Abstract
Purpose
Lung cancer (LC) is the most common malignancy in the world. It is well that hypoxia is common in lung cancer, which contributes to lung cancer progression and metastasis [1]. miRNA-27a as a repressor factor is a lowly expression within non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the molecular mechanism between miR-27a and hypoxia in lung cancer progression remains poorly understood. This study aims to explore hypoxia promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells via regulating the NRF2/miR‑27a/BUB1 pathway.
Methods
We detect the expression of miR-27a after exposure to hypoxia conditions in lung cancer cells via qPCR. Using MTT assay and colony assay to assess the ability of proliferation in lung cancer cells under hypoxia or transfect miR-27a mimics. The capability of migration and invasion was evaluated by wound healing assay and Boyden-chamber assay. The mRNA and protein expression of EMT markers was respectively detected by qPCR and western blot. We detected NRF2 occupancy at the miR-27a promoter by ChIP-Seq analysis. Meanwhile, the luciferase assay verified BUB1 as a direct target of miR-27a.
Results
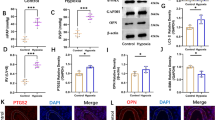
We found hypoxia promotes lung cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process by inhibiting the miR-27a expression. miR-27a mimics significantly reduced the promotion effect of hypoxia on the invasion and proliferation of lung cancer cells. NRF2 as regulating the oxidation/anti-oxidation factor was activated under hypoxia conditions. The activation of NRF2 repressed miR-27a expression. On the contrary, the inhibitory effect of hypoxia on miR-27a was reversed when the NFE2L2 gene was silenced. Ectopic expression of NRF2 inhibited miR-27a expression under normoxia. We further validated BUB1 as a direct target of the miR-27a by luciferase assay.
Conclusion
Hypoxia promotes invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of Lung cancer cells by regulating the NRF2/miR-27a/BUB1 axis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jing X, et al., Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer, 2019. 18(1): p.157.
Verduzco D, Lloyd M, Xu L, Ibrahim-Hashim A, Balagurunathan Y, Gatenby RA, et al. Intermittent hypoxia selects for genotypes and phenotypes that increase survival, invasion, and therapy resistance. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(3): e0120958.
Salem A, Asselin MC, Reymen B, Jackson A, Lambin P, West CML, O'Connor JPB, Faivre-Finn C. Targeting hypoxia to improve non-small cell lung cancer outcome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2018;110(1):14–30.
Kuper A, Baumann J, Gopelt K, Baumann M, Sanger C, Metzen E, et al. Overcoming hypoxia-induced resistance of pancreatic and lung tumor cells by disrupting the PERK-NRF2-HIF-axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(1):82.
Lee SL, Ryu H, Son AR, Seo B, Kim J, Jung SY, et al. TGF-beta and hypoxia/reoxygenation promote radioresistance of A549 lung cancer cells through activation of Nrf2 and EGFR. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:6823471.
Sanchez-Ortega M, Carrera AC, Garrido A. Role of NRF2 in lung cancer. Cells. 2021;10(8):1–28.
Croce CM. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(10):704–14.
Geng Y, Deng L, Su D, Xiao J, Ge D, Bao Y, et al. Identification of crucial microRNAs and genes in hypoxia-induced human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:4605–16.
Li W, Huang K, Wen F, Cui G, Guo H, He Z, et al. Intermittent hypoxia-induced downregulation of microRNA-320b promotes lung cancer tumorigenesis by increasing CDT1 via USP37. Mol Ther Nucleic Acid. 2021;24:528–41.
Heegaard NH, Schetter AJ, Welsh JA, Yoneda M, Bowman ED, Harris CC. Circulating micro-RNA expression profiles in early stage nonsmall cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012;130(6):1378–86.
Acunzo M, Romano G, Palmieri D, Lagana A, Garofalo M, Balatti V, et al. Cross-talk between MET and EGFR in non-small cell lung cancer involves miR-27a and Sprouty2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(21):8573–8.
Liang Q, Zhang H. MAP17 contributes to non-small cell lung cancer progression via suppressing miR-27a-3p expression and p38 signaling pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 2021;22(1):19–29.
Li X, Lv F, Li F, Du M, Liang Y, Ju S, et al. LINC01089 inhibits tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer via the miR-27a/SFRP1/Wnt/beta-catenin axis. Front Oncol. 2020;10: 532581.
Lu X, Kang N, Ling X, Pan M, Du W, Gao S. MiR-27a-3p promotes non-small cell lung cancer through SLC7A11-mediated-ferroptosis. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 759346.
Yang Y, Zang A, Jia Y, Shang Y, Zhang Z, Ge K, et al. Genistein inhibits A549 human lung cancer cell proliferation via miR-27a and MET signaling. Oncol Lett. 2016;12(3):2189–93.
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(5):2315–9.
Ruan J, Zhang L, Yan L, Liu Y, Yue Z, Chen L, et al. Inhibition of hypoxia-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition by luteolin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6(1):232–8.
