Abstract
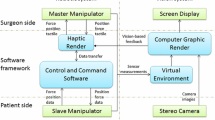
In this paper, a vision-based haptic feedback system has been proposed with the aim to assist the movement of an endoscopic device during capsule endoscopy (CE) procedures. We present a general system architecture consisting of three modules responsible for vision, haptic guidance and control of movements. The vision module generates 3D local maps as well as local navigation trajectory for endoluminal navigation. The haptic guidance module consists of a haptic device that allows the user to control the movement of the capsule along the generated path. The haptics module also helps the operator by transforming the 3D maps and the relative paths into a guiding virtual force. Measuring the current relative distance between the user input and the maps boundaries, the haptic guidance module will check if the user is moving away or toward the colonic walls and will generate a feedback force with the aim to assist the operator during the navigation procedure. The user will also sense an attractive virtual feedback force toward the generated path that will help the user in the navigation. Finally, the movement control module is the interface between the haptics module and the chosen manipulator. The final goal is to develop a complete active CE robotic platform with haptic feedback in order to enhance safety, to reduce cost (using the same system as a training simulator as well as real endoscopic platform) and to help the operator during the navigation by combining all 3D local maps into a full 3D reconstructed colon.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
World health organization. [Online]. Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/, [May 20, 2016]
International agency for research on cancer - estimated incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. [Online]. Available: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Pages/fact-sheets-cancer.aspx/, [May 20, 2016]
Cancer research uk. [Online]. Available: http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/cancer-info/cancerstats/types/bowel/survival/stage/, [May 20, 2016]
Sliker LJ, Ciuti G (2014) “Flexible and capsule endoscopy for screening, diagnosis and treatment,”. Expert Rev Med Dev 11(6):649–666
Fan Y, Meng M-H, Li B (2010) 3D reconstruction of wireless capsule endoscopy images. In: Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC), pp 5149–5152
Sliker L, Ciuti G, Rentschler M, Menciassi A (2015) Magnetically driven medical devices: a review. Expert Rev Med Dev 12(6):737–752
Sliker LJ, Kern MD, Schoen JA, Rentschler ME (2012) Surgical evaluation of a novel tethered robotic capsule endoscope using micro-patterned treads. Surg Endos 26(10):2862–2869
Valdastri P, Webster RJ III, Quaglia C, Quirini M, Menciassi A, Dario P (2009) A new mechanism for mesoscale legged locomotion in compliant tubular environments. IEEE Trans Robot 25(5):1047–1057
Carpi F, Pappone C (2009) Magnetic maneuvering of endoscopic capsules by means of a robotic navigation system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 56(5):1482–1490
Ciuti G, Valdastri P, Menciassi A, Dario P (2010) Robotic magnetic steering and locomotion of capsule endoscope for diagnostic and surgical endoluminal procedures. Robotica 28(02):199– 207
Lucarini G, Mura M, Ciuti G, Rizzo R, Menciassi A (2015) Electromagnetic control system for capsule navigation: Novel concept for magnetic capsule maneuvering and preliminary study. J Med Biol Eng 35(4):428–436
Lucarini G, Ciuti G, Mura M, Rizzo R, Menciassi A (2015) A new concept for magnetic capsule colonoscopy based on an electromagnetic system. Int J Adv Robot Syst 12:25
Ciuti G, Donlin R, Valdastri P, Arezzo A, Menciassi A, Morino M, Dario P et al (2010) Robotic versus manual control in magnetic steering of an endoscopic capsule. Endoscopy 42(2):148
Okamura AM (2004) Methods for haptic feedback in teleoperated robot-assisted surgery. Ind Robot Int J 31 (6):499–508
Reilink R, Stramigioli S, Kappers AM, Misra S (2011) Evaluation of flexible endoscope steering using haptic guidance. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 7(2):178–186
Ghanbari A, Horan B, Nahavandi S, Chen X, Wang W (2014) Haptic microrobotic cell injection system. IEEE Syst J 8(2):371–383
Pacchierotti C, Magdanz V, Medina-Sánchez M, Schmidt O G, Prattichizzo D, Misra S (2015) Intuitive control of self-propelled microjets with haptic feedback. J Micro-Bio Robot 10(1–4):37–53
Mehrtash M, Khamesee MB, Tarao S, Tsuda N, Chang J-Y (2012) Human-assisted virtual reality for a magnetic-haptic micromanipulation platform. Microsyst Technol 18(9–10):1407–1415
Maier-Hein L, Groch A, Bartoli A, Bodenstedt S, Boissonnat G, Chang P-L, Clancy N, Elson DS, Haase S, Heim E et al (2014) Comparative validation of single-shot optical techniques for laparoscopic 3-d surface reconstruction. IEEE Trans Med Imag 33(10):1913–1930
Maier-Hein L, Mountney P, Bartoli A, Elhawary H, Elson D, Groch A, Kolb A, Rodrigues M, Sorger J, Speidel S et al (2013) Optical techniques for 3d surface reconstruction in computer-assisted laparoscopic surgery. Med Image Anal 17(8):974–996
Ciuti G, Visentini-Scarzanella M, Dore A, Menciassi A, Dario P, Yang G-Z (2012) Intra-operative monocular 3D reconstruction for image-guided navigation in active locomotion capsule endoscopy. In: 4th IEEE RAS & EMBS international conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics (BioRob), pp 768–774
Siciliano B, Khatib O (2008) Springer handbook of robotics. Springer, Berlin
Linner T, Shrikathiresan A, Vetrenko M, Ellmann B Modeling and operating robotic environent using gazebo/ros. In: Proceedings of the 28th international symposium on automation and robotics in construction (ISARC2011), pp 957–962
Bouguet JY (2004) Camera calibration toolbox for matlab
Engel J, Stückler J, Cremers D (2015) Large-scale direct slam with stereo cameras. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS)
Mur-Artal R, Montiel J, Tardos J (2015) Orb-slam: a versatile and accurate monocular slam system. IEEE Trans Robot 31(5):1147–1163
Visentini-Scarzanella M, Stoyanov D, Yang G-Z (2012) Metric depth recovery from monocular images using shape-from-shading and specularities. In: 2012 19th IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP). IEEE, pp 25–28
Hast A, Nysjö J, Marchetti A (2013) Optimal ransac-towards a repeatable algorithm for finding the optimal set
Quigley M, Conley K, Gerkey B, Faust J, Foote T, Leibs J, Wheeler R, Ng AY (2009) Ros: an open-source robot operating system. ICRA Workshop Open Source Softw 3(3.2):5
Chitta S, Sucan I, Cousins S (2012) Moveit![ros topics]. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 1(19):18–19
Abu-Kheil Y, Ciuti G, Mura M, Dias J, Dario P, Seneviratne L (2015) Vision and inertial-based image mapping for capsule endoscopy. In: 2015 International conference on information and communication technology research (ICTRC). IEEE, pp 84–87
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Reem Ashour (Khalifa University Robotic Institute, Abu Dhabi, UAE) for her suggestions and support in the development of the Gazebo environment and in the development of the haptic force field generation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mura, M., Abu-Kheil, Y., Ciuti, G. et al. Vision-based haptic feedback for capsule endoscopy navigation: a proof of concept. J Micro-Bio Robot 11, 35–45 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12213-016-0090-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12213-016-0090-2