Abstract
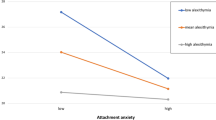
Social interactions are a major factor in organizing the earliest experiences in the memory system. In the current study, we tested the role of parental reminiscing on the relationship between parental attachment and recollection of earliest memories. The present study focused mainly on possible mediating properties of parental elaboration between the relationship of attachment and the recall of the earliest memories. We found a full mediation pattern, showing that high parental avoidance was associated with less parental elaboration, which was then linked to the earliest memories coming from a later age and poor recollection of these memories. On the other hand, although parental anxiety was related to the earliest memories coming from a later age and rich recollection of the earliest memories, the degree of parental elaboration was not found as a mediator. Findings are discussed in line with the role of the early relational and communicative input on adults’ recollections of early events.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The dataset generated during and/or analyzed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on request.
Notes
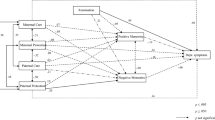
We tested the fit of two competing models. In our proposed model, parental attachment variables were used as the independent variables and parental elaboration was the mediator while in the alternative model, parental elaboration was the predictor and the attachment was the mediator. When comparing the models, we models were tested independently. Although both models had acceptable fits, we compared χ2/df values and AIC-BIC indices to determine the superior model. χ2 was significant for both models, however the proposed model (1.81) has smaller compared to the alternative model (2.16). In line, AIC-BCC comparison indices were found to be smaller for the proposed model (105.54-107.75) than the proposed model (107.31-109.25), both of which suggest the plausibility of the proposed model over the alternative model.
Maternal attachment variables and paternal attachment variables were tested both simultaneously in a single model and separately in distinct models. SEM with either model revealed comparable patterns for maternal and paternal attachment models. For that reason, we used the model where maternal and paternal anxiety and avoidance were tested in the same model.
References
Alexander, K. W., O’Hara, K. D., Bortfeld, H. V., Anderson, S. J., Newton, E. K., & Kraft, R. H. (2010). Memory for emotional experiences in the context of attachment and social interaction style. Cognitive Development, 25(4), 325–338.
Alexander, K. W., Goodman, G. S., Schaaf, J. M., Edelstein, R. S., Quas, J. A., & Shaver, P. R. (2002). The role of attachment and cognitive inhibition in children’s memory and suggestibility for a stressful event. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 83(4), 262–290.
Alexander, K. W., Quas, J. A., & Goodman, G. S. (2002). Theoretical advances in understanding children’s memory for distressing events: The role of attachment. Developmental Review, 22(3), 490–519.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2014). Amos (Version 23.0) [Computer Program]. Chicago: IBM SPSS.
Artioli, F., Cicogna, P. C., Occhionero, M., & Reese, E. (2012). The people I grew up with”: The role of sociodemographic factors in early memories in an Italian sample. Memory (Hove, England), 20(2), 189–197.
Aznar, A., & Tenenbaum, H. R. (2020). Gender comparisons in mother-child emotion talk: A meta-analysis. Sex Roles, 82(3), 155–162.
Bauer, P. J. (2005). Developments in declarative memory: Decreasing susceptibility to storage failure over the second year of life. Psychological Science, 16 (1), 41–47.
Bauer, P. (2007). Remembering the times of our lives. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum Associates.
Bauer, P. J., & Burch, M. M. (2004). Developments in early memory: Multiple mediators of foundational processes. In J. M. Lucariello, J. A. Hudson, R. Fivush, & P. J. Bauer (Eds.), The development of the mediated mind (pp. 101–125). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Bauer, P. J., Tasdemir-Ozdes, A., & Larkina, M. (2014). Adults’ reports of their earliest memories: Consistency in events, ages, and narrative characteristics over time. Consciousness and Cognition, 27, 76–88.
Bentler, P. M. (1980). Multivariate analysis with latent variables: Causal modeling. Annual Review of Psychology, 31 (1), 419–456.
Bentler, P. M. (1990). Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin, 107, 238–246.
Bergen, P. V., Salmon, K., Dadds, M. R., & Allen, J. (2009). The effects of mother training in emotion-rich, elaborative reminiscing on children’s shared recall and emotion knowledge. Journal of Cognition and Development, 10 (3), 162–187.
Berntsen, D., & Rubin, D. C. (2004). Cultural life scripts structure recall from autobiographical memory. Memory & Cognition, 32(3), 427–442.
Bifulco, A. (2021). Childhood trauma in women and fragmented interview narratives–some interdisciplinary methodological and clinical implications. East European Journal of Psycholinguistics, 8(1).
Bluck, S., Alea, N., Habermas, T., & Rubin, D. C. (2005). A tale of three functions: The self-reported uses of autobiographical memory. Social Cognition, 23(1), 91.
