Abstract
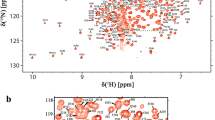
The 26S proteasome is responsible for the selective, ATP-dependent degradation of polyubiquitinated proteins in eukaryotic cells. It consists of a 20S barrel-shaped core particle capped by two 19S regulatory particle at both ends. The Rpn5 subunit is a non-ATPase subunit located in the lid subcomplex of the 19S regulatory particle and is identified to inhibit the Rpn11 deubiquitinase activity in the isolated lid. The protein contains a C-terminal proteasome–CSN–eIF3 (PCI) domain and an N-terminal α-solenoid domain, the latter has been shown to be highly flexible in the isolated lid and may participate in interactions with different subunits of the proteasome. We herein report the 1H, 13C and 15N atoms chemical shift assignments of the N-terminal domain (residues 1–136) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rpn5, which provide the basis for further studies of the structure, dynamics and interactions of the Rpn5 subunit by NMR technique.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck F, Unverdorben P, Bohn S, Schweitzer A, Pfeifer G, Sakata E, Nickell S, Plitzko JM, Villa E, Baumeister W, Förster F (2012) Near-atomic resolution structural model of the yeast 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:14870–14875
Chen S, Wu J, Lu Y, Ma Y, Lee B, Yu Z, Ouyang Q, Finley DJ, Kirschner MW, Mao Y (2016) Structural basis for dynamic regulation of the human 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:12991–12996
Dambacher CM, Worden EJ, Herzik MA, Martin A, Lander GC (2016) Atomic structure of the 26S proteasome lid reveals the mechanism of deubiquitinase inhibition. Elife 5:e13027
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
des Georges A, Dhote V, Kuhn L, Hellen CUT, Pestova TV, Frank J, Hashem Y (2015) Structure of mammalian eIF3 in the context of the 43S preinitiation complex. Nature 525:491–495
Estrin E, Lopez-Blanco JR, Chacon P, Martin A (2013) Formation of an intricate helical bundle dictates the assembly of the 26S proteasome lid. Structure 21:1624–1635
Finley D (2009) Recognition and processing of ubiquitin-protein conjugates by the proteasome. Annu Rev Biochem 78:477–513
Förster F, Lasker K, Nickell S, Sali A, Baumeister W (2010) Toward an integrated structural model of the 26S proteasome. Mol Cell Proteomics 9:1666–1677
Glickman MH, Ciechanover A (2002) The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev 82:373–428
Glickman MH, Rubin DM, Coux O, Wefes I, Pfeifer G, Cjeka Z, Baumeister W, Fried VA, Finley D (1998) A subcomplex of the proteasome regulatory particle required for ubiquitin-conjugate degradation and related to the COP9-signalosome and eIF3. Cell 94:615–623
Goldberg AL (2003) Protein degradation and protection against misfolded or damaged proteins. Nature 426:895–899
Groll M, Ditzel L, Lowe J, Stock D, Bochtler M, Bartunik HD, Huber R (1997) Structure of 20S proteasome from yeast at 2.4 Å resolution. Nature 386:463–471
Heinemeyer W, Fischer M, Krimmer T, Stachon U, Wolf DH (1997) The active sites of the eukaryotic 20 S proteasome and their involvement in subunit precursor processing. J Biol Chem 272:25200–25209
Hershko A, Ciechanover A, Varshavsky A (2000) Basic Medical Research Award. The ubiquitin system. Nat Med 6:1073–1081
Hu Y, Wu Y, Li Q, Zhang W, Jin C (2015) Solution structure of yeast Rpn9: insights into proteasome lid assembly. J Biol Chem 290:6878–6889
Huang X, Luan B, Wu J, Shi Y (2016) An atomic structure of the human 26S proteasome. Nat Struct Mol Biol 23:778–785
Isono E, Nishihara K, Saeki Y, Yashiroda H, Kamata N, Ge L, Ueda T, Kikuchi Y, Tanaka K, Nakano A, Toh-e A (2007) The assembly pathway of the 19S regulatory particle of the yeast 26S proteasome. Mol Biol Cell 18:569–580
Johnson BA, Blevins RA (1994) NMR view: a computer program for the visualization and analysis of NMR data. J Biomol NMR 4:603–614
