Abstract
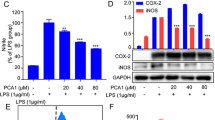
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an important enzyme, plays a pathological role in diseases, which can be inhibited by proanthocyanidins (PCs) effectively. In this paper, we investigated the inhibitive mechanism of COX-2 performed by PCs. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed to identify the mRNA expression level of COX-2 in A549 cell, which was induced by interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). The pGL3 luciferase reporter vector containing the COX-2 gene promoter fragment (pGL3/COX-2p) was transfected into A549 cell induced by IL-1β, the interference on the COX-2 promoter activity from PCs was analyzed using a dualluciferase reporter assay, and the expressions of the nuclear factor κB composed of subunit p65 (NF-κB/p65) and the inhibitor-κB (I-κB) were measured by the Western blotting and immunocytochemistry. The results exhibited that PCs not only inhibited the transcript of COX-2 mRNA and the COX-2 promoter activity, but also suppressed the nuclear translocation of NF-κB/p65 protein and the degradation of I-κB protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pelletier J P, Martel-Pelletier J, Abramson S B. Osteorthritis, an inflammatory disease: Potential implication for the selection of new therapeutic targets [J]. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 2001, 44(6): 1237–1247.
Hida T, Yatabe Y, Achiwa H, et al. Increased expression of cyclooxygenase 2 occurs frequently in human lung cancers, specifically in adenocarcinomas [J]. Cancer Research, 1998, 58(17): 3761–3764.
Spielman L, Winger D, Ho L, et al. Induction of the complement component C1qB in brain of transgenic mice with neuronal overexpression of human cyclooxygenase-2 [J]. Acta Neuropathol, 2002, 103(2): 157–162.
Lu Y, Zhao W Z, Chang Z, et al. Procyanidins from grape seeds protect against phorbol ester-induced oxidative cellular and genotoxic damage [J]. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 2004, 25(8): 1083–1089.
Sharma S D, Meeran S M, Katiyar S K. Proanthocyanidins inhibit in vitro and in vivo growth of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting the prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin E2 receptors [J]. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, 2010, 9(3): 569–580.
Yang F, Bleich D. Transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 gene in pancreatic β-cells [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2004, 279(34): 403–411.
Saunders M A, Sansores-Garcia L, Gilroy D W, et al. Selective suppression of CCAAT/enhancerbinding protein β binding and cyclooxygenase-2 promoter activity by sodium salicylate in quiescent human fibroblasts [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(22): 897–904.
Shaik M S, Chatterjee A, Singh M. Effect of a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, nimesulide, on the growth of lung tumors and their expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptor-γ [J]. Clinical Cancer Research, 2004, 10(4): 1521–1529.
Mestre J R, Rivadeneira D E, Mackrell P J, et al. Overlapping CRE and E-box promoer elements can independently regulate COX-2 gene transcription in macrophages [J]. FEBS Letters, 2001, 496(2–3): 147–151.
Thomas B, Berenbaum F, Humbert L, et al. Critical role of C/EBPδ and C/EBPβ factors in the stimulation of the cyclooxygenas-2 gene transcription by interleukin-1β in articular chondrocytes [J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 2000, 267: 6798–6808.
Baeuerle P A. IκB-NF-κB structure: At the interface of inflammation control [J]. Cell, 1998, 95: 729–731.
Jacobs M D, Harrison S C. Structure of an IκBα/NF-κB complex [J]. Cell, 1998, 95: 749–758.
Benitah S A, Valerón P F, Lacal J C. ROCK and nuclear factor-κB-dependent activation of cyclooxygenase-2 by rho GTPases: Effects on tumor growth and therapeutic consequences [J]. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 2003, 14(7): 3041–3054.
Wen D, Nong Y, Morgan J G, et al. A selective small molecule IκB kinase β inhibitor blocks nuclear factor κB-mediated inflammatory responses in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes, chdrocytes, and mast cells [J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 2006, 317(3): 989–1001.
Heiss E, Herhaus C, Klimo K, et al. Nuclear factor κB is a molecular target for sulforaphane-mediated anti-inflammatory mechanisms [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2001, 276(34): 8–15.
Kaltschmidt B, Linker R A, Deng J, et al. Cyclooxygenae-2 is a neuronal target gene of NF-κB [J]. BMC Molecular Biology, 2002, 3: 16–27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: the Special Supported by Guangdong Key Program (No. GX0307) and the Guangdong Science and Technology Planning Project in the Field of Social Development (No. 35025)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Tt., Liang, T., Zhao, Yc. et al. Inhibitive effect of proanthocyanidins on cyclooxygenase-2 expression in A549 cells induced by cytokine interleukin-1 beta. J. Shanghai Jiaotong Univ. (Sci.) 17, 500–504 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-012-1312-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12204-012-1312-y