Bohanek, J. G., Fivush, R., Zaman, W., Lepore, C. E., Merchant, S., & Duke, M. P. (2009). Narrative interaction in family dinnertime conversations. Merrill-Palmer quarterly (Wayne State University. Press), 55(4), 488.
Boland,A. M., Haden, C.A., & Ornstein, P.A. (2003). Boosting children’s memory by training mothers in the use of an elaborative conversational style as an event unfolds. Journal of Cognition and Development, 4(1), 39–65. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327647JCD4,1-02
Bollen, K. A. (1989). Structural equations with latent variables. New York: Wiley.
Brown, T. A. (2015). Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research. Guilford Publications.
Bowlby, J. (1980). Attachment and loss: Vol.3. Loss: Sadness and depression. New York.
Cohen, P., Kasen, S., Bifulco, A., Andrews, H., & Gordon, K. (2005). The accuracy of adult narrative reports of developmental trajectories. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 29 (5), 345–355.
Conway, M. A. (2005). Memory and the self. Journal of Memory and Language, 53(4), 594–628.
Demiray, B. B., Gülgöz, B., S., & Bluck, S. (2009). Examining the life story account of the reminiscence bump: Why we remember more from young adulthood. Memory (Hove, England), 17(7), 708–723.
Chae, Y., Goodman, G. S., & Edelstein, R. S. (2011). Autobiographical memory development from an attachment perspective: The special role of negative events. Advances in Child Development and Behaviour, 40, 2.
Dykas, M. J., Woodhouse, S. S., Jones, J. D., & Cassidy, J. (2014). Attachment-related biases in adolescents’ memory. Child Development, 85(6), 2185–2201.
Edelstein, R. S. (2006). Attachment and emotional memory: Investigating the source and extent of avoidant memory impairments. Emotion, 6, 340–345.
Edelstein, R. S., Ghetti, S., Quas, J. A., Goodman, G. S., Alexander, K. W., Redlich, A. D., & Cordón, I. M. (2005). Individual differences in emotional memory: Adult attachment and long-term memory for child sexual abuse. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 31(11), 1537–1548.
Ein-Dor, T., Mikulincer, M., & Shaver, P. R. (2011). Attachment insecurities and the processing of threat-related information: Studying the schemas involved in insecure people’s coping strategies. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 101(1), 78.
Farrar, M. J., Fasig, L. G., & Welch-Ross, M. K. (1997). Attachment and emotion in autobiographical memory development. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 67, 389–408.
Fitzgerald, J. M., & Broadbridge, C. L. (2013). Latent constructs of the autobiographical memory questionnaire: A recollection-belief model of autobiographical experience. Memory, 21 (2), 230–248
Fivush, R. (2011). The development of autobiographical memory. Annual review of Psychology, 62, 559–582.
Fivush, R., & Nelson, K. (2006). Parent-child reminiscing locates the self in the past. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 24, 235–251. https://doi.org/10.1348/026151005X57747
Fivush, R., & Sales, J. M. (2006). Coping, attachment, and mother–child narratives of stressful events. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 52, 125–150.
Fivush, R., & Vasudeva, A. (2002). Remembering to relate: Socioemotional correlates of mother?child reminiscing. Journal of Cognition and Development, 3, 73?90.
Fivush, R., Haden, C. A., & Reese, E. (2006). Elaborating on elaborations: Role of maternal reminiscing style in cognitive and socioemotional development. Child Development, 77, 1568–1588.
Fivush, R., Marin, K., McWilliams, K., & Bohanek, J. G. (2009). Family reminiscing style: Parent gender and emotional focus in relation to child well-being. Journal of Cognition and Development, 10(3), 210–235.
Fraley, R. C. (2002). Attachment stability from infancy to adulthood: Meta-analysis and dynamic modeling of developmental mechanisms. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 6(2), 123–151.
Fraley, R. C., & Brumbaugh, C. C. (2007). Adult attachment and preemptive defenses: Converging evidence on the role of defensive exclusion at the level of encoding. Journal of Personality, 75, 1033–1050.
Fraley, R. C., & Shaver, P. R. (1999). Loss and bereavement: Attachment theory and recent controversies concerning” grief work” and the nature of detachment.
Fraley, R. C., Heffernan, M. E., Vicary, A. M., & Brumbaugh, C. C. (2011). The experiences in close relationships—Relationship Structures Questionnaire: A method for assessing attachment orientations across relationships. Psychological Assessment, 23(3), 615.
Fraley, R. C., Brumbaugh, C. C., & Marks, M. J. (2005). The evolution and function of adult attachment: a comparative and phylogenetic analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 89(5), 731.
Fraley, R. C., Garner, J. P., & Shaver, P. R. (2000). Adult attachment and the defensive regulation of attention and memory: Examining the role of preemptive and postemptive defensive processes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 79, 816–826.
