Abstract
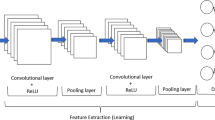
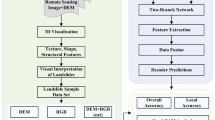
The classification of vegetation types worldwide plays a significant role in studies involving remote sensing. This method, used notably in agriculture, aids producers in devising more efficient agricultural management models. It relies on satellite and aircraft technologies to analyze agricultural lands. Nevertheless, the recent emergence of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has introduced faster and more cost-effective alternatives to traditional satellite and aircraft systems. These UAVs provide higher resolution images, leading to a shift in remote sensing practices. For deep learning in UAV-based image classification, convolutional neural network (CNN) techniques are commonly employed due to their advantageous features and exceptional extraction capabilities. This study proposes a hybrid approach based on CNN, combining 2D depthwise separable convolution (DSC) with a conventional 2D CNN and a Squeeze-and-Excitation network (SENet). The inclusion of SENet aims to boost classification performance without significantly increasing the overall parameter count. By integrating 2D DSC, computational costs and the number of trainable parameters are notably reduced. The multipath network structure’s core purpose is to amplify the extracted features from UAV-derived images. The effectiveness of this multipath hybrid approach was evaluated using an orthophoto from Harran University’s campus captured by a UAV. The primary goal was to distinguish between mature and immature lavender plants. The results indicate a high accuracy, with immature lavender plants classified at 99.77% accuracy and mature lavender plants at 95.15% accuracy. These findings from experimental studies demonstrate the high effectiveness of our hybrid method in identifying immature lavender plants.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Ahmad M, Khan AM, Mazzara M et al (2022) A fast and Compact 3-D CNN for Hyperspectral Image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 19:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2020.3043710
Ainiwaer M, Ding J, Kasim N (2020) Deep learning-based rapid recognition of oasis-desert ecotone plant communities using UAV low-altitude remote-sensing data. Environ Earth Sci 79:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-08965-w
Akca S, Polat N (2022) Semantic segmentation and quantification of trees in an orchard using UAV orthophoto. Earth Sci Informatics 15:2265–2274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-022-00871-y
Akkamiş M, Çalişkan S (2020) Türkiye İnsansız Hava Araçları Dergisi İnsansız Hava Araçları ve Tarımsal Uygulamalarda Kullanımı Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and Usage in Agricultural Applications. 2:8–16
Anisimova A, Safonova N, Dobrushyna M (2023) Semantic peculiarities of the concept language policyin a multilingual aspect. Int J Multiling Educ 1–12
Aslan İ, Polat N (2022) Availability of Iphone 13 pro laser data in 3D modeling. Adv LiDAR 2:10–14
Aslancan H, Saribaş R (2011) Lavanta Yetiştiriciliği. Directorate of Fruit Research Institute. 41
Ben Hamida A, Benoit A, Lambert P, Ben Amar C (2018) 3-D deep learning approach for remote sensing image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56:4420–4434. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2818945
Bouguettaya A, Zarzour H, Kechida A, Taberkit AM (2022) Deep learning techniques to classify agricultural crops through UAV imagery: a review. Neural Comput Appl 34:9511–9536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-022-07104-9
Chen Y, Jiang H, Li C et al (2016) Deep feature extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54:6232–6251. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2016.2584107
Chen LC, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I et al (2018) DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with Deep Convolutional nets, atrous Convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40:834–848. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184
Cheng Z, Gong W, Tang H et al (2021) UAV photogrammetry-based remote sensing and preliminary assessment of the behavior of a landslide in Guizhou, China. Eng Geol 289:106172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106172
Chollet F (2017) Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. Proc - 30th IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017 2017-Jan:1800–1807. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.195
Deng L, Li J, Huang JT et al (2013) Recent advances in deep learning for speech research at Microsoft. ICASSP. IEEE Int Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process - Proc 8604–8608. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP.2013.6639345
Dereli MA, Polat N, Uysal M (2019) Düşük Maliyetli İHA ile Yüksek Çözünürlüklü SYM Üretimi. Nevşehir Bilim ve Teknol Derg 8:56–62. https://doi.org/10.17100/nevbiltek.448558
Ferentinos KP (2018) Deep learning models for plant Disease detection and diagnosis. Comput Electron Agric 145:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2018.01.009
Fırat H (2023a) Multiple classification of human peripheral blood cells using modified Inception Module. J Eng Sci Res 5:272–284
Fırat H (2023b) Classification of White Blood cells using the squeeze-excitation residual network. J Inf Technol 16:189–205
Fırat H, Hanbay D (2023) Comparison of 3D CNN based deep learning architectures using hyperspectral images. J Fac Eng Archit Gazi Univ 38:521–534. https://doi.org/10.17341/gazimmfd.977688
Firat H, Asker ME, Hanbay D (2022) Hybrid 3D convolution and 2D depthwise separable convolution neural network for hyperspectral image classification. Balk J Electr Comput Eng 10:35–46. https://doi.org/10.17694/bajece.1039029
