Abstract
Background
A number of non-coding circular RNAs (circRNAs) have recently been implicated in the modulation of gene expression in cancer models. We therefore sought to explore if circZNF236 has a role in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC).
Methods
We first examined circZNF236 expression in 32 pairs of OSCC and noncancerous tissues. We then investigated a functional role for circZNF236 using knockdown and overexpression approaches in OSCC cancer cell lines. Cell counting kit-8, wound healing, Transwell, and flow cytometry were employed to assess circZNF236 function in vitro. The association between circZNF236 and miR-145-5p, or that between miR-145-5p and malignant brain tumor domain containing 1 (MBTD1) was predicted by bioinformatics and demonstrated by dual-luciferase reporter assays, RNA pull-down assays as well as RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays. A mouse OSCC xenograft model was employed to demonstrate the impacts of circZNF236 inhibition on tumor development in vivo.
Results
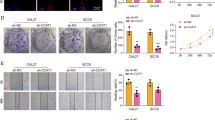
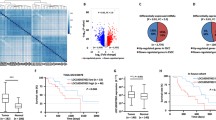
OSCC tissues and cells had higher levels of circZNF236 expression compared with normal controls. Furthermore, high circZNF236 levels in patients with OSCC correlated with a poor prognosis. CircZNF236 silencing decreased the malignant properties of OSCC cells and suppressed OSCC tumor formation in the mouse model. We then noticed that miR-145-5p can be regulated by circZNF236, and that circZNF2361 promoted OSCC development by absorbing miR-145-5p and consequently upregulating MBTD1 expression.
Conclusion
CircZNF236 modulates OSCC via the miR-145-5p/MBTD1 axis. These results support the potential of circZNF236 as a treatment target for OSCC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Additional data can be obtained from the corresponding author.
References
Chai AWY, Lim KP, Cheong SC. Translational genomics and recent advances in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;61:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.011.
Zhang L, Meng X, Zhu XW, Yang DC, Chen R, Jiang Y, et al. Long non-coding RNAs in oral squamous cell carcinoma: biologic function, mechanisms and clinical implications. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):102. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1021-3.
Huang F, Xin C, Lei K, Bai H, Li J, Chen Q. Noncoding RNAs in oral premalignant disorders and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020;43(5):763–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-020-00521-9.
Menini M, De Giovanni E, Bagnasco F, Delucchi F, Pera F, Baldi D, et al. Salivary micro-RNA and oral squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review. J Pers Med. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020101.
Fan HY, Jiang J, Tang YJ, Liang XH, Tang YL. CircRNAs: a new chapter in oral squamous cell carcinoma biology. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:9071–83. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S263655.
Verduci L, Tarcitano E, Strano S, Yarden Y, Blandino G. CircRNAs: role in human diseases and potential use as biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):468. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03743-3.
Li P, Zhu K, Mo Y, Deng X, Jiang X, Shi L, et al. Research progress of circRNAs in head and neck cancers. Front Oncol. 2021;11:616202. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.616202.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(11):675–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7.
Chen LL. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):475–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0243-y.
Li R, Jiang J, Shi H, Qian H, Zhang X, Xu W. CircRNA: a rising star in gastric cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(9):1661–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03345-5.
Chen S, Chen C, Hu Y, Song G, Shen X. The diverse roles of circular RNAs in pancreatic cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021;226:107869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107869.
Yin Y, Long J, He Q, Li Y, Liao Y, He P, et al. Emerging roles of circRNA in formation and progression of cancer. J Cancer. 2019;10(21):5015–21. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.30828.
Zheng S, Qian Z, Jiang F, Ge D, Tang J, Chen H, et al. CircRNA LRP6 promotes the development of osteosarcoma via negatively regulating KLF2 and APC levels. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(7):4126–38.
Chen N, Zhao G, Yan X, Lv Z, Yin H, Zhang S, et al. A novel FLI1 exonic circular RNA promotes metastasis in breast cancer by coordinately regulating TET1 and DNMT1. Genome Biol. 2018;19(1):218. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1594-y.
Tang X, Ren H, Guo M, Qian J, Yang Y, Gu C. Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:910–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2021.01.018.
Yang Q, Li F, He AT, Yang BB. Circular RNAs: expression, localization, and therapeutic potentials. Mol Ther. 2021;29(5):1683–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.01.018.
Li X, Yang L, Chen LL. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 2018;71(3):428–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.034.
Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, Fang N, Wang T, Xu T, et al. CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: a review. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0776-8.
Xin D, Xin Z. CircRNA_100782 promotes roliferation and metastasis of gastric cancer by downregulating tumor suppressor gene Rb by adsorbing miR-574-3p in a sponge form. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(17):8845–54. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202009_22824.
Lu J, Wang YH, Yoon C, Huang XY, Xu Y, Xie JW, et al. Circular RNA circ-RanGAP1 regulates VEGFA expression by targeting miR-877-3p to facilitate gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2020;471:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.038.
Guo J, Su Y, Zhang M. Circ_0000140 restrains the proliferation, metastasis and glycolysis metabolism of oral squamous cell carcinoma through upregulating CDC73 via sponging miR-182-5p. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:407. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01501-7.
Dong ZR, Ke AW, Li T, Cai JB, Yang YF, Zhou W, et al. CircMEMO1 modulates the promoter methylation and expression of TCF21 to regulate hepatocellular carcinoma progression and sorafenib treatment sensitivity. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01361-3.
Tu J, Chen W, Zheng L, Fang S, Zhang D, Kong C, et al. Circular RNA Circ0021205 Promotes cholangiocarcinoma progression through MiR-204–5p/RAB22A Axis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:653207. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.653207.
Wang S, Wang T, Gu P. microRNA-145-5p inhibits migration, invasion, and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting ARF6. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;13:3473–84. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S300678.
Zhong X, Wen X, Chen L, Gu N, Yu X, Sui K. Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via the miR-145–5p/ARF6 axis. J Gene Med. 2021;23(5):e3330. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.3330.
Fan S, Chen P, Li S. miR-145-5p inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal carcinoma cells by targeting ABRACL. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6692544. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6692544.
Wu W, Bai S, Zhu D, Li K, Dong W, He W, et al. Overexpression of malignant brain tumor domain containing protein 1 predicts a poor prognosis of prostate cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;17(5):4640–6. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10109.
Fu D, Lu C, Qu X, Li P, Chen K, Shan L, et al. LncRNA TTN-AS1 regulates osteosarcoma cell apoptosis and drug resistance via the miR-134-5p/MBTD1 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(19):8374–85. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102325.
Acknowledgements
Language assistance in this manuscript was provided by TopEdit (https://www.topeditsci.com).
Funding
Our study was financed by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M670865) and Natural Science Foundation of Jilin Province (YDZJ202201ZYTS251).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QL and MH conceived the experiments. YC and HC performed the experiments. QL wrote the article. All authors made contributions to the study and approved publication of this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare no conflicting interests.
Ethical approval
Our research was permitted and supervised by the Ethics Committee of Stomatological Hospital of Jilin University. The OSCC patients were treated in line with the Deceleration of Helsinki and granted signed informed consent. The experiments with mice were permitted and supervised by the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Jilin University.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Q., Che, H., Che, Y. et al. CircZNF236 facilitates malignant progression in oral squamous cell carcinoma by sequestering miR-145-5p. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 1690–1701 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-03064-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-03064-7