia 56: 343 – 351.
Polhill, R. M. (1968). Miscellaneous notes on African species of Crotalaria L. II. Kew Bull. 22: 169 – 337.
____ (1981). Crotalarieae. pp. 399 – 401. In: R. M. Polhill & P. H. Raven (eds.) Advances in Legume Systematics I. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
Preuss, S. & Pikaard, C. S. (2007). rRNA gene silencing and nucleolar dominance: Insights into a chromosme-scale epigenetic on/off switch. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1769: 383 – 392.
Raina, S. N. & Verma, R. C. (1979). Cytogenetics of Crotalaria I. Mitotic complements in twenty species of Crotalaria L. Cytologia 44: 365 – 375.
Samuel, R., Smith, J. B. & Bennett, M. D. (1986). Nuclear DNA variation in Piper (Piperaceae). Canad. J. Genet. Cytol. 28: 1041 – 1043.
Sharma, A. K. (1970). Polyploidy and chromosome size. Chromosomes Today 3: 248 – 252.
Sharma, A. & Sen, S. (2002). Chromosome Botany, pp. 92 – 99. Science Publishers, Inc. Enfield, NH.
____ & Sharma, A. (1984). Trends in chromosome evolution in the plant kingdom. In: A. K. Sharma (ed.), Chromosomes in evolution of eukaryotic groups 2, pp. 227 – 239. CRC Press, New Delhi.
Sousa, S. M. & Delgado, A. (1998). Leguminosas mexicanas: fitogeografía, endemismo y orígenes. In: T. P. Ramamoorthy, R. Bye, A. Lot & J. Fa (eds), Diversidad biológica de México: orígenes y distribución, pp. 449 – 500. Instituto de Biología, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.
Tapia-Pastrana, F. & Mercado-Ruaro, P. (2001). A combination of the ‘squash’ and ‘splash’ techniques to obtain the karyotype and assess meiotic behavior in Prosopis laevigata L. (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae). Cytologia 66: 11 – 17.
____, Gallegos-Pacheco, E., de Teodoro-Pardo, C. & Mercado-Ruaro, P. (2005). New cytogenetic information of two Mexican populations of Crotalaria incana L. (Leguminosae-Papilionoideae). Cytologia 70: 207 – 212.
Turner, B. & Fearing, O. (1960). Chromosome numbers in the Leguminosae III. Species of the southwestern United States and Mexico. Amer. J. Bot. 47: 603 – 608.
Verma, R. C. & Raina, S. N. (1983). Cytogenetics of Crotalaria VIII. Male meiosis in 26 species. Cytologia 48: 719 – 733.
____, Kesavacharyulu K. & Raina, S. N. (1984). Cytogenetics of Crotalaria IX. Mitotic complements in nineteen species. Cytologia 49: 157 – 169.
Ward, D. E. (1983). Chromosome counts from New Mexico and southern Colorado. Phytologia 54: 302 – 309.
Windler, D. R. (1974). Chromosome numbers for native North American unifoliolate species of Crotalaria (Leguminosae). Brittonia 26: 172 – 176.
Acknowledgements
The author thanks Alfonso Delgado-Salinas, Instituto de Biología UNAM, for critical revision and valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Details of material examined:
Crotalaria juncea. México, Cuixmala, Jalisco 19°28'N, 104°58'W; 110 m alt.. Gómez & Trejo 71 (MEXU).
Crotalaria mollicula. El Salvador, Mpio. Texistepeque. Santa Ana. 14°11'06"N. 89°28'02"W; 450 m alt. Linares & Martínez s.n (MEXU).
Crotalaria sagittalis. México, Morelos 18°56'N, 99°13'W; 1680 m. Tapia & Gómez 58 (MEXU).
Crotalaria pumila. México, D.F., Reserva Ecológica del Pedregal de San Ángel, 19°16'N; 99°10'W; 2263 m alt. Tapia & Gómez 59 (MEXU).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tapia-Pastrana, F. Karyological characterisation of four American species of Crotalaria (Leguminosae: Papilionoideae) by the splash method. Kew Bull 67, 427–433 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12225-012-9385-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12225-012-9385-1