Fuentes A, Yoon S, Kim S, PD (2017) A robust deep-learning-based detector for real-time tomato plant diseases and pests recognition 17(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/s17092022
Guenther SE (2023) Preliminary Live-Trapping Studies of Marten Author (s): Antoon de Vos and Stanley E. Guenther Source : The Journal of Wildlife Management, Vol. 16, No. 2 (Apr., 1952), pp. 207–214 Published by : Wiley on behalf of the Wildlife Society Stable UR. 16:207–214
Hamylton SM, Morris RH, Carvalho RC et al (2020) Evaluating techniques for mapping island vegetation from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images: pixel classification, visual interpretation and machine learning approaches. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 89:102085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2020.102085
Haq MA, Rahaman G, Baral P, Ghosh A (2021) Deep learning based supervised image classification using UAV images for Forest areas classification. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 49:601–606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-020-01231-3
Hu J, Shen L, Albanie S et al (2020) Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42:2011–2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372
Jaud M, Grasso F, Le Dantec N et al (2016) Potential of UAVs for monitoring mudflat morphodynamics (application to the Sein E Estuary, France). ISPRS Int J Geo-Information 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi5040050
Javernick L, Brasington J, Caruso B (2014) Modeling the topography of shallow braided rivers using structure-from-motion photogrammetry. Geomorphology 213:166–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2014.01.006
Kara N, Baydar H (2013) Determination of lavender and lavandin cultivars (Lavandula sp.) containing high quality essential oil in Isparta, Turkey. Turkish J F Crop 18:58–65
Lu Y, Yi S, Zeng N et al (2017) Neurocomputing identification of rice Diseases using deep convolutional neural networks R. Neurocomputing 267:378–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.06.023
Lucieer A, Turner D, King DH, Robinson SA (2014) Using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) to capture micro-topography of antarctic moss beds. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 27:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2013.05.011
Ozkan M, Polat N (2022) Comparison between multicopter UAV and total station for volume calculation. 4th Intercontinental Geoinformation Days (IGD), 25-27, Tabriz, Iran
Polat N (2023) UAV-based construction progress monitoring: enhancing efficiency and safety. Adv Eng Days c:60–62
Polat N, Uysal M (2017) DTM generation with UAV based photogrammetric point cloud. Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spat Inf Sci - ISPRS Arch 42:77–79. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-archives-XLII-4-W6-77-2017
Radovic M, Adarkwa O, Wang Q (2017) Object recognition in aerial images using convolutional neural networks. J Imaging 3:21. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging3020021
Roy SK, Krishna G, Dubey SR, Chaudhuri BB (2020) HybridSN: exploring 3-D-2-D CNN feature hierarchy for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 17:277–281. https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2019.2918719
Sladojevic S, Arsenovic M, Anderla A et al (2016) Deep neural networks based recognition of plant diseases by leaf image classification. Comput Intell Neurosci 2016:3289801. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3289801
Snavely RA, Zhang B, Akli K et al (2007) Laser generated proton beam focusing and high temperature isochoric heating of solid matter. Phys Plasmas 14:92703. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2774001
Sultonov F, Park JH, Yun S et al (2022) Mixer U-Net: an Improved Automatic Road extraction from UAV Imagery. Appl Sci 12:1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12041953
Tsouros DC, Bibi S, Sarigiannidis PG (2019) A review on UAV-based applications for precision agriculture. Inf 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10110349
Türkoğlu M, Hanbay K, Sivrikaya IS, Hanbay D (2020) Classification of apricot diseases by using deep convolution neural network. BEÜ Fen Bilim Derg 9:334–345
Uysal M, Toprak AS, Polat N (2015) DEM generation with UAV Photogrammetry and accuracy analysis in Sahitler hill. Meas J Int Meas Confed 73:539–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2015.06.010
Üzen H, Turkoglu M, Aslan M, Hanbay D (2023) Depth-wise squeeze and Excitation Block-based efficient-unet model for surface defect detection. Vis Comput 39:1745–1764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02442-0
Wallelign S, Polceanu M, Buche C (2017) Soybean plant disease identification using convolutional neural network. The Thirty-First International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference (FLAIRS-31) 2018 146–151
Woodget AS, Carbonneau PE, Visser F, Maddock IP (2015) Quantifying submerged fluvial topography using hyperspatial resolution UAS imagery and structure from motion photogrammetry. Earth Surf Process Landforms 40:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3613
Xu Y, Wu L, Xie Z, Chen Z (2018) Building extraction in very high resolution remote sensing imagery using deep learning and guided filters. Remote Sens 10:144. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010144
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
İ. A. Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Resources. N. P. Data collection, Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: H. Babaie
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aslan, İ., Polat, N. Deep learning-based classification of mature and immature lavender plants using UAV orthophotos and a hybrid CNN approach. Earth Sci Inform 17, 1713–1727 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01200-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-023-01200-7