Grysman, A. (2015). Collecting narrative data on Amazon’s Mechanical Turk. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 29(4), 573–583.
Habermas, T., & Köber, C. (2014). Autobiographical reasoning is constitutive for narrative identity: The role of the life story for personal continuity. In K. C. McLean, & M. Syed (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of identity development. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Harmon Jones, S. K., & Richardson, R. (2021). Maternal care, infant fear memory retention, and the moderating role of variations in separation induced ultrasonic vocalizations. Developmental Psychobiology, 63 (6), e22177.
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis. Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach edn. New York: Guilford Publications, 1, 20.
Hayne, H., & MacDonald, S. (2003). The socialization of autobiographical memory in children and adults: The roles of culture and gender. In R. Fivush & C. A. Haden (Eds.), Autobiographical memory and the construction of a narrative self: Developmental and cultural perspectives (pp. 99–120). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Hoyle, R. H. (Ed.). (2012). Handbook of structural equation modeling. Guilford press.
Jack, F. & Hayne, H. (2007). Eliciting adults’ earliest memories: Does it matter how we ask the question? Memory, 15 (6), 647–663. https://doi.org/10.1080/09658210701467087
Jack, F., & Hayne, H. (2010). Childhood amnesia: Empirical evidence for a two-stage phenomenon. Memory (Hove, England), 18, 831–844.
Jack, F., MacDonald, S., Reese, E., & Hayne, H. (2009). Maternal reminiscing style during early childhood predicts the age of adolescents’ earliest memories. Child Development, 80, 496–505.
Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (2nd ed.). New York: The Guilford Press
Kohn, J. L., Rholes, W. S., & Schmeichel, B. J. (2012). Self-regulatory depletion and attachment avoidance: Increasing the accessibility of negative attachment-related memories. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 48(1), 375–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2011.06.020
Kreppner, K. (2002). Retrospect and prospect in the psychological study of families as systems. Retrospect and Prospect in the Psychological Study of Families, 225–257.
Laible, D. (2004). Mother-child discourse in two contexts: links with child temperament, attachment security, and socioemotional competence. Developmental Psychology, 40 (6), 979–992. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.40.6.979
Laible, D. J., & Thompson, R. A. (2000). Mother–child discourse, attachment security shared positive affect, andearly conscience development. Child Development, 71 1424–1440.
Lawson, M., Chae, Y., Noriega, I., & Valentino, K. (2021). Parent–child attachment security is associated with preschoolers’ memory accuracy for emotional life events through sensitive parental reminiscing. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 209, 105–168
Low, J., & Durkin, K. (2001). Individual differences and consistency in maternal talk style during joint story encoding and retrospection: Associations with children’s long-term recall. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 25 (1), 27–36.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., & Williams, J. (2004). Confidence limits for the indirect effect: Distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39 (1), 99–128.
Main, M. (1995). Recent studies in attachment: Overview, with selected implications for clinical work. In S. Goldberg, R. Muir, & J. Kerr (Eds.), Attachment theory: Social, developmental, and clinical perspectives (pp. 407–474). Analytic Press, Inc.
Main, M., Kaplan, N., & Cassidy, J. (1985). Security in infancy, childhood, and adulthood A move to the level of representation. In I. Bretherton & E. Waters (Eds.), Growing points of attachment theory and research. Monographs of the society of research on child development, 50. (1–2, Serial No. 209).
McConnell, M., & Moss, E. (2011). Attachment across the life span: Factors that contribute to stability and change. Australian Journal of Educational & Developmental Psychology, 11, 60–77.
Mikulincer, M., & Shaver, P. R. (2007). Attachment in adulthood: Structure, dynamics, and change. Guilford Press.
Mikulincer, M., Dolev, T., & Shaver, P. R. (2004). Attachment-related strategies during thought suppression: Ironic rebounds and vulnerable self-representations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 87(6), 940.
Mikulincer, M., & Orbach, I. (1995). Attachment styles and repressive defensiveness: The accessibility and architecture of affective memories. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 68, 917–925. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.68.5.917
Mullen, M. K. (1994). Earliest recollections of childhood:A demographic analysis. Cognition, 52 (1), 55–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-0277(94)90004-3
Nelson, K., & Fivush, R. (2004). The emergence of autobiographical memory: A social cultural developmental theory. Psychological Review, 111, 486–511.
Newcombe, R., & Reese, E. (2004). Evaluations and orientations in mother–child reminiscing as a function of attachment security: A longitudinal investigation. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 28, 230–245.
Mason, W., & Suri, S. (2012). Conducting behavioral research on Amazon’s Mechanical Turk. Behavior Research Methods, 44(1), 1–23.
Öner, S., & Gülgöz, S. (2016). Latent constructs model explaining the attachment-linked variation in autobiographical remembering. Memory (Hove, England), 24(3), 364–382.
