Abstract
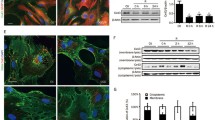
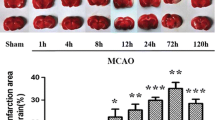
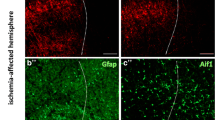
Connexin43 (Cx43) gap junctions expressed in astrocytes can significantly impact neuronal survival in stroke. However, little is known regarding Cx43 spatial and temporal expression during the initial stages of brain ischemia. Using immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis, we examined Cx43 spatial and temporal expression as a function of neuronal injury within the first 24 h after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO). Western blot analysis showed a significant increase in Cx43 protein expression in the core ischemic area at 2 and 3 h after pMCAO. However, after 6 h of pMCAO Cx43 levels were significantly reduced. This reduction was due to cell death and concomitant Cx43 degradation in the expanding focal ischemic region, while the peri-infarct zone revealed intense Cx43 staining. The neuronal cell-death marker Fluoro-Jade C labeled injured neurons faintly at 1 h post-pMCAO with a time-dependent increase in both intensity and size of punctate staining. In addition, decreased microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) immunoreactivity and thionin staining similarly indicated cell damage beginning at 1 h after pMCAO. Taken together, Cx43 expression is sensitive to neuronal injury and can be detected as early as 2 h post-pMCAO. These findings underscore Cx43 gap junction as a potential early target for therapeutic intervention in ischemic stroke.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cx26:
-
Connexin26
- Cx30:
-
Connexin30
- Cx43:
-
Connexin43
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- GFAP:
-
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
- MCA:
-
Middle Cerebral Artery
- pMCAO:
-
Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- MAP2:
-
Microtubule-associated protein 2
- OCT:
-
Optimal Cutting Temperature Compound
- PBS:
-
Phosphate Buffered Saline
- RIPA:
-
Radioimmunoprecipitation Assay
- TBS-T:
-
Tris-buffered saline with Tween 20
References
Abudara V, Bechberger J, Freitas-Andrade M, De Bock M, Wang N, Bultynck G, Naus CC, Leybaert L, Giaume C (2014) The connexin43 mimetic peptide Gap19 inhibits hemichannels without altering gap junctional communication in astrocytes. Front Cell Neurosci 8:306
Anderson MF, Blomstrand F, Blomstrand C, Eriksson PS, Nilsson M (2003) Astrocytes and stroke: networking for survival? Neurochem Res 28:293–305
Barreto G, White RE, Ouyang Y, Xu L, Giffard RG (2011) Astrocytes: targets for neuroprotection in stroke. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 11:164–173
Broussalis E, Killer M, McCoy M, Harrer A, Trinka E, Kraus J (2012) Current therapies in ischemic stroke. Part a. Recent developments in acute stroke treatment and in stroke prevention. Drug Discov Today 17:296–309
Caceres A, Banker GA, Binder L (1986) Immunocytochemical localization of tubulin and microtubule-associated protein 2 during the development of hippocampal neurons in culture. J Neurosci 6:714–722
Cechetto DF, Wilson JX, Smith KE, Wolski D, Silver MD, Hachinski VC (1989) Autonomic and myocardial changes in middle cerebral artery occlusion: stroke models in the rat. Brain Res 502:296–305
Chen Q, Boire A, Jin X, Valiente M, Er EE, Lopez-Soto A, Jacob LS, Patwa R, Shah H, Xu K, Cross JR, Massague J (2016) Carcinoma-astrocyte gap junctions promote brain metastasis by cGAMP transfer. Nature 533:493–498
Chever O, Lee CY, Rouach N (2014) Astroglial connexin43 hemichannels tune basal excitatory synaptic transmission. J Neurosci 34:11228–11232
Chiang T, Messing RO, Chou WH (2011) Mouse model of middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Vis Exp 13(48):e2761
Cronin M, Anderson PN, Cook JE, Green CR, Becker DL (2008) Blocking connexin43 expression reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Mol Cell Neurosci 39:152–160
Damjanac M, Rioux Bilan A, Barrier L, Pontcharraud R, Anne C, Hugon J, Page G (2007) Fluoro-jade B staining as useful tool to identify activated microglia and astrocytes in a mouse transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 1128:40–49
Davidson JO, Green CR, Nicholson LF, O'Carroll SJ, Fraser M, Bennet L, Gunn AJ (2012) Connexin hemichannel blockade improves outcomes in a model of fetal ischemia. Ann Neurol 71:121–132
Dawson DA, Hallenbeck JM (1996) Acute focal ischemia-induced alterations in MAP2 immunostaining: description of temporal changes and utilization as a marker for volumetric assessment of acute brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:170–174
del Zoppo GJ, Sharp FR, Heiss WD, Albers GW (2011) Heterogeneity in the penumbra. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1836–1851
