Abstract
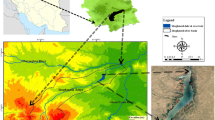
Water resources play an essential role in achieving a multifaceted development society, and their superiority allocation affects the development rate of cities. The model of this research for allocating optimal water resources is constructed with objectives including social, economic, and ecological objectives, and the constraints including water supply, water demand, water transmission, and non-negativity, based on which the objectives are integrated using the Pareto front, and the dimensionless processing and entropy weighting method. Next, the improved marine predator algorithm (IMPA), which uses chaos initialization in the initial population, incorporates the golden sine algorithm in the process seeking and enhances the search capability using the quadratic interpolation method in the result comparison, is contrasted with several algorithms based on different functions for optimal values, standard deviation, and mean values. Then, using Huaying City as the research area, the water distribution scheme for the region in 2021 is obtained. The allocation schemes of local confirm the superiority of IMPA in terms of accuracy and stability, which provides a new idea for water allocation in Huaying City. The results of the experiment show that IMPA is an effective and available choice for solving water resources optimization researches.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Aggarwal S, Chatterjee P, Bhagat RP, Purbey KK, Nanda SJ (2018) A social spider optimization algorithm with chaotic initialization for robust clustering. Procedia Comput Sci 143:450–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.417
Ahmadianfar I, Samadi-Koucheksaraee A, Bozorg-Haddad O (2017) Extracting optimal policies of hydropower multi-reservoir systems utilizing enhanced differential evolution algorithm. Water Resour Manage 31:4375–4397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1753-z
Ahmadianfar I, Shirvani-Hosseini S, He J, Samadi-Koucheksaraee A, Yaseen ZM (2022a) An improved adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system model using conjoined metaheuristic algorithms for electrical conductivity prediction. Sci Rep 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08875-w
Ahmadianfar I, Shirvani-Hosseini S, Samadi-Koucheksaraee A, Yaseen ZM (2022b) Surface water sodium (Na+) concentration prediction using hybrid weighted exponential regression model with gradient-based optimization. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:53456–53481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19300-0
Ahmadianfar I, Samadi-Koucheksaraee A, Asadzadeh M (2022c) Extract nonlinear operating rules of multi-reservoir systems using an efficient optimization method. Sci Rep 12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21635-0
Ahmadianfar I, Samadi-Koucheksaraee A, Razavi S (2023) Design of optimal operating rule curves for hydropower multi-reservoir systems by an influential optimization method. Renew Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.04.113
Alam S, Dobbie G, Koh YS, Riddle P, Rehman SU (2014) Research on particle swarm optimization based clustering: a systematic review of literature and techniques. Swarm Evol Comput 17:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2014.02.001
Arora S, Singh S (2019) Butterfly optimization algorithm: a novel approach for global optimization. Soft Comput 23:715–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3102-4
Benaissi S, Chikouche N, Hamza R (2023) A novel image encryption algorithm based on hybrid chaotic maps using a key image. Optik 272:170316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.170316
Chen L, Wu T, Wang Z, Lin X, Cai Y (2023) A novel hybrid BPNN model based on adaptive evolutionary Artificial Bee colony algorithm for water quality index prediction. Ecol Ind 146:109882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109882
Dhiman G, Kumar V (2019) Seagull optimization algorithm: theory and its applications for large-scale industrial engineering problems. Knowl Based Syst 165:169–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.11.024
Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Colorni A (1996) Ant system: optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B (Cybernetics) 26(1):29–41. https://doi.org/10.1109/3477
Fang Y, Ahmadianfar I, Samadi-Koucheksaraee A, Azarsa R, Scholz M, Yaseen ZM (2021) An accelerated gradient-based optimization development for multi-reservoir hydropower systems optimization. Energy Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.11.010
Faramarzi A, Heidarinejad M, Mirjalili S, Gandomi AH (2020) Marine predators Algorithm: a nature-inspired metaheuristic. Expert Syst Appl 152:113377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113377
Haddout S, Hoguane AM, Priya KL, Ljubenkov I (2020) Water shortages and pandemics in Africa. The Round Table 109(4):480–481. https://doi.org/10.1080/00358533.2020.1790784
