Abstract
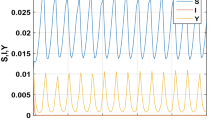
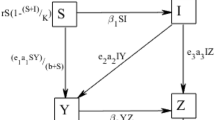
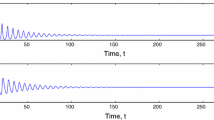
In this paper, we have developed a ratio-dependent predator-prey model with disease in prey. The total population is subdivided into three sub-classes, namely susceptible prey, infected prey and predator population. A susceptible prey survival threshold has been incorporated for Allee effect in the model. We have studied the positivity and boundedness of the solutions of the system and analyzed the existence of various equilibrium points and stability of the system at those equilibrium points for both strong and weak Allee effect. It is observed that a Hopf bifurcation may occur about the interior equilibrium taking susceptible prey survival threshold for Allee effect as bifurcation parameter. Our analytical findings are illustrated through computer simulation using MATLAB, which show the reliability of our model from the eco-epidemiological point of view.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R.M., May, R.M.: The invasion persistence and spread of infectious diseases within animal and plant communities. Phil. Trans. R. Sot. Lond. B 314, 533–570 (1986)
Arditi, R., Ginzburg, L.R.: Coupling in predator-prey dynamics: ratio-dependence. J. Theo. bio. 139, 311–326 (1989)
Arditi, R., Saiah, H.: Empirical evidence of the role of heterogeneity in ratio-dependent consumption. Ecology 73, 1544–1551 (1992)
Beretta, E., Capasso, V.: On the general structure of epidemic systems: global asymptotic stability. Comput. Math. Appl. 12A, 677–694 (1986)
Butler, G.J., Freedman, H.I., Waltman, P.: Uniformly persistent systems. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 96, 425–429 (1986)
Castillo-Chevez, C., Feng, Z.: Global stability of an age-structure model for TB and its applications to optimal vaccination strategies. Math. Biosci. 151, 135–154 (1998)
Castillo-Chevez, C., Song, B.: Dynamical models of tuberculosis and their applications. Math. Biosci. Eng. 1, 361–404 (2004)
Celik, C., Duman, O.: Allee effect in a discrete-time predator-prey system. Chaos. Solitons. Fractals 40, 1956–1962 (2009)
Chen, F., Chen, L., Xie, X.: On a Leslie-Gower predator-prey model incorporating a prey refuge. Nonlin. Anal. Real World Appl. 10, 2905–2908 (2009)
Chen, H., Sun, J.: Global stability of delay multigroup endemic models with group mixing and nonlinear incidence rates. Appl. Math. Comput. 218, 4391–4400 (2011)
Enatsu, Y., Messina, E., Muroya, Y., Nakata, Y., Russo, E., Vecchio, A.: Stability analysis of delayed SIR epidemic models with a class of nonlinear incidence rates. Appl. Math. Comput. 218, 5327–5336 (2012)
Freedman, H.I.: Deterministic Mathematical Models in Population Ecology. Marcel Dekker, New York (1980)
Freedman, H.I., Waltman, P.: Mathematical analysis of some three-species food chain models. Math. Biosci. 33, 257–276 (1977)
Freedman, H.I., Waltman, P.: Persistence in a model of three competitive populations. Math. BIosci. 73, 89–101 (1985)
Freedman, H.I., Waltman, P.: Persistence in a model of three interacting predator-prey populations. Math. Biosci. 68, 213–231 (1984)
Hadeler, K.P., Freedman, H.I.: Predator-prey populations with parasitic infection. J. Math. Biol. 27, 609–631 (1989)
Hale, J.K.: Theory of Functional Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1977)
Haque, A.: A predator-prey model with disease in the pradator species only. Nonlin. Anal. Real World Appl. 11(010), 2224–2236 (2010)
Haque, M., Greenhalgh, D.: When Predato avoids infected Prey: a model based theoretical studies. IMA J. Math. Med. Biol. 27, 75–94 (2009)
Haque, M., Sarwardi, S., Preston, S., Venturino, E.: Effect of delay in a Lotka-Volterra type Predator-Prey model with a transmission disease in the predator species. Math. Biosci. 234(1), 47–57 (2011)
Haque, M., Venturino, E.: Modelling disease spreading in symbiotic communities. Wildlife Destruction, Conservation and biodiversity. Nova Science Publishers, New York (2009)
Haque, M., Zhen, J., Venturino, E.: Rich dynamics of Lotka-Volterra type Predator-Prey model system with viral disease in Prey species. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 32, 875–898 (2009)