Lander GC, Estrin E, Matyskiela ME, Bashore C, Nogales E, Martin A (2012) Complete subunit architecture of the proteasome regulatory particle. Nature 482:186–191
Lander GC, Martin A, Nogales E (2013) The proteasome under the microscope: the regulatory particle in focus. Curr Opin Struct Biol 23:243–251
Lingaraju GM, Bunker RD, Cavadini S, Hess D, Hassiepen U, Renatus M, Fischer ES, Thoma NH (2014) Crystal structure of the human COP9 signalosome. Nature 512:161–165
Murata S, Yashiroda H, Tanaka K (2009) Molecular mechanisms of proteasome assembly. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:104–115
Pick E, Hofmann K, Glickman MH (2009) PCI complexes: Beyond the proteasome, CSN, and eIF3 Troika. Mol Cell 35:260–264
Saeki Y, Tanaka K (2012) Assembly and function of the proteasome. Methods Mol Biol 832:315–337
Sattler M, Schleucher J, Griesinger C (1999) Heteronuclear multidimensional NMR experiments for the structure determination of proteins in solution employing pulsed field gradients. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 34:93–158
Schweitzer A, Aufderheide A, Rudack T, Beck F, Pfeifer G, Plitzko JM, Sakata E, Schulten K, Forster F, Baumeister W (2016) Structure of the human 26S proteasome at a resolution of 3.9 angstrom. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:7816–7821
Tomko RJ, Taylor DW, Chen ZA, Wang HW, Rappsilber J, Hochstrasser M (2015) A Single alpha helix drives extensive remodeling of the proteasome lid and completion of regulatory particle assembly. Cell 163:432–444
Unverdorben P, Beck F, Sledz P, Schweitzer A, Pfeifer G, Plitzko JM, Baumeister W, Forster F (2014) Deep classification of a large cryo-EM dataset defines the conformational landscape of the 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:5544–5549
Verma R, Aravind L, Oania R, McDonald WH, Yates JR 3rd, Koonin EV, Deshaies RJ (2002) Role of Rpn11 metalloprotease in deubiquitination and degradation by the 26S proteasome. Science 298:611–615
Wang XR, Cimermancic P, Yu C, Schweitzer A, Chopra N, Engel JL, Greenberg C, Huszagh AS, Beck F, Sakata E, Yang YY, Novitsky EJ (2017) Molecular details underlying dynamic structures and regulation of the human 26S proteasome. Mol Cell Proteomics 16:840–854
Wehmer M, Rudack T, Beck F, Aufderheide A, Pfeifer G, Plitzko JM, Forster F, Schulten K, Baumeister W, Sakata E (2017) Structural insights into the functional cycle of the ATPase module of the 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:1305–1310
Worden EJ, Padovani C, Martin A (2014) Structure of the Rpn11-Rpn8 dimer reveals mechanisms of substrate deubiquitination during proteasomal degradation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:220–227
Yen HC, Espiritu C, Chang EC (2003) Rpn5 is a conserved proteasome subunit and required for proper proteasome localization and assembly. J Biol Chem 278:30669–30676
Yu Z, Kleifeld O, Lande-Atir A, Bsoul M, Kleiman M, Krutauz D, Book A, Vierstra RD, Hofmann K, Reis N, Glickman MH, Pick E (2011) Dual function of Rpn5 in two PCI complexes, the 26S proteasome and COP9 signalosome. Mol Biol Cell 22:911–920
Acknowledgements
All NMR experiments were performed at the Beijing NMR Center and the NMR facility of National Center for Protein Sciences at Peking University. This research was supported by Grant 2016YFA0501201 from the National Key R&D Program of China and Grant 31570757 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China to C.J.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhao, C., Hu, Y. et al. NMR 1H, 13C, 15N backbone and side chain resonance assignment of the N-terminal domain of yeast proteasome lid subunit Rpn5. Biomol NMR Assign 13, 1–4 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-018-9840-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-018-9840-5