Hagihara Y, Hagihara K, Nakagawa Y, Watanabe H (1981) A multi-objective optimal water resources allocation process. IFAC Proc Volumes 14(2):3901–3906. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-6670(17)64056-4
He H, Yin M, Chen A, Liu J, Xie X, Yang Z (2018) Optimal allocation of water resources from the wide-mild water shortage perspective. Water 10(10):1289. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101289
Holland JH (1992) Genetic algorithms. Sci Am 267(1):66–73
Hou J, Mi W, Sun J (2014) Optimal spatial allocation of water resources based on pareto ant colony algorithm. Int J Geogr Inf Sci 28(2):213–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2013.849809
Houssein EH, Ibrahim IE, Kharrich M, Kamel S (2022) An improved marine predators algorithm for the optimal design of hybrid renewable energy systems. Eng Appl Artif Intell 110:104722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2022.104722
Hu G, Zhu X, Wei G, Chang CT (2021) An improved marine predators algorithm for shape optimization of developable ball surfaces. Eng Appl Artif Intell 105:104417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104417
Huang G, Dan Moore R (1993) Grey linear programming, its solving approach, and its application. Int J Syst Sci 24(1):159–172. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207729308949477
Jønch-Clausen T (1979) Optimal allocation of regional water resources. Hydrol Res 10(1):7–24. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.1979.0002
Karaboga D, Akay B (2009) A comparative study of artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl Math Comput 214(1):108–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2009.03.090
Kaur N, Rattan M, Gill SS, Kaur G, Walia GK, Kaur R (2022) Marine predators algorithm for performance optimization of nanoscale FinFET. Mater Today: Proc 66:3529–3533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, IEEE vol 4, pp 1942–1948
Kummu M, Guillaume JH, de Moel H, Eisner S, Flörke M, Porkka M, Siebert S, Veldkamp TI, Ward PJ (2016) The world’s road to water scarcity: shortage and stress in the 20th century and pathways towards sustainability. Sci Rep 6(1):38495. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38495
Lei GJ, Liu CS, Wang W (2022) Study on ecological allocation of mine water in mining area based on long-term rainfall forecast. Water Resour Manage 36:5545–5563. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-9601(02)00259-1
Li S, Chen H, Wang M, Heidari AA, Mirjalili S (2020) Slime mould algorithm: a new method for stochastic optimization. Futur Gener Comput Syst 111:300–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.03.055
Li R, Chang Y, Wang Z (2021) Study of optimal allocation of water resources in Dujiangyan irrigation district of China based on an improved genetic algorithm. Water Supply 21(6):2989–2999. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2020.302
Li M, Hao JK, Wu Q (2022) Learning-driven feasible and infeasible tabu search for airport gate assignment. Eur J Oper Res 302(1):172–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2021.12.019
Liu H, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Gong Q, Huang Z (2010) A novel hybrid optimization algorithm based on glowworm swarm and fish school. J Comput Inform Syst 6(13):4533–4542
Ma T, Sun S, Fu G, Hall JW, Ni Y, He L, Yi J, Zhao N, Du Y, Pei T, Cheng W, Song C, Fang C, Zhou C (2020) Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality. Nat Commun 11(1):650. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14532-5
Maass A, Hufschmidt MM, Dorfman R, Thomas Jr HA, Marglin SA, Fair GM (1962) Design of water resource system. Soil Sci 94(2):135
Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2016) The whale optimization algorithm. Adv Eng Softw 95:51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01
Rezaei F, Safavi HR (2022) Sustainable conjunctive water use modeling using dual fitness particle swarm optimization algorithm. Water Resour Manage 36:989–1006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03064-w
Samadi-Koucheksaraee A, Ahmadianfar I, Bozorg-Haddad O, Asghari-Pari S (2018) Gradient evolution optimization algorithm to optimize Reservoir Operation systems. Water Resour Manage 33:603–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2122-2
Sangaiah AK, Khanduzi R (2022) Tabu search with simulated annealing for solving a location–protection–disruption in hub network. Appl Soft Comput 114:108056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.108056
Sharma AN, Dongre SR, Gupta R, Ormsbee L (2022) Multiphase procedure for identifying district metered areas in water distribution networks using community detection, NSGA-III optimization, and multiple attribute decision making. J Water Resour Plan Manag 148(8):04022040. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0001586
Shiklomanov IA (1991) The world’s water resources. In: Proceedings of the international symposium to commemorate (Vol. 25, pp 93–126). Paris, France: Unesco
