Abstract
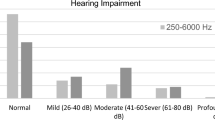
This single case study describes the audiological and vestibular findings of a female patient, aged 62, with diabetes mellitus and rheumatoid arthritis. Based on this case study, we hypothesize that individuals with diabetes mellitus and rheumatoid arthritis are more vulnerable to vestibular impairment. The current findings indicate that central vestibular lesions and bilateral sensorineural hearing loss are related to rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes. Therefore concluding early detection and follow-up is required to understand pathophysiology in detail.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
References
Emamifar A, Bjoerndal K, Hansen IM (2016) Is Hearing impairment associated with rheumatoid arthritis? A Rev Open Rheumatol J 15(10):26–32. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874312901610010026.PMID:27053970;PMCID:PMC4797675
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Chen H (2003) Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 112(12):1821–1830
Festa A, D’Agostino R Jr, Howard G, Mykkänen L, Tracy RP, Haffner SM (2000) Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: the Insulin resistance atherosclerosis study (IRAS). Circulation 102(1):42–47
Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM (2001) C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 286(3):327–334
Schmidt MI, Duncan BB, Sharrett AR, Lindberg G, Savage PJ, Offenbacher S, Heiss G (1999) Markers of inflammation and prediction of diabetes mellitus in adults (atherosclerosis risk in communities study): a cohort study. The Lancet 353(9165):1649–1652
Barzilay JI, Abraham L, Heckbert SR, Cushman M, Kuller LH, Resnick HE, Tracy RP (2001) The relation of markers of inflammation to the development of glucose disorders in the elderly: the cardiovascular health study. Diabetes 50(10):2384–2389
McCabe BF (1979) Autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol, Rhinol Laryngol 88(5):585–589
Huang CM, Chen HJ, Huang PH, Tsay GJ, Lan JL, Sung FC (2018) Retrospective cohort study on risk of hearing loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using claims data. BMJ Open 8(1):e018134
Murdin L, Patel S, Walmsley J, Yeoh LH (2008) Hearing difficulties are common in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