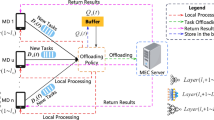
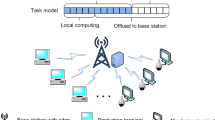
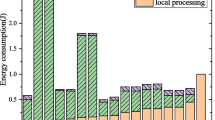
Abstract
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) and Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) have been treated as promising technologies to process the delay-sensitive tasks in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) network. The cooperation among multiple MEC servers is essential to improve the processing capacity of MEC systems. However, the dynamic IIoT environment with unknown changing models, including time-varying wireless channels, diversified task requests, and dynamic load on wireless resources and multiple MEC servers, may continuously affect the task offloading decision and NOMA user pairing, which brings great challenges to the resource management in the NOMA-MEC-based IIoT network. In order to solve this problem, we design a distributed deep reinforcement learning (DRL) based solution to improve the task satisfaction ratio by jointly optimizing the task offloading decision and the sub-channel assignment to support the binary computing offloading policy. For each IIoT device agent, to deal with the problem of partial state observability, the Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) is employed to predict the load states of sub-channels and MEC servers, which is further used for the decision of the RL agent. Simulation results show that the proposed prediction-based-DRL (P-DRL) method can achieve higher task satisfaction ratio than exiting schemes.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiu T, Chi J, Zhou X, Ning Z, Atiquzzaman M, Wu DO (2020) Edge computing in industrial Internet of Things: Architecture, advances and challenges. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 22(4):2462–2488
Illa PK, Padhi N (2018) Practical guide to smart factory transition using IoT, big data and edge analytics. IEEE Access 6:55162–55170
Hu YC, Patel M, Sabella D, Sprecher N, Young V (2015) Mobile edge computing - a key technology towards 5G. ETSI White Paper 11(11):1–16
Tran TX, Pompili D (2019) Joint task offloading and resource allocation for multi-server mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 68(1):856–868
Zhao M, Wang W, Wang Y, Zhang Z (2019) Load scheduling for distributed edge computing: A communication-computation tradeoff. Peer Peer Netw Appl 12:1418–1432
Li M, Gao J, Zhao L, Shen X (2020) Deep reinforcement learning for collaborative edge computing in vehicular networks. IEEE Trans Cognit Commun Netw 6(4):1122–1135
Bu C, Wang J (2021) Computing tasks assignment optimization among edge computing servers via SDN. Peer Peer Netw Appl 14:1190–1206
Tan L, Kuang Z, Zhao L, Liu A (2021) Energy-efficient joint task offloading and resource allocation in OFDMA-based collaborative edge computing. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun Early Access 1–14
Ding Z, Lei X, Karagiannidis GK, Schober R, Yuan J, Bhargava VK (2017) A survey on non-orthogonal multiple access for 5G networks: Research challenges and future trends. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 35(10):2181–2195
Ding Z, Fan P, Poor HV (2019) Impact of non-orthogonal multiple access on the offloading of mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans Commun 67(1):375–390
Maraqa O, Rajasekaran AS, Al-Ahmadi S, Yanikomeroglu H, Sait SM (2020) A survey of rate-optimal power domain NOMA with enabling technologies of future wireless networks. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 22(4):2192–2235
Akbar A, Jangsher S, Bhatti FA (2021) NOMA and 5G emerging technologies: A survey on issues and solution techniques. Comput Netw 190:107950
Kiani A, Ansari N (2018) Edge computing aware NOMA for 5G networks. IEEE Internet Things J 5(2):1299–1306
Roostaei R, Dabiri Z, Movahedi Z (2021) A game-theoretic joint optimal pricing and resource allocation for Mobile Edge Computing in NOMA-based 5G networks and beyond. Comput Netw 198:108352
Zhu J, Wang J, Huang Y, Fang F, Navaie K, Ding Z (2020) Resource allocation for hybrid NOMA MEC offloading. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 19(7):4964–4977
Hossain M, Ansari N (2022) Network slicing for NOMA-enabled edge computing. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput Early Access
Liu L, Sun B, Tan X, Tsang D (2022) Energy-efficient resource allocation and subchannel assignment for NOMA-enabled multiaccess edge computing. IEEE Syst J 16(1):1558–1569
Fang F, Xu Y, Ding Z, Shen C, Peng M, Karagiannidis GK (2020) Optimal resource allocation for delay minimization in NOMA-MEC Networks. IEEE Trans Commun 68(12):7867–7881
Wang K, Ding Z, So DKC, Karagiannidis GK (2021) Stackelberg game of energy consumption and latency in MEC systems with NOMA. IEEE Trans Commun 69(4):2191–2206
Shi L, Ye Y, Chu X, Lu G (2021) Computation energy efficiency maximization for a NOMA-based WPT-MEC network. IEEE Internet Things J 8(13):10731–10744
Budhiraja I, Kumar N, Tyagi S, Tanwar S (2021) Energy consumption minimization scheme for NOMA-based mobile edge computation networks underlaying UAV. IEEE Syst J 15(4):5724–5733