Desplantez T, Verma V, Leybaert L, Evans WH, Weingart R (2012) Gap26, a connexin mimetic peptide, inhibits currents carried by connexin43 hemichannels and gap junction channels. Pharmacol Res 65:546–552
D'Hondt C, Iyyathurai J, Himpens B, Leybaert L, Bultynck G (2014) Cx43-hemichannel function and regulation in physiology and pathophysiology: insights from the bovine corneal endothelial cell system and beyond. Front Physiol 5:348
Enkvist MO, McCarthy KD (1994) Astroglial gap junction communication is increased by treatment with either glutamate or high K+ concentration. J Neurochem 62:489–495
Fonseca CG, Green CR, Nicholson LF (2002) Upregulation in astrocytic connexin 43 gap junction levels may exacerbate generalized seizures in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain Res 929:105–116
Freitas-Andrade M, Naus CC (2016) Astrocytes in neuroprotection and neurodegeneration: the role of connexin43 and pannexin1. Neuroscience 323:207–221
Freitas-Andrade M, Carmeliet P, Stanimirovic DB, Moreno M (2008) VEGFR-2-mediated increased proliferation and survival in response to oxygen and glucose deprivation in PlGF knockout astrocytes. J Neurochem 107:756–767
Freitas-Andrade M, Bechberger JF, MacVicar BA, Viau V, Naus CC (2017) Pannexin1 knockout and blockade reduces ischemic stroke injury in female, but not in male mice. Oncotarget 8:36973–36983
Froger N, Orellana JA, Calvo CF, Amigou E, Kozoriz MG, Naus CC, Saez JC, Giaume C (2010) Inhibition of cytokine-induced connexin43 hemichannel activity in astrocytes is neuroprotective. Mol Cell Neurosci 45:37–46
George PM, Steinberg GK (2015) Novel stroke therapeutics: unraveling stroke pathophysiology and its impact on clinical treatments. Neuron 87:297–309
Giaume C, Theis M (2010) Pharmacological and genetic approaches to study connexin-mediated channels in glial cells of the central nervous system. Brain Res Rev 63:160–176
Hossmann KA (2012) The two pathophysiologies of focal brain ischemia: implications for translational stroke research. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1310–1316
Kozoriz MG, Bechberger JF, Bechberger GR, Suen MW, Moreno AP, Maass K, Willecke K, Naus CC (2010) The connexin43 C-terminal region mediates neuroprotection during stroke. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69:196–206
Kozoriz MG, Lai S, Vega JL, Saez JC, Sin WC, Bechberger JF, Naus CC (2013) Cerebral ischemic injury is enhanced in a model of oculodentodigital dysplasia. Neuropharmacology 75:549–556
Lansberg MG, Bluhmki E, Thijs VN (2009) Efficacy and safety of tissue plasminogen activator 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke: a metaanalysis. Stroke 40:2438–2441
Le HT, Sin WC, Lozinsky S, Bechberger J, Vega JL, Guo XQ, Saez JC, Naus CC (2014) Gap junction intercellular communication mediated by connexin43 in astrocytes is essential for their resistance to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 289:1345–1354
Li WE, Ochalski PA, Hertzberg EL, Nagy JI (1998) Immunorecognition, ultrastructure and phosphorylation status of astrocytic gap junctions and connexin43 in rat brain after cerebral focal ischaemia. Eur J Neurosci 10:2444–2463
Lo EH, Dalkara T, Moskowitz MA (2003) Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:399–415
Maes M, Crespo Yanguas S, Willebrords J, Weemhoff JL, da Silva TC, Decrock E, Lebofsky M, Pereira IVA, Leybaert L, Farhood A, Jaeschke H, Cogliati B, Vinken M (2017) Connexin hemichannel inhibition reduces acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicol Lett 278:30–37
Meier C, Rosenkranz K (2014) Cx43 expression and function in the nervous system-implications for stem cell mediated regeneration. Front Physiol 5:106
Nakase T, Naus CC (2004) Gap junctions and neurological disorders of the central nervous system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1662:149–158
Nakase T, Fushiki S, Naus CC (2003a) Astrocytic gap junctions composed of connexin 43 reduce apoptotic neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia. Stroke 34:1987–1993
Nakase T, Fushiki S, Sohl G, Theis M, Willecke K, Naus CC (2003b) Neuroprotective role of astrocytic gap junctions in ischemic stroke. Cell Commun Adhes 10:413–417
Nakase T, Sohl G, Theis M, Willecke K, Naus CC (2004) Increased apoptosis and inflammation after focal brain ischemia in mice lacking connexin43 in astrocytes. Am J Pathol 164:2067–2075
Nakase T, Yoshida Y, Nagata K (2006) Enhanced connexin 43 immunoreactivity in penumbral areas in the human brain following ischemia. Glia 54:369–375
Orellana JA, Saez PJ, Shoji KF, Schalper KA, Palacios-Prado N, Velarde V, Giaume C, Bennett MV, Saez JC (2009) Modulation of brain hemichannels and gap junction channels by pro-inflammatory agents and their possible role in neurodegeneration. Antioxid Redox Signal 11:369–399