Hiemstra S, Niemeijer M, Koedoot E, Wink S, Klip JE, Vlasveld M, et al. Comprehensive landscape of Nrf2 and p53 pathway activation dynamics by oxidative stress and DNA damage. Chem Res Toxicol. 2017;30(4):923–33.
Singh A, Daemen A, Nickles D, Jeon SM, Foreman O, Sudini K, et al. NRF2 activation promotes aggressive lung cancer and associates with poor clinical outcomes. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(3):877–88.
Hammad A, Namani A, Elshaer M, Wang XJ, Tang X. “NRF2 addiction” in lung cancer cells and its impact on cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2019;467:40–9.
Zhang X, Sai B, Wang F, Wang L, Wang Y, Zheng L, et al. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):40.
Shi Y, Fan S, Wu M, Zuo Z, Li X, Jiang L, et al. YTHDF1 links hypoxia adaptation and non-small cell lung cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4892.
Babar IA, Czochor J, Steinmetz A, Weidhaas JB, Glazer PM, Slack FJ. Inhibition of hypoxia-induced miR-155 radiosensitizes hypoxic lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;12(10):908–14.
Xia M, Sheng L, Qu W, Xue X, Chen H, Zheng G, et al. MiR-194–5p enhances the sensitivity of nonsmall-cell lung cancer to doxorubicin through targeted inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1. World J Surg Oncol. 2021;19(1):174.
Zhang H, Zhu S, Zhang C, Liu W, Zhu J. miR-199a-5p inhibits the proliferation of rat airway smooth muscle cells and the expression of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha under hypoxia conditions. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;31(9):1183–8.
Byun Y, Choi YC, Jeong Y, Lee G, Yoon S, Jeong Y, et al. MiR-200c downregulates HIF-1alpha and inhibits migration of lung cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019;24:28.
Li Y, Zhao L, Qi Y, Yang X. MicroRNA214 upregulates HIF1alpha and VEGF by targeting ING4 in lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(6):4935–45.
Zhang J, Han L, Yu J, Li H, Li Q. miR-224 aggravates cancer-associated fibroblast-induced progression of non-small cell lung cancer by modulating a positive loop of the SIRT3/AMPK/mTOR/HIF-1alpha axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(7):10431–49.
Ge YL, Jin FL, Zhang DH. Radio-sensitizing effects of microRNA-27a elevation in lung cancer cells by inhibiting ZEB1 expression and activating DNA damage repair pathway. J Biol Regul Homeost Agent. 2021;35(1):45–57.
He W, Qin M, Cai Y, Gao X, Cao S, Wang Z, et al. Downregulation of HOXC6 by miR-27a ameliorates gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2021;11(9):4329–46.
Lignitto L, LeBoeuf SE, Homer H, Jiang S, Askenazi M, Karakousi TR, et al. Nrf2 activation promotes lung cancer metastasis by inhibiting the degradation of Bach1. Cell. 2019;178(2):316–29.
Bakhtiyari N, Sharifi A, Aftabi Y, Gilani N, Zafari V, Ansarin A, et al. Association between NOX4 and Nrf2 genes in non-small-cell lung carcinoma: a case-control study. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2021;10(2):327–33.
Wang L, Yang X, An N, Liu J. Bioinformatics analysis of BUB1 expression and gene regulation network in lung adenocarcinoma. Transl Cancer Res. 2020;9(8):4820–33.
Ricke RM, Jeganathan KB, van Deursen JM. BUB1 overexpression induces aneuploidy and tumor formation through aurora B kinase hyperactivation. J Cell Biol. 2011;193(6):1049–64.
Nyati S, Schinske-Sebolt K, Pitchiaya S, Chekhovskiy K, Chator A, Chaudhry N, et al. The kinase activity of the Ser/Thr kinase BUB1 promotes TGF-beta signaling. Sci Signal. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2005379.
Qi W, Bai Y, Wang Y, Liu L, Zhang Y, Yu Y, et al. BUB1 predicts poor prognosis and immune status in liver hepatocellular carcinoma. APMIS. 2022;130(7):371–382.
Wang Z, Katsaros D, Shen Y, Fu Y, Canuto EM, Benedetto C, et al. Biological and clinical significance of MAD2L1 and BUB1, genes frequently appearing in expression signatures for breast cancer prognosis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(8): e0136246.
Guo L, Li H, Li W, Tang J. Construction and investigation of a combined hypoxia and stemness index lncRNA-associated ceRNA regulatory network in lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Med Genom. 2020;13(1):166.
Funding
This work was funded by Sichuan Medical Association (Q18010, 2018-ZRQN-093).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this study.
Ethical approval
This project has been approved by Southwest Medical University for experimental animal ethics. The approval number is:20211009–032.
Human and animal rights
The study was approved by the Southwest Medical University ethics committee. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Deng, J., Wang, S. et al. Hypoxia promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells via regulating the NRF2/miR‑27a/BUB1 pathway. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 510–522 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02965-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02965-x