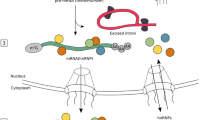
Abstract
Disease development requires the activation of complex multi-factor processes involving numerous long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), which describe non-protein-coding RNAs longer than 200 nucleotides. Emerging evidence indicates that lncRNAs act as essential regulators that perform pivotal roles in the pathogenesis and progression of human diseases. The mechanisms underlying lncRNA involvement in diverse diseases have been extensively explored, and lncRNAs are considered powerful biomarkers for clinical practice. The lncRNA noncatalytic region of tyrosine kinase adaptor protein 1 (NCK1) antisense 1 (NCK1-AS1), also known as NCK1 divergent transcript (NCK1-DT), is encoded on human chromosome 3q22.3 and produces a 27,274-base-long transcript. NCK1-AS1 has increasingly been characterized as a causative agent for multiple diseases. The abnormal expression and involvement of NCK1-AS1 in various biological processes have been associated with several diseases. Further exploration of the mechanisms through which NCK1-AS1 contributes to disease development and progression will provide a foundation for potential clinical applications of NCK1-AS1 in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases. This review summarizes the current understanding of the various functions and mechanisms through which NCK1-AS1 contributes to various diseases and the clinical application prospects for NCK1-AS1.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Jin T, Nguyen ND, Talos F, Wang D. ECMarker: interpretable machine learning model identifies gene expression biomarkers predicting clinical outcomes and reveals molecular mechanisms of human disease in early stages. Bioinformatics. 2021;37(8):1115–24.
Wang C, Xu W, An J, Liang M, Li Y, Zhang F, et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 accelerates vascular calcification by upregulating Runx2. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1203.
Gutierrez-Achury J, Romanos J, Bakker SF, Kumar V, de Haas EC, Trynka G, et al. Contrasting the genetic background of type 1 diabetes and celiac disease autoimmunity. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(Suppl 2):S37-44.
Kim J, Ghasemzadeh N, Eapen DJ, Chung NC, Storey JD, Quyyumi AA, et al. Gene expression profiles associated with acute myocardial infarction and risk of cardiovascular death. Genome Med. 2014;6(5):40.
Couturaud F, Leroyer C, Tromeur C, Julian JA, Kahn SR, Ginsberg JS, et al. Factors that predict thrombosis in relatives of patients with venous thromboembolism. Blood. 2014;124(13):2124–30.
Moorthy D, Merrill R, Namaste S, Iannotti L. The impact of nutrition-specific and nutrition-sensitive interventions on hemoglobin concentrations and anemia: a meta-review of systematic reviews. Adv Nutr. 2020;11(6):1631–45.
Dekker M, Waissi F, Timmerman N, Silvis MJM, Timmers L, de Kleijn DPV. Extracellular vesicles in diagnosing chronic coronary syndromes the bumpy road to clinical implementation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239128.
Bordoni L, Samulak JJ, Sawicka AK, Pelikant-Malecka I, Radulska A, Lewicki L, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide and the reverse cholesterol transport in cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):18675.
Xu H, Yu S, Yuan X, Xiong J, Kuang D, Pestell RG, et al. DACH1 suppresses breast cancer as a negative regulator of CD44. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):4361.
Oni-Orisan A, Alsaleh N, Lee CR, Seubert JM. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and cardioprotection: the road to translation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;74:199–208.
Troiani T, Martinelli E, Morgillo F, Capasso A, Nappi A, Sforza V, et al. Targeted approach to metastatic colorectal cancer: what comes beyond epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies and bevacizumab? Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2013;5(1):51–72.
Moga MA, Bălan A, Dimienescu OG, Burtea V, Dragomir RM, Anastasiu CV. Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers for endometriosis and endometriosis-related ovarian cancer—an overview. J Clin Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050735.
Farley J, Ozbun LL, Birrer MJ. Genomic analysis of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cell Res. 2008;18(5):538–48.
Ma Y, Zhan S, Lu H, Wang R, Xu Y, Zhang G, et al. B7–H3 regulates KIF15-activated ERK1/2 pathway and contributes to radioresistance in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(10):824.
Chisari CG, Toro MD, Cimino V, Rejdak R, Luca M, Rapisarda L, et al. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and higher relapse frequency may predict poor recovery after optic neuritis in MS patients. J Clin Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8112022.
Rodríguez M, Bajo-Santos C, Hessvik NP, Lorenz S, Fromm B, Berge V, et al. Identification of non-invasive miRNAs biomarkers for prostate cancer by deep sequencing analysis of urinary exosomes. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):156.
Liu X, She Y, Wu H, Zhong D, Zhang J. Long non-coding RNA Gas5 regulates proliferation and apoptosis in HCS-2/8 cells and growth plate chondrocytes by controlling FGF1 expression via miR-21 regulation. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25(1):18.
