Abstract
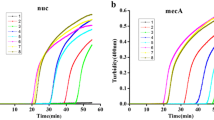
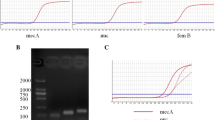
A rapid method that included simple boiling DNA extraction followed by a fast polymerase chain reaction (PCR) cycling protocol designed to detect mecA, which characterizes methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), was performed. Briefly, the PCR cycling protocol consisted of pre-denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, 30 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 2 s, annealing at 52 °C for 5 s, extension for 10 s, and final extension at 72 °C for 1 min. A good level of reliability of the method was verified. The study has shown that the method described here represents a rapid and accurate DNA extraction and PCR-based identification system of MRSA, thus allowing clinicians to make early identification and early implementation of control measures.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- mecA :
-
Methicillin-resistant gene
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
References
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2008) Performance standards for antimicrobial testing. 18th informational supplement M100-S18. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Ida T, Okamoto R, Shimauchi C, Okubo T, Kuga A, Inoue M (2001) Identification of aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes by susceptibility testing: epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Japan. J Clin Microbiol 39:3115–3121
Khatib R, Jose J, Musta A, Sharma M, Fakih MG, Johnson LB, Riederer K, Shemes S (2011) Relevance of vancomycin-intermediate susceptibility and heteroresistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. J Antimicrob Chemother 66:1594–1599
Shittu AO, Okon K, Adesida S, Oyedara O, Witte W, Strommenger B, Layer F, Nubel U (2011) Antibiotic resistance and molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in Nigeria. BMC Microbiol 11:92–100
Smith S, Morin PA (2005) Optimal storage conditions for highly dilute DNA samples: a role for trehalose as a preserving agent. J Forensic Sci 50:1–8
Van Belkum A, Bax R, Beerbooms P, Goessens WHF, Van Leeuwen N, Quint WG (1993) Comparison of phage typing and DNA finger printing by polymerase chain reaction for discrimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Clin Microbiol 31:798–803
Vannuffel P, Gigi J, Ezzedine H, Vandercam B, Delmee M, Wauters G, Gala JL (1995) Specific detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus species by multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol 33:2864–2867
Wang D, Lin B, Zhu H, Hae H, Wu C, By W, Zhao X (2011) Study of the amplification capacity of a two-temperature PCR and its application in bovine sex identification. J Anim Vet Adv 10:715–722
Yamamoto T, Nishiyama A, Takano T, Yabe S, Higuchi W, Razvina O, Shi D (2010) Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: community transmission, pathogenesis, and drug resistance. J Infect Chemother 16:225–524
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adwan, K. Fast DNA isolation and PCR protocols for detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Folia Microbiol 59, 5–8 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0259-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0259-1