Abstract
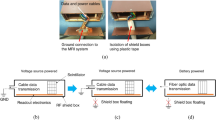
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the RF field responses of partial-ring RF-shielded oval-shaped positron emission tomography (PET) inserts that are used in combination with an MRI body RF coil. Partial-ring PET insert is particularly suitable for interventional investigation (e.g., trimodal PET/MRI/ultrasound imaging) and intraoperative (e.g., robotic surgery) PET/MRI studies. In this study, we used electrically floating Faraday RF shield cages to construct different partial-ring configurations of oval and cylindrical PET inserts and performed experiments on the RF field, spin echo and gradient echo images for a homogeneous phantom in a 3 T clinical MRI system. For each geometry, partial-ring configurations were studied by removing an opposing pair or a single shield cage from different positions of the PET ring. Compared to the MRI-only case, reduction in mean RF homogeneity, flip angle, and SNR for the detector opening in the first and third quadrants was approximately 13%, 15%, and 43%, respectively, whereas the values were 8%, 23%, and 48%, respectively, for the detector openings in the second and fourth quadrants. The RF field distribution also varied for different partial-ring configurations. It can be concluded that the field penetration was high for the detector openings in the first and third quadrants of both the inserts.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ishi S, et al. Optimized workflow and imaging protocols for whole-body oncologic PET/MRI. Jpn J Radiol. 2016;34(11):754–62.
Catana C, et al. PET/MRI for neurologic applications. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:1916–25.
Werner P, et al. Current status and future role of brain PET/MRI in clinical and research settings. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;42:512–26.
Bashir U, et al. PET/MRI in oncological imaging: state of the art. Diagnostics (Basel). 2015;5:333–57.
Fraum TJ, Fowler KJ, McConathy J. PET/MRI: emerging clinical applications in oncology. Academic Radiol. 2015;23:220–36.
Jadvar H, Colletti PM. Competitive advantages of PET/MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2014;83:84–94.
Nensa F, et al. Clinical applications of PET/MRI: current status and future perspectives. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2014;20:438–47.
Iagaru A, et al. Simultaneous whole-body time-of-flight 18F-FDG PET/MRI: a pilot study comparing SUVmax with PET/CT and assessment of MR image quality. Clin Nucl Med. 2015;40:1–8.
Shen G, et al. Diagnostic performance of whole-body PET/MRI for detecting malignancies in cancer patients: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0154497.
Schmand M, et al. BrainPET: First human tomograph for simultaneous (functional) PET and MR imaging. J Nucl Med. 2007;48(Suppl. 2):45P.
Kolb A, et al. Technical performance evaluation of a human brain PET/MRI system. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:1776–88.
Kang J, et al. A feasibility study of photosensor charge signal transmission to preamplifier using long cable for development of hybrid PET-MRI. Med Phys. 2010;42:5655–64.
González AJ, et al. The MINDView brain PET detector, feasibility study based on SiPM arrays. Nucl Instr Meth Phys Res A. 2016;818:82–90.
Akram MSH, et al. MRI compatibility study of an integrated PET/RF-coil prototype system at 3 T. J Mag Reson. 2017;283:62–70.
Lee BJ, et al. MR performance in the presence of a radio frequency-penetrable positron emission tomography (PET) insert for simultaneous PET/MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 2018;37:2060–9.
Olcott P, et al. Prototype positron emission tomography insert with electro-optical signal transmission for simultaneous operation with MRI. Phys Med Biol. 2015;60:3459–78.
Grant AM, et al. Simultaneous PET/MR imaging with a radio frequency-penetrable PET insert. Med Phys. 2016;44:112–20.
Akram MSH. A prototype oval PET insert for MRI systems targeted for body imaging. 2017 Report on PET Imaging Physics Research, National institutes for quantum science and technology (QST), Japan. Website: https://www.nirs.qst.go.jp/usr/medical-imaging/ja/study/pdf/QST_R_7.pdf
Akram MSH, et al. Study on the radiofrequency transparency of electrically floating and ground PET inserts in a 3T clinical MRI system. Med Phys. 2022;49:2965–78.