Orellana JA, Hernandez DE, Ezan P, Velarde V, Bennett MV, Giaume C, Saez JC (2010) Hypoxia in high glucose followed by reoxygenation in normal glucose reduces the viability of cortical astrocytes through increased permeability of connexin 43 hemichannels. Glia 58:329–343
Ponsaerts R, De Vuyst E, Retamal M, D'Hondt C, Vermeire D, Wang N, De Smedt H, Zimmermann P, Himpens B, Vereecke J, Leybaert L, Bultynck G (2010) Intramolecular loop/tail interactions are essential for connexin 43-hemichannel activity. FASEB J 24:4378–4395
Ramos-Cabrer P, Campos F, Sobrino T, Castillo J (2011) Targeting the ischemic penumbra. Stroke 42:S7–11
Retamal MA, Schalper KA, Shoji KF, Orellana JA, Bennett MV, Saez JC (2007a) Possible involvement of different connexin43 domains in plasma membrane permeabilization induced by ischemia-reperfusion. J Membr Biol 218:49–63
Retamal MA, Froger N, Palacios-Prado N, Ezan P, Saez PJ, Saez JC, Giaume C (2007b) Cx43 hemichannels and gap junction channels in astrocytes are regulated oppositely by proinflammatory cytokines released from activated microglia. J Neurosci 27:13781–13792
Rovegno M, Soto PA, Saez PJ, Naus CC, Saez JC, von Bernhardi R (2015) Connexin43 hemichannels mediate secondary cellular damage spread from the trauma zone to distal zones in astrocyte monolayers. Glia 63:1185–1199
Sadler TR, Khodavirdi AC, Hinton DR, Holschneider DP (2009) Snap-frozen brain tissue sections stored with desiccant at ambient laboratory conditions without chemical fixation are resistant to degradation for a minimum of 6 months. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 17:165–171
Schmued LC, Stowers CC, Scallet AC, Xu L (2005) Fluoro-jade C results in ultra high resolution and contrast labeling of degenerating neurons. Brain Res 1035:24–31
Sena E, van der Worp HB, Howells D, Macleod M (2007) How can we improve the pre-clinical development of drugs for stroke? Trends Neurosci 30:433–439
Shinotsuka T, Yasui M, Nuriya M (2014) Astrocytic gap junctional networks suppress cellular damage in an in vitro model of ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 444:171–176
Siushansian R, Bechberger JF, Cechetto DF, Hachinski VC, Naus CC (2001) Connexin43 null mutation increases infarct size after stroke. J Comp Neurol 440:387–394
Skyschally A, Walter B, Schultz Hansen R, Heusch G (2013) The antiarrhythmic dipeptide ZP1609 (danegaptide) when given at reperfusion reduces myocardial infarct size in pigs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's. Arch Pharm 386:383–391
Solan JL, Lampe PD (2005) Connexin phosphorylation as a regulatory event linked to gap junction channel assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta 1711:154–163
Solan JL, Lampe PD (2009) Connexin43 phosphorylation: structural changes and biological effects. Biochem J 419:261–272
Tamura K, Alessandri B, Heimann A, Kempski O (2011) The effect of a gap-junction blocker, carbenoxolone, on ischemic brain injury and cortical spreading depression. Neuroscience 194:262–271
Theodoric N, Bechberger JF, Naus CC, Sin WC (2012) Role of gap junction protein Connexin43 in astrogliosis induced by brain injury. PLoS One 7:e47311
Wang N et al (2013) Selective inhibition of Cx43 hemichannels by Gap19 and its impact on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol 108:309
Willebrords J, Cogliati B, Pereira IVA, da Silva TC, Crespo Yanguas S, Maes M, Govoni VM, Lima A, Felisbino DA, Decrock E, Nogueira MS, de Castro IA, Leclercq I, Leybaert L, Rodrigues RM, Vinken M (2017) Inhibition of connexin hemichannels alleviates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Sci Rep 7:8268
Yoon JJ, Green CR, O'Carroll SJ, Nicholson LF (2010a) Dose-dependent protective effect of connexin43 mimetic peptide against neurodegeneration in an ex vivo model of epileptiform lesion. Epilepsy Res 92:153–162
Yoon JJ, Nicholson LF, Feng SX, Vis JC, Green CR (2010b) A novel method of organotypic brain slice culture using connexin-specific antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to improve neuronal survival. Brain Res 1353:194–203
Yoshimoto T, Siesjo BK (1999) Posttreatment with the immunosuppressant cyclosporin a in transient focal ischemia. Brain Res 839:283–291
Acknowledgements
This study was funded through a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) to CCN and WCS, and a CIHR Team Grant (R1478A47) on “Vascular Cognitive Impairment: Animal Models of Co-morbidity.” MFA was supported by a fellowship from the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada. CCN holds a Canada Research Chair.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freitas-Andrade, M., She, J., Bechberger, J. et al. Acute connexin43 temporal and spatial expression in response to ischemic stroke. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 12, 193–204 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-017-0430-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-017-0430-6