Abstract
The purpose of this paper was to construct a porous micro-surface with a rough tertiary structure and to prepare a long-term sustained-release of antibacterial hydrophobic membrane in moist, multi-extreme environments. The hydrophobic groups were cross-linked by mixing, electrostatic spraying and impregnation at the hydroxide end of the PVA. When the contact angle of the membrane surface was increased from 30.8° to 140.3° and up to 156° in aqueous solution at pH 11, the membrane showed super-hydrophobicity. Adding nanoparticles to the spray layer to construct porous microspheres could increase the surface of the membrane and improve the slow-release effect of PVA-coated silver nanoparticles. Silver nanoparticles had been added to various locations of the hydrophobic composite membrane layer, and their antibacterial properties had been investigated in wet and dry environments. The results showed that the antibacterial effect of embedding in the PVA fiber layer on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus was optimum, and when the antibacterial circle was up to 3.1 cm, the sustained-release durability was the optimum. It was found that the composite PDMS/\({\mathrm{TiO}}_{2}\) antibacterial hydrophobic membranes on the surface could be recycled and reused.
Highlights
A tertiary rough porous structured membrane was prepared by electrostatic spinning and spray lamination.
The tertiary roughness structure improved the contact angle and antibacterial properties of the composite film.
Nano-silver loaded in PVA can be effectively sustained-released by surface composite porous microspheres.
The hydrophilic material PVA reached super-hydrophobicity under alkaline solutions.
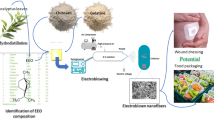
Graphical Abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
J. Lin, B. Ding, J. Yu, Direct fabrication of highly nanoporous polystyrene fibers via electrospinning[J]. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2, 521–528 (2010)
Y. Wan, Z. Lin, D. Gan, T. Cui, M. Wan, F. Yao, Q. Zhang, H. Luo, Effect of graphene oxide incorporation into electrospun cellulose acetate scaffolds on breast cancer cell culture[J]. Fibers Polym. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-019-9133-3
B.C. Shiu, Y. Zhang, T.T. Li, Y. Ye, C.W. Lou, J.H. Lin, Electrospinning PVP/Urushiol/Ag nanofilms: use as wrapper of stainless steel yarns[J]. Prog. Org. Coat. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2022.106797
J. Zuo, Z. Liu, C. Zhou, Y. Zhou, X. Wen, S. Xu, J. Cheng, P. Pi, A durable superwetting clusters-inlayed mesh with high efficiency and flux for emulsion separation[J]. J. Hazard Mater. 403, 123620 (2021)
T. Jarusuwannapoom, W. Hongrojjanawiwat, S. Jitjaicham, L. Wannatong, M. Nithitanakul, C. Pattamaprom, P. Koombhongse, R. Rangkupan, P. Supaphol, Effect of solvents on electro-spinnability of polystyrene solutions and morphological appearance of resulting electrospun polystyrene fibers[J]. Eur. Polym. J. 41, 409–421 (2005)
G.H. Zhang, P.P. Wang, X.X. Zhang, C.H. Xiang, L.L. Li, The preparation of PCL/ MSO/SiO2 hierarchical superhydrophobic mats for oil-water separation by one-step method[J]. Eur. Polym. J. 116, 386–393 (2019)
M. Wang, X. Cheng, G. Jiang, J. Xie, W. Cai, J. Li, Y. Wang, Preparation and pervaporation performance of PVA membrane with biomimetic modified silica nanoparticles as coating[J]. J. Membr. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2022.120535
Z. Wang, H. Ma, B. Chu, B.S. Hsiao, Super-hydrophobic modification of porous natural polymer “luffa sponge” for oil absorption[J]. Polymer 126, 470–476 (2017)