Zhao X, Li X, Zhou L, Ni J, Yan W, Ma R, et al. LncRNA HOXA11-AS drives cisplatin resistance of human LUAD cells via modulating miR-454-3p/Stat3. Cancer Sci. 2018;109(10):3068–79.
Xia L, Nie D, Wang G, Sun C, Chen G. FER1L4/miR-372/E2F1 works as a ceRNA system to regulate the proliferation and cell cycle of glioma cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(5):3224–33.
Yin H, Wang X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zeng Y, Xiong Y, et al. Integrated analysis of long noncoding RNA associated-competing endogenous RNA as prognostic biomarkers in clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018;109(10):3336–49.
Chai Y, Wu HT, Liang CD, You CY, Xie MX, Xiao SW. Exosomal lncRNA ROR1-AS1 Derived from Tumor Cells Promotes Glioma Progression via Regulating miR-4686. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:8863–72.
Wu J, Wang N, Yang Y, Jiang G, Zhan H, Li F. LINC01152 upregulates MAML2 expression to modulate the progression of glioblastoma multiforme via Notch signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(1):115.
Agwa SHA, Elzahwy SS, El Meteini MS, Elghazaly H, Saad M, Abd Elsamee AM, et al. ABHD4-regulating RNA panel: novel biomarkers in acute coronary syndrome diagnosis. Cells. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061512.
Liu Z, Wang P, Yuan S, Wang Y, Cao P, Wen F, et al. LncRNA BC200/miR-150-5p/MYB positive feedback loop promotes the malignant proliferation of myelodysplastic syndrome. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(2):126.
Feng Y, Xu Y, Gao Y, Chen Y, Wang X, Chen Z. A novel lncRNA SOX2OT promotes the malignancy of human colorectal cancer by interacting with miR-194-5p/SOX5 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):499.
Huang X, Sun L, Wen S, Deng D, Wan F, He X, et al. RNA sequencing of plasma exosomes revealed novel functional long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(9):3338–49.
Long Y, Wang L, Li Z. SP1-induced SNHG14 aggravates hypertrophic response in in vitro model of cardiac hypertrophy via up-regulation of PCDH17. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(13):7115–26.
Luo M, Huang P, Pan Y, Zhu Z, Zhou R, Yang Z, et al. Weighted gene coexpression network and experimental analyses identify lncRNA SPRR2C as a regulator of the IL-22-stimulated HaCaT cell phenotype through the miR-330/STAT1/S100A7 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(1):86.
Cheng JT, Wang L, Wang H, Tang FR, Cai WQ, Sethi G, et al. Insights into biological role of LncRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cells. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101178.
Zhang J, Hu K, Yang YQ, Wang Y, Zheng YF, Jin Y, et al. LIN28B-AS1-IGF2BP1 binding promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell progression. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):741.
Vidovic D, Huynh TT, Konda P, Dean C, Cruickshank BM, Sultan M, et al. ALDH1A3-regulated long non-coding RNA NRAD1 is a potential novel target for triple-negative breast tumors and cancer stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27(1):363–78.
Ma X, Yuan T, Yang C, Wang Z, Zang Y, Wu L, et al. X-inactive-specific transcript of peripheral blood cells is regulated by exosomal Jpx and acts as a biomarker for female patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2017;9(11):665–77.
Song J, Ye A, Jiang E, Yin X, Chen Z, Bai G, et al. Reconstruction and analysis of the aberrant lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on competitive endogenous RNA in CESC. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(8):6665–73.
Huang L, Gan X, He L, Wang L, Yu J. Silencing of long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation and migration via inhibition of microRNA-134 in cervical cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(3):2314–22.
Zhang WY, Liu YJ, He Y, Chen P. Suppression of long noncoding RNA NCK1-AS1 increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin in cervical cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(4):4302–13.
Li H, Jia Y, Cheng J, Liu G, Song F. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 promotes proliferation and induces cell cycle progression by crosstalk NCK1-AS1/miR-6857/CDK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):198.
Li Y, Zhuang X, Zhuang L, Liu H. AS1 expression in prostate cancer and its effects on proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Cancer Biomark. 2021;32(3):271–9.
Guan Z, Song Y, Ma J, Li F, Zhao X, Liang G, et al. Altered expression of lncRNA NCK1-AS1 distinguished patients with prostate cancer from those with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(6):6379–84.
Guan B, Ma J, Yang Z, Yu F, Yao J. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 exerts oncogenic property in gastric cancer by targeting the miR-22-3p/BCL9 axis to activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Environ Toxicol. 2021;36(8):1640–53.
Li W, Duan J, Shi W, Lei L, Lv P. Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 serves an oncogenic role in gastric cancer by regulating miR-137/NUP43 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:9929–39.