Vaska P, Cao T. The state of instrumentation for combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Semin Nucl Med. 2013;43:11–8.
Vandenberghe S, Marsden PK. PET-MRI: a review of challenges and solutions in the development of integrated multimodality imaging. Phys Med Biol. 2015;60:R115–54.
Shimizu K et al. Multi-pixel photon counter module for MRI compatible application. IEEE NSS/MIC M3CP-85. 2015.
Leifer MC. Resonant modes of the birdcage coil. J Magn Reson. 1997;124:51–60.
Collins CM, et al. A method for accurate calculation of B1 fields in three dimensions. Effects of shield geometry on field strength and homogeneity in the birdcage coil. J Magn Reson. 1997;125:233–41.
Akamatsu G, et al. Design consideration of compact cardiac TOF-PET systems: a simulation study. Phys Med Biol. 2021;66:074002.
Redpath TW. Signal-to-noise ratio in MRI. British J Radiol. 1998;71:704–7.
Akram MSH, et al. Geometry optimization of electrically floating PET inserts for improved RF penetration for a 3T MRI system. Med Phys. 2018;45:4627–41.
Surti S, et al. Design study of an in situ PET scanner for use in proton beam therapy. Phys Med Biol. 2011;56:2667–85.
Lopes PC, et al. First in situ TOF-PET study using digital photon counters for proton range verification. Phys Med Biol. 2016;61:6203–30.
Torres-Espallardo I, et al. Evaluation of resistive-plate-chamber-based TOF-PET applied to in-beam particle therapy monitoring. Phys Med Biol. 2015;60:N187–208.
Crespo P, Shakirin G, Enghardt W. On the detector arrangement for in-beam PET for hadron therapy monitoring. Phys Med Biol. 2006;51:2143–63.
Ott OW. Electromagnetic compatibility engineering. New Jersey: Wiley; 2009.
Stollberger R, et al. RF field mapping in vivo. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 1988;P106:7170.
Insko EK, Bolinger L. Mapping of radiofrequency field. J Magn Reson Ser A. 1993;103:82–5.
Jackson EF et al. Acceptance testing and quality assurance procedures for magnetic resonance imaging facilities. AAPM report no. 100, American Assoc Phys Med. 2010.
Ibrahim TS, et al. B1 field homogeneity and SAR calculations for the birdcage coil. Phys Med Biol. 2001;46:609–19.
Vaughan JT, et al. 7T vs. 4T: RF power, homogeneity, and signal-to-noise comparison in head images. Magn Reson Med. 2001;46:24–30.
Collins CM, Wang Z. Calculation of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields and their effects in MRI of human subjects. Magn Reson Med. 2011;65:1470–82.
Wang J, et al. Measurement and correction of transmitter and receiver induced nonuniformities in vivo. Magn Reson Med. 2005;53:408–17.
Watanabe H, Takaya N, Mitsumori F. Non-uniformity correction of human brain imaging at high field by RF field mapping of B1+ and B1-. J Magn Reson. 2011;212:426–30.
Cunningham CH, Pauly JM, Nayak KS. Saturated double-angle method for rapid B1 mapping. Magn Reson Med. 2006;55:1326–33.
Redpath TW, Wiggins CJ. Estimating achievable signal-to-noise ratios of MRI transmit–receive coils from radiofrequency power measurements: applications in quality control. Phys Med Biol. 2000;45:217–27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethics approval
No approval of research ethics committees was required to accomplish the goals of this study because no human or animal study was conducted in this technical study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Akram, M.S.H., Levin, C.S., Nishikido, F. et al. Study on the radiofrequency transparency of partial-ring oval-shaped prototype PET inserts in a 3 T clinical MRI system. Radiol Phys Technol 17, 60–70 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-023-00747-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-023-00747-w