L. Zhou, C.Z. Su, B.Y. Chen, Q. Zhao, X.Y. Wang, X.Y. Zhao, G.N. Ju, Durable ER@ SiO2@ PDMS superhydrophobic composite designed by double crosslinking strategy for efficient oil-water separation[J]. Polymer 245, 124722 (2022)
Q. Chen, Z. Wang, A copper organic phosphonate functionalizing boron nitride nanosheet for PVA film with excellent flame retardancy and improved thermal conductive property[J]. Compos. Part A (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-3037-2
L. Xing, C. Hu, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, L. Shi, R. Ran, A mechanically robust double-network hydrogel with high thermal responses via doping hydroxylated boron nitride nanosheets[J]. J. Mater. Sci. 54(4), 3368–3382 (2019)
Z. Yulin, S. Mingwei, D. Yongfu, Li. Binwei, S. Linying, R. Rong, Preparation and properties of polyacrylamide/ polyvinyl alcohol physical double network hydrogel[J]. RSC Adv. 6(113), 112468–112476 (2016)
Y. Wang, J. Yan, Z. Wang, Wu. Jianning, G. Meng, Z. Liu, X. Guo, One-pot fabrication of triple-network structure hydrogels with high-strength and self-healing properties[J]. Mater. Lett. 207, 53–56 (2017)
J. Wang, J. Qu, Y. Liu, S. Wang, X. Liu, Y. Chen, Q. Peiyao, M. Guohao, X. Liu, “Crocodile skin” ultra-tough, rapidly self-recoverable, anti-dry, anti-freezing, MoS2-based ionic organohydrogel as pressure sensors[J]. Colloids Surf. A (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126458
K. Neibert, V. Gopishetty, A. Grigoryev, I. Tokarev, N. Al-Hajaj, J. Vorstenbosch, A. Philip, S. Minko, D. Maysinger, Wound-healing with mechanically robust and biodegradable hydrogel fibers loaded with silver nanoparticles[J]. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 1(5), 621–630 (2012)
G. Cheng, C. Yin, H. Tu, S. Jiang, Q. Wang, X. Zhou, X. Xing, C. Xie, X. Shi, Y. Du, Controlled co-delivery of growth factors through layer-by-layer assembly of core–shell nanofibers for improving bone regeneratio[J]. ACS Nano 13(6), 6372–6382 (2019)
N. Mishra, A. Dhwaj, D. Verma, A. Prabhakar, Cost-effective microabsorbance detection based nanoparticle immobilized microfluidic system for potential investigation of diverse chemical contaminants present in drinking water[J]. Anal. Chim. Acta (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339734
H. Xu, X. Wang, J. Niu, Y. Nan, J. Pu, H. Zhou, D. Jizhou, B. Hou, Construction of MXene/PDMS-based triboelectric nanogenerators for high-performance cathodic protection[J]. Adv. Mater. Interfaces (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202102085
D.L. Puhl, D. Mohanraj, D.W. Nelson, R.J. Gilbert, Designing electrospun fiber platforms for efficient delivery of genetic material and genome editing tools[J]. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 183, 114161 (2022)
X. Gu, Y. Matsumura, Y. Tang, S. Roy, R. Hoff, B. Wang, W.R. Wagner, Sustained viral gene delivery from a micro-fibrous, elastomeric cardiac patch to the ischemic rat heart[J]. Biomaterials 133, 132–143 (2017)
A. Rosales, V. Gutiérrez, J. Ocampo-Hernández, M.L. Jiménez-González, I.E. Medina-Ramírez, L. Ortiz-Frade, K. Esquivel, Hydrophobic agents and pH modification as comparative chemical effect on the hydrophobic and photocatalytic properties in SiO2- coating[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.153375
C.J. Chu, M.H. Cheng, P.Y. Chung, M.H. Chi, K.S. Jeng, J.T. Chen, Reversible morphology control of three-dimensional block copolymer nanostructures by the solvent annealing-induced wetting in anodic aluminum oxide templates[J]. Int. J. Polym Mater. Polym. Biomater. 65, 695–701 (2016)
Z. Zhang, D.U. Ahn, Y. Ding, Instabilities of PS/PMMA bilayer patterns with a corrugated surface and interface[J]. Macromolecules 45, 1972–1981 (2012)