Hethcote, H.: The mathematics of infectious diseases. SIAM Rev. 42, 599–653 (2000)
Hethcote, H., Wang, W., Han, L., Ma, Z.: A predator-prey model with infected prey. Theo. Popul. Biol. 66, 259–268 (2004)
Holling, C.S.: The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 45, 3–60 (1965)
Hsieh, Y.H., Hsiao, C.K.: Predator-Prey model with disease infection in both populations. Math. Med. Biol. 25, 247–266 (2008)
Hsu, S.B., Hwang, T.W.: Hopf bifurcation analysis for a predator-prey system of Holling and Leslie type. Taiwan J. Math. 3, 35–53 (1999)
Huang, Y., Chen, F., Zhong, L.: Stability analysis of a prey-predator model with Holling type II resopnse function incorporating a prey refuge. Appl. Math. Comput. 182, 672–683 (2006)
Javidi, M., Nyamorady, N.: Allee effects in a predator-prey system with a saturated recovery function and harvesting. Int. J. Adv. Math. Sci. 1(2), 33–44 (2013)
Ji, C., Jiang, D., Shi, N.: Analysis of a predator-prey model with modified Leslie-Gower and Holling typeII schemes with stochastic perturbation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 359, 482–498 (2009)
Jia, J., Liu, J.: A food chain model with ratio-dependent functional response, impulsive perturbations and feedback controls. Br. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 2(3), 126–136 (2012)
Ko, W., Ryu, K.: Qualitative analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling type II functional response incorporating a prey refuge. J. Differ. Equ. 231, 534–550 (2006)
Korobeinikov, A.: A Lyapunov function for Leslie-Gower predator-prey models. Appl. Math. Lett. 14, 697–699 (2001)
Korobeinikov, A., Maini, P.K., Walker, W.J.: Estimation of effective vaccination rate: pertussis in New Zealand as a case study. J. Theor. Biol. 224, 269–275 (2003)
Korobeinikov, A., Maini, P.K.: A Lyapunov function and global properties for SIR and SEIR epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence. Math. Biosci. Eng. 1, 57–60 (2004)
Korobeinikov, A., Maini, P.K.: Nonlinear incidence and stability of infectious disease models. Math. Med. Biol. 22, 113–128 (2005)
Kot, M.: Elements of Mathematical Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Kuang, Y., Beretta, E.: Global qualitative analysis of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system. J. Math. Biol. 36, 389–406 (1998)
Kuznetsov, Y., Rinaldi, S.: Remarks on food chain dynamics. Math. Biosci. 134, 1–33 (1996)
Lai, X., Liu, S., Lin, R.: Rich dynamical behaviours for predator-prey model with weak Allee effect. Appl. Anal. 89, 1271–1292 (2010)
Li, Y., Li, C.: Stability and Hopf bifurcation analysis on a delayed Leslie-Gower predator-prey system incorporating a prey refuge. Appl. Math. Comput. 219, 4576–4589 (2013)
Li, J., Yang, Y., Zhou, Y.: Global stability of an epidemic model with latent stage and vaccination. Nonlin. Anal. 12, 2163–2173 (2011)
Liu, W.M., Levin, S.A., Iwasa, Y.: Influence of non-linear incidence rates upon the behaviour of SIRS epidemiological models. J. Math. Biol. 23, 187–204 (1986)
Maiti, A., Pal, A.K., Samanta, G.P.: Effect of time delay on a food chain model. Appl. Math. Comput. 200, 189–203 (2008)
Maiti, A., Pal, A.K., Samanta, G.P.: Usefulness of biocontrol of pests in tea: a mathematical model. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 3, 96–113 (2008)
Maiti, A., Samanta, G.P.: Complex dynamics of a food chain model with mixed selection of functional responses. Bull. Cal. Math. Soc. 97, 393–412 (2005)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology. Springer, New York (1993)
Pal, A.K., Samanta, G.P.: Stability analysis of an eco-epidemiological model incorporating a prey refuge. Nonlin. Anal. Model. Control 15(4), 473–491 (2010)
Pal, P.J., Saha, T., Sen, M., Banerjee, M.: A delayed predator-prey model with strong Allee effect in prey population growth. Nonlin. Dyn. 68, 23–42 (2012)
Pielou, E.C.: Mathematical Ecology. Wiley, New York (1977)
Rahman, MdS, Chakravarty, S.: A predator-prey model with disease in prey. Nonlin. Anal. Model. Cont. 18, 191–209 (2013)
Ruan, S., Wang, W.: Dynamical behavior with non-linear incidence rate. J. Diff. Equ. 22, 135–163 (2003)