Zhou X, Bao W, Zhang D, Yang Y, Du X, Qiu G. NCK1-AS1 promotes the progression of lung squamous cell carcinoma through transcriptionally upregulating NCK1 via interacting with MYC. Cancer Biol Ther. 2021;22(3):196–203.
Zha LF, Zhang LD, Pan HM, Ma HD. Upregulation of lncRNA NCK1-AS1 predicts poor prognosis and contributes to non-small cell lung cancer proliferation by regulating CDK1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021;25(3):1351–7.
Li J, Wu X, Cao W, Zhao J. Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by acting as a ceRNA of miR-137. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(10):6908–20.
Luo X, Zhou J, Quan L, Liang Y, Huang P, Chen F, et al. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via regulating miR-512-5p/p21 axis. Pathol Res Pract. 2020;216(11):153157.
Wang B, Wang K, Jin T, Xu Q, He Y, Cui B, et al. NCK1-AS1 enhances glioma cell proliferation, radioresistance and chemoresistance via miR-22–3p/IGF1R ceRNA pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110395.
Huang L, Li X, Ye H, Liu Y, Liang X, Yang C, et al. Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 promotes the tumorigenesis of glioma through sponging microRNA-138-2-3p and activating the TRIM24/Wnt/β-catenin axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):63.
Chen M, Cheng Y, Yuan Z, Wang F, Yang L, Zhao H. NCK1-AS1 increases drug resistance of glioma cells to temozolomide by modulating miR-137/TRIM24. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020;35(2):101–8.
Fu X, Chen X, Si Y, Yao Y, Jiang Z, Chen K. Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 is overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and predicts survival. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):8302–10.
Wan L, Gu D, Jin X. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 promotes malignant cellular phenotypes of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via miR-137/NCK1 axis. Mol Biotechnol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00469-1.
Le F, Ou Y, Luo P, Zhong X. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 in plasma distinguishes oral ulcer from early-stage oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Biol Res (Thessalon). 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40709-020-00126-1.
Hu H, Li H, Feng X. Downregulation of lncRNA NCK1-AS1 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by upregulating miR-135a. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:10531–7.
Zhou W, Wang J, Zhang J, Wang Y, Jiang L, Guo T, et al. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 aggravates hepatocellular carcinoma by the miR-22–3p/YARS axis to activate PI3K/AKT signaling. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2022;31(1):48–59.
Lin Q, Jia Y, Zhang D, Jin H. NCK1-AS1 promotes the progression of melanoma by accelerating cell proliferation and migration via targeting miR-526b-5p/ADAM15 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):367.
Qiao Z, Dai H, Zhang Y, Li Q, Zhao M, Yue T. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 promotes cancer cell proliferation and increase cell stemness in urinary bladder cancer patients by downregulating miR-143. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:1661–8.
Cheng Y, Shen X, Zheng M, Zou G, Shen Y. Knockdown Of lncRNA NCK-AS1 regulates cisplatin resistance through modulating miR-137 in osteosarcoma cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:11057–68.
Chang H, Li B, Zhang X, Meng X. NCK1-AS1 promotes NCK1 expression to facilitate tumorigenesis and chemo-resistance in ovarian cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;522(2):292–9.
Zhang B, Wang J, Du L, Shao L, Zou Y, Liu H, et al. Knockdown of NCK1-AS1 inhibits the development of atherosclerosis by targeting miR-1197/COX10 axis. J Biol Eng. 2022;16(1):2.
Zhang T, Li J, He Y, Yang F, Hao Y, Jin W, et al. A small molecule targeting myoferlin exerts promising anti-tumor effects on breast cancer. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3726.
Lehman HL, Kidacki M, Stairs DB. Twist2 is NFkB-responsive when p120-catenin is inactivated and EGFR is overexpressed in esophageal keratinocytes. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):18829.
Clarke TB, Francella N, Huegel A, Weiser JN. Invasive bacterial pathogens exploit TLR-mediated downregulation of tight junction components to facilitate translocation across the epithelium. Cell Host Microbe. 2011;9(5):404–14.
Zeng L, Zampetaki A, Margariti A, Pepe AE, Alam S, Martin D, et al. Sustained activation of XBP1 splicing leads to endothelial apoptosis and atherosclerosis development in response to disturbed flow. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(20):8326–31.
Solomou EE, Keyvanfar K, Young NS. T-bet, a Th1 transcription factor, is up-regulated in T cells from patients with aplastic anemia. Blood. 2006;107(10):3983–91.
Hu W, Liu C, Bi ZY, Zhou Q, Zhang H, Li LL, et al. Comprehensive landscape of extracellular vesicle-derived RNAs in cancer initiation, progression, metastasis and cancer immunology. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):102.