Öner, S., Demiray, B., & Gülgöz, S. (2020). Family Reminiscence Scale. Psychometric properties of a new measure of early communicative context.
Ontai, L. L., & Virmani, E. A. (2010). Predicting elements of early maternal elaborative discourse from 12 to 18 months of age. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 25 (1), 98–111.
Peer, E., Vosgerau, J., & Acquisti, A. (2014). Reputation as a sufficient condition for data quality on Amazon Mechanical Turk. Behavior Research Methods, 46(4), 1023–1031.
Peterson, C., & Nguyen, D. T. (2010). Parent–child relationship quality and infantile amnesia in adults. British Journal of Psychology, 101(4), 719–737.
Peterson, C., Smorti, A., & Tani, F. (2008). Parental influences on earliest memories. Memory (Hove, England), 16(6), 569–578.
Pillemer, D. (1998). What is remembered about early childhood events? Clinical Psychology Review, 18, 895–913.
Poole, D. A., & Lindsay, D. S. (2001). Children’s eyewitness reports after exposure to misinformation from parents. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 7,27–50.
Qin, J., Ogle, C. M., & Goodman, G. S. (2008). Adults’ memories of childhood: True and false reports. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied, 14,373–391.
Reese, E. (2002). Social factors in the development of autobiographical memory: The state of the art. Social Development, 11, 124–142.
Reese, E., & Brown, N. (2000). Reminiscing and recounting in the preschool years. Applied Cognitive Psychology, 14(1), 1–17.
Reese, E., Jack, F., & White, N. (2010). Origins of adolescents’ autobiographical memories. Cognitive Development, 25(4), 352–367.
Rubin, D. C., Schrauf, R. W., & Greenberg, D. L. (2003). Belief and recollection of autobiographical memories. Memory & Cognition, 31(6), 887–901.
Saffrey, C., & Ehrenberg, M. (2007). When thinking hurts: Attachment, rumination, and postrelationship adjustment. Personal Relationships, 14(3), 351–368.
Sales, J. M., Fivush, R., & Peterson, C. (2003). Parental reminiscing about positive and negative events. Journal of Cognition and Development, 4, 185–209.
Salmon, K., & Reese, E. (2016). The benefits of reminiscing with young children. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 25 (4), 233–238.
Steiger, J. H. (1990). Structural model evaluation and modification. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 25, 214–212.
Thompson, R. (2000). The legacy of early attachments. Child Development, 71, 145–152.
Tucker, L. R., & Lewis, C. (1973). A reliability coefficient for maximum likelihood factor analysis. Psychometrika, 38, 1–10.
Van de Schoot, R., Lugtig, P., & Hox, J. (2012). A checklist for testing measurement invariance. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 9(4), 486–492.
Vandevivere, E., Braet, C., Bosmans, G., Mueller, S. C., & De Raedt, R. (2014). Attachment and Children’s Biased Attentional Processing: Evidence for the Exclusion of Attachment-Related Information. PloS one, 9(7), e103476.
Virmani, E. A., Jochem, R. A., Raikes, H. A., Meyer, S. C., Waters, A., & Thompson, R. A. (2009). Avoiding conversations about negative emotions: The role of attachment, parent validation, and child characteristics. Poster presented at the biennial meeting of the Society for Research in Child Development, Denver, CO.
Wang, Q. (2001). Culture effects of adults’ earliest childhood recollection and self-description: Implications of the relation between memory and self. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 81, 220–233.
Wang, Q. (2006). Relations of maternal style and child self-concept to autobiographical memories in Chinese, Chinese immigrant, and European American 3-year-olds. Child Development, 77, 1794–1809.
Wang, Q., & Conway, M. A. (2006). Autobiographical memory, self, and culture. In L. G. Nilsson, & N. Ohta (Eds.), Memory and society: Psychological perspectives (pp. 9–27). New York: Psychology Press.
Wareham, P., & Salmon, K. (2006). Mother?child reminiscing about everyday experiences: Implications for psychological interventions in the preschool years. Clinical Psychology Review, 26 (5), 535–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2006.05.001
Waters, T. E., Camia, C., Facompré, C. R., & Fivush, R. (2019). A meta-analytic examination of maternal reminiscing style: Elaboration, gender, and children’s cognitive development. Psychological Bulletin, 145(11), 1082.
Wenner, J. A., Burch, M. M., Lynch, J. S., & Bauer, P. J. (2008). Becoming a teller of tales: Associations between children’s fictional narratives and parent–child reminiscence narratives. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 101(1), 1–19.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance with ethical statement
This study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the university with which the first author was affiliated. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants participated the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Öner, S., Gülgöz, S. Adults’ recollection of the earliest memories: early parental elaboration mediated the link between attachment and remembering. Curr Psychol 42, 30037–30048 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03811-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03811-7