Samanta, G.P., Manna, D., Maiti, A.: Bioeconomic modelling of a three-species fishery with switching effect. Korean J. Comput. Appl. Math. 12(1–2), 219–231 (2003)
Sharma, S., Samanta, G.P.: Analysis of an epidemic model with non-linear incidence and vaccination. Int. J. Ecol. Econ. Stat. 28(1), 104–129 (2013)
Sharma, S., Samanta, G.P.: Dynamical behaviour of a two prey one predator system. Differ. Eqn. Dyn. Syst. (2013). doi:10.1007/s12591-012-0158-y
Sharma, S., Samanta, G.P.: Dynamical behaviour of an HIV/AIDS epidemic model. Differ. Eqn. Dyn. Syst. (2013). doi:10.1007/s12591-013-0173-7
Shi, X.Y., Cui, J., Zhou, X.Y.: Stability and Hopf bifurcation analysis of an eco-epidemic model with a stage structure. Nonlin. Anal. 74, 1088–1106 (2011)
Sun, C., Lin, Y., Han, M.: Stability and hopf bifurcation for an epidemic disease model with delay. Chaos Soliton Fract. 30, 204–216 (2006)
Takeuchi, Y., Oshime, Y., Matsuda, H.: Persistence and periodic orbits of a three-competitor model with refuges. Math. Biosci. 108, 105–125 (1992)
Tewa, J.J., Djeumen, V.Y., Bowong, S.: Predator-Prey model with Holling response function of type II and SIS infectious disease. Appl. Math. Model. 37, 4825–4841 (2013)
Venturino, E.: Epidemics in Predator-Prey models: disease in the Predators. IMA. J. Math. Appl. Med. Biol. 19, 285–205 (2002)
Venturino, E.: Epidemics in predator-prey models: disease in the prey. In: Arino, O., Axelrod, D., Kimmel, M., Langlais, M. (eds.) Mathematical Population Dynamics: Analysis of Heterogeneity, Theory of Epidemics, vol. 1, pp. 381–393. Wuerz, Winnipeg (1995)
Venturino, E.: The influence of diseases on Lotka-Volterra systems. Rocky. Mt. J. Math. 24, 381–402 (1994)
Wang, S., Ma, Z.: Analysis of an ecoepidemiological model with prey refuges. J. Appl. Math. (2012). doi:10.1155/2012/371685
Wang, W., Zhu, Y., Cai, Y., Wang, W.: Dynamical complexity induced by Allee effect in a predator-prey model. Nonlin. Anal. Real World Appl. 16, 103–119 (2014)
Xiao, Y.N., Chen, L.S.: A ratio-dependent predator-prey model with disease in the prey. Appl. Mth. Comput. 131, 397–414 (2002)
Xiao, Y.N., Chen, L.S.: Analysis of a three species eco-epidemiological model. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 258(2), 733–754 (2001)
Xiao, Y.N., Chen, L.S.: Modelling and analysis of a predator-prey model with disease in the prey. Math. Biosci. 171, 59–82 (2001)
Xiao, D., Ruan, S.: Global analysis of an epidemic model with nonmonotone incidence rate. Math. Biosci. 208, 419–429 (2007)
Xiao, D., Ruan, S.: Global dynamics of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system. J. Math. Bio. 43, 268–290 (2001)
Xue, Y., Duan, X.: Dynamic analysis of an SIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate and double delays. Int. J. Info. Syst. Sci. 7, 92–102 (2011)
Yu, W., Cao, J.: Hopf bifurcation and stability of periodic solutions for Van der Pol equation with time delay. Nonlin. Anal. TMA 62, 141–165 (2005)
Zhang, J.F., Li, W.T., Yan, X.P.: Hopf bifurcation and stability of periodic solutions in a delayed eco-epidemiological system. Appl. Math. Comput. 198, 865–876 (2008)
Zhou, X., Cui, J.: Stability and Hopf bifurcation analysis of an eco-epidemiological model with delay. J. Frank. Inst. 347, 1654–1680 (2010)
Zhou, X., Liu, Y., Wang, G.: The stability of predator-prey systems subject to the Allee effects. Theo. Popul. Biol. 67, 23–31 (2005)
Zhou, X.Y., Shi, X.Y., Song, X.Y.: Analysis of a delay prey-predator model with disease in the prey species only. J. Korean Math. Soc. 46(4), 713–731 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors are very grateful to the anonymous referees and the Editor-in-Chief (Chin-Hong Park, Ph.D) for their careful reading, valuable comments and helpful suggestions, which have helped them to improve the presentation of this work significantly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, S., Samanta, G.P. A ratio-dependent predator-prey model with Allee effect and disease in prey. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 47, 345–364 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-014-0779-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-014-0779-0