Oeckinghaus A, Postler TS, Rao P, Schmitt H, Schmitt V, Grinberg-Bleyer Y, et al. κB-Ras proteins regulate both NF-κB-dependent inflammation and Ral-dependent proliferation. Cell Rep. 2014;8(6):1793–807.
Kalailingam P, Tan HB, Pan JY, Tan SH, Thanabalu T. Overexpression of CDC42SE1 in A431 cells reduced cell proliferation by inhibiting the Akt pathway. Cells. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020117.
Franco AT, Corken A, Ware J. Platelets at the interface of thrombosis, inflammation, and cancer. Blood. 2015;126(5):582–8.
Koh I, Cha J, Park J, Choi J, Kang SG, Kim P. The mode and dynamics of glioblastoma cell invasion into a decellularized tissue-derived extracellular matrix-based three-dimensional tumor model. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):4608.
Kreis NN, Friemel A, Ritter A, Roth S, Rolle U, Louwen F, et al. Function of p21 (Cip1/Waf1/CDKN1A) in migration and invasion of cancer and trophoblastic cells. Cancers (Basel). 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070989.
Saénz-de-Santa-María I, Celada L, Chiara MD. The leader position of mesenchymal cells expressing N-cadherin in the collective migration of epithelial cancer. Cells. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030731.
Ong MS, Deng S, Halim CE, Cai W, Tan TZ, Huang RY, et al. Cytoskeletal proteins in cancer and intracellular stress: a therapeutic perspective. Cancers (Basel). 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12010238.
Polacheck WJ, Zervantonakis IK, Kamm RD. Tumor cell migration in complex microenvironments. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(8):1335–56.
Zajdel M, Rymkiewicz G, Sromek M, Cieslikowska M, Swoboda P, Kulinczak M, et al. Tumor and cerebrospinal fluid microRNAs in primary central nervous system lymphomas. Cancers (Basel). 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111647.
Wu XP, Yang YP, She RX, Xing ZM, Chen HW, Zhang YW. microRNA-329 reduces bone cancer pain through the LPAR1-dependent LPAR1/ERK signal transduction pathway in mice. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835919875319.
Wang Z, Tang Y, Xie L, Huang A, Xue C, Gu Z, et al. The prognostic and clinical value of CD44 in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00309.
Yi N, Zhao X, Ji J, Xu M, Jiao Y, Qian T, et al. Serum galectin-3 as a biomarker for screening, early diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic effect evaluation of pancreatic cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(19):11583–91.
Gude F, Riveiro V, Rodríguez-Núñez N, Ricoy J, Lado-Baleato Ó, Lourido T, et al. Development and validation of a clinical score to estimate progression to severe or critical state in COVID-19 pneumonia hospitalized patients. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19794.
Wang Y, Zhong X, Zhou L, Lu J, Jiang B, Liu C, et al. Prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: an umbrella review. Front Oncol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01466.
Amatatsu M, Arigami T, Uenosono Y, Yanagita S, Uchikado Y, Kijima Y, et al. Programmed death-ligand 1 is a promising blood marker for predicting tumor progression and prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018;109(3):814–20.
Allard WJ, Matera J, Miller MC, Repollet M, Connelly MC, Rao C, et al. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(20):6897–904.
Takeuchi H, Kitagawa Y. Circulating tumor cells in gastrointestinal cancer. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010;17(5):577–82.
Sun YF, Yang XR, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Xu Y. Circulating tumor cells: advances in detection methods, biological issues, and clinical relevance. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137(8):1151–73.
Reiser H, Klingenberg R, Hof D, Cooksley-Decasper S, Fuchs N, Akhmedov A, et al. Circulating FABP4 is a prognostic biomarker in patients with acute coronary syndrome but not in asymptomatic individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35(8):1872–9.
Chong CR, Jänne PA. The quest to overcome resistance to EGFR-targeted therapies in cancer. Nat Med. 2013;19(11):1389–400.
Rizzuti IF, Mascheroni P, Arcucci S, Ben-Mériem Z, Prunet A, Barentin C, et al. Mechanical control of cell proliferation increases resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. Phys Rev Lett. 2020;125(12):128103.
Caetano-Pinto P, Jansen J, Assaraf YG, Masereeuw R. The importance of breast cancer resistance protein to the kidneys excretory function and chemotherapeutic resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2017;30:15–27.
Park NH, Cheng W, Lai F, Yang C, de Florez Sessions P, Periaswamy B, et al. Addressing drug resistance in cancer with macromolecular chemotherapeutic agents. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(12):4244–52.
West KA, Castillo SS, Dennis PA. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway and chemotherapeutic resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 2002;5(6):234–48.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZS: designed the work, YW and JP: wrote this manuscript, ZS and YW: made figures. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Pan, J. & Sun, Z. LncRNA NCK1-AS1-mediated regulatory functions in human diseases. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 323–332 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02948-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-02948-y