P.-W. Fan, W.-L. Chen, T.-H. Lee, J.-T. Chen, Annealing effect on electrospun polymer fibers and their transformation into polymer microspheres [J]. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 33, 343–349 (2012)
H.-F. Tseng, M.-H. Cheng, K.-S. Jeng, J.-W. Li, J.-T. Chen, Asymmetric polymer particles with anisotropic curvatures by annealing polystyrene microspheres on poly(vinyl alcohol) films [J]. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 37, 1825–1831 (2016)
R. Mead-Hunter, A.J. King, B.J. Mullins, Plateau Rayleigh instability simulation [J]. Langmuir 28, 6731–6735 (2012)
P.-W. Fan, W.-L. Chen, T.-H. Lee, Y.-J. Chiu, J.-T. Chen, Rayleigh-instability-driven morphology transformation by thermally annealing electrospun polymer fibers on substrates[J]. Macromolecules 45, 5816–5822 (2012)
H. Wang, T. Chang, X. Li, W. Zhang, Z. Hu, A.M. Jonas, Scaled down glass transition temperature in confined polymer nanofibers [J]. Nanoscale 8, 14950–14955 (2016)
A.W. Tan, J.M. Torkelson, Poly(methyl methacrylate) nanotubes in AAO templates: designing nanotube thickness and characterizing the T g -confinement effect by DSC[J]. Polymer 82, 327–336 (2016)
R.K. Das, M. Das, Study of silver nanoparticle/polyvinyl alcohol nanocomposite[J]. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 23(1), 101–109 (2019)
K. Swaroop, S. Francis, H.M. Somashekarappa, Gamma irradiation synthesis of Ag/PVA hydrogels and its antibacterial activity[J]. Mater. Today Proc. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2016.04.076
Yu. Huang Lei, Y.X. Lei, Yu. Lin, Xu. Yuanhong, N. Yusheng, Silver nanoparticles with vanadium oxide nanowires loaded into electrospun dressings for efficient healing of bacterium-infected wounds[J]. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 622, 117–125 (2022)
L. Li, D. Zhou, D. Huang, Gi. Xue, Double glass transition temperatures of poly(methyl methacrylate) confined in alumina nanotube templates[J]. Macromolecules 47, 297–303 (2014)
H. Peng, H. Yang, X. Ma, T. Shi, Z. Li, S. Xue, Q. Wang, In situ fabrication of flower-like ZnO on aluminum alloy surface with superhydrophobicity[J]. Colloids Surf. A (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128800
M. Lim, H. Kwon, D. Kim, J. Seo, H. Han, S.B. Khan, Highly-enhanced water resistant and oxygen barrier properties of cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) hybrid films for packaging applications[J]. Prog. Org. Coat. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2015.03.005
F. Xue, X. Shi, W. Bai, Y. Li, S. Zhu, Y. Liu, L. Feng, Enhanced durability and versatile superhydrophobic coatings via facile one-step spraying technique[J]. Colloids Surf. A (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128411
Acknowledgements
I sincerely thank Prof. Xinmei Li and the National Natural Science Foundation (52161017, 51865055) of China for their help and support, as well as the regional research and innovation project (XJ2022G048), which I chaired and the Xinjiang Institute of Physics and Chemistry and its testing staff for their help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RY: investigations, experimental analysis, processing data and writing papers. XL: funding acquisition, administration, resources, writing review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
I declare that we have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, R., Li, X. Functionalized PVA/PDMS-Modified Nanocomposite Electrospun Film with Tertiary Roughness for Humid and Bacterial Applications. Fibers Polym 24, 1237–1251 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-023-00099-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-023-00099-7