Shirvani-Hosseini S, Samadi-Koucheksaraee A, Ahmadianfar I, Gharabaghi B (2022) Data Mining Methods for Modeling in Water Science. Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol 1043. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-2519-1_8
Singh A (2022) Better water and land allocation for long-term agricultural sustainability. Water Resour Manage 36:3505–3522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03208-y
Stephenson D (1969) Optimum allocation of water resources by mathematical programming. J Hydrol 9(1):20–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(69)90012-2
Tanyildizi E, Demir G (2017) Golden sine algorithm: a novel math-inspired algorithm. Adv Electr Comput Eng 17(2):71–78. https://doi.org/10.4316/AECE.2017.02010
Tian J, Yu W, Ma L (2010) AntShrink: ant colony optimization for image shrinkage. Pattern Recognit Lett 31(13):1751–1758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2010.01.004
Wang Z, Wang Q, Liu Z, Wu T (2024) A deep learning interpretable model for river dissolved oxygen multistep and interval prediction based on multi-source data fusion. J Hydrol 629:130637
Wu X, Wang Z (2022) Multi-objective optimal allocation of regional water resources based on slime mould algorithm. J Supercomputing 78(16):18288–18317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04599-w
Wu J, Wang Z, Hu Y, Tao S, Dong J (2023) Runoff forecasting using Convolutional neural networks and optimized bi-directional long short-term memory. Water Resour Manage 37(2):937–953. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03414-8
Yang X, Yang Z, Shen Z, Li J (2005) Node ordinal encoded genetic algorithm for the optimal allocation of water resources. Prog Nat Sci 15(5):448–452
Yang H, Jiang F, Wu X, Zhao G, Shi X, Liu G, Wang M (2023) Optimizing the cutting edge geometry of micro drill based on the entropy weight method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 125(5–6):2673–2689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-10884-6
Yao Z, Wang Z, Cui X, Zhao H (2023a) Research on multi-objective optimal allocation of regional water resources based on improved sparrow search algorithm. J Hydroinformatics 25(4):1413–1437. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2023.037
Yao Z, Wang Z, Wang D, Wu J, Chen L (2023b) An ensemble CNN-LSTM and GRU adaptive weighting model based improved sparrow search algorithm for predicting runoff using historical meteorological and runoff data as input. J Hydrol 625:129977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129977
Yao Z, Wang Z, Wu T, Lu W (2024) A hybrid data-driven deep learning prediction framework for lake water level based on the fusion of meteorological and hydrological multi-source data. Nat Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-023-10284-3
Yue W, Yu S, Xu M, Rong Q, Xu C, Su M (2022) A copula-based interval linear programming model for water resources allocation under uncertainty. J Environ Manage 317:115318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115318
Zhang Y, Shen Y (2019) Wastewater irrigation: past, present, and future. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Water 6(3):e1234. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1234
Zhang F, Zhang Y (2020) A multi-objective optimization prediction approach for water resources based on swarm intelligence. Earth Sci Inf 14:457–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-020-00521-1
Zhou X, Zhang Y, Sheng Z, Manevski K, Andersen MN, Han S, Li H, Yang Y (2021) Did water-saving irrigation protect water resources over the past 40 years? A global analysis based on water accounting framework. Agric Water Manage 249:106793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106793
Zou M, Kang S (2022) Closing the irrigation water productivity gap to alleviate water shortage in an endorheic basin. Sci Total Environ 853:158449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158449
Acknowledgements
It was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LY23H180001) and Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Sediment Science and Northern River Training, the Ministry of Water Resources, China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research (Grant No. IWHR-SEDI-2023-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhaocai Wang: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Writing - original draft. Haifeng Zhao: Methodology, Validation, Writing - review & editing, Supervision. Xiaoguang Bao: Data curation, Software. Tunhua Wu: Methodology, Software, Writing - original draft. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Zhao, H., Bao, X. et al. Multi-objective optimal allocation of water resources based on improved marine predator algorithm and entropy weighting method. Earth Sci Inform 17, 1483–1499 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01230-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-024-01230-9