Qian L, Wu Y, Yu N, Jiang F (2021) Learning driven NOMA assisted vehicular edge computing via underlay spectrum sharing. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 70(1):977–992
Li C, Wang H, Song R (2021) Intelligent offloading for NOMA-assisted MEC via dual connectivity. IEEE Internet Things J 8(4):2802–2813
Liang Z, Liu Y, Lok T, Huang K (2021) Multi-cell mobile edge computing: Joint service migration and resource allocation. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 20(9):5898–5912
Guo F, Lu H, Li B, Li D, Chen CW (2021) NOMA-assisted multi-MEC offloading for IoVT networks. IEEE Wirel Commun 28(4):26–33
Wan Z, Xu D, Xu D, Ahmad I (2021) Joint computation offloading and resource allocation for NOMA-based multi-access mobile edge computing systems. Comput Netw 196:108256
Lai P, He Q, Cui G, Chen F (2022) Cost-effective user allocation in 5G NOMA-based mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Trans Mob Comput Early Access
Yilmaz S, Özbek B (2022) Multi-helper NOMA for cooperative mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst Early Access
Fang F, Wang W, Ding Z, Leung VCM (2021) Energy-efficient resource allocation for NOMA-MEC networks with imperfect CSI. IEEE Trans Commun 69(5):3436–3449
Yu H, Zhou Z, Jia Z, Zhao X (2021) Multi-timescale multi-dimension resource allocation for NOMA-edge computing-based power IoT with massive connectivity. IEEE Trans Green Commun Netw 5(3):1101–1113
Chen X, Bi Y, Chen X, Zhao H (2022) Dynamic service migration and request routing for microservice in multi-cell mobile edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J Early Access
Tuong VD, Truong TP, Nguyen T, Noh W, Cho S (2021) Partial computation offloading in NOMA-assisted mobile-edge computing systems using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet Things J 8(17):13196–13208
Chen Z, Zhang L, Pei Y, Jiang C (2022) NOMA-based multi-user mobile edge computation offloading via cooperative multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans Cognit Commun Netw 8(1):350–364
Zhu H, Wu Q, Wu X, Fan Q (2021) Decentralized power allocation for MIMO-NOMA vehicular edge computing based on deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Internet Things J Early Access
Nduwayezu M, Yun J (2022) Latency and energy aware rate maximization in MC-NOMA-based multi-access edge computing: A two-stage deep reinforcement learning approach. Comput Netw 207:108834
Wang K, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Shao Z, Luo X, Yang Y (2020) Online task scheduling and resource allocation for intelligent NOMA-based industrial Internet of Things. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 38(5):803–815
Tuong VD, Noh W, Cho S (2021) Delay minimization for NOMA-enabled mobile edge computing in industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Trans Ind Inf Early Access 1–10
Qian L, Wu Y, Jiang F, Yu N, Lu W, Lin B (2021) NOMA assisted multi-task multi-access mobile edge computing via deep reinforcement learning for industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Trans Industr Inf 17(8):5688–5698
Peng H, Shen X (2020) Deep reinforcement learning based resource management for multi-access edge computing in vehicular networks. IEEE Trans Netw Sci Eng 7(4):2416–2428
Tang M, Wong V (2020) Deep reinforcement learning for task offloading in mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Tran Mob Comput Early Access 1–12
Ning Z, Huang J, Wang X, Rodrigues J, Guo L (2019) Mobile edge computing-enabled internet of vehicles: Toward energy-efficient scheduling. IEEE Network 33(5):198–205
Liang F, Yu W, Liu X, Griffith D, Golmie N (2021) Toward computing resource reservation scheduling in industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J 8(10):8210–8222
Baek J, Kaddoum G (2021) Heterogeneous task offloading and resource allocations via deep recurrent reinforcement learning in partial observable multifog networks. IEEE Internet Things J 8(2):1041–1056
Kapetanakis S, Kudenko D (2002) Reinforcement learning of coordination in cooperative multi-agent systems. Proc Natl Conf Artif Intell Conf Innov Appl Artif Intell (AAAI/IAAI), Menlo Park, CA, USA, pp:326–331
Wang S, Lv T, Zhang X, Lin Z, Huang P (2020) Learning-based multi-channel access in 5G and beyond networks with fast time-varying channels. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 69(5):5203–5218
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural. Computing 9(8):1735–1780
Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Rusu A, Veness J, Bellemare M (2015) Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 518:529–533
Lyu X, Tian H, Jiang L, Vinel A, Maharjan S, Gjessing S, Zhang Y (2018) Selective offloading in mobile edge computing for the green Internet of Things. IEEE Network 32(1):54–60
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant: 62,171,051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Zhou, W., Yang, Z. et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based task scheduling and resource allocation for NOMA-MEC in Industrial Internet of Things. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 16, 170–188 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-022-01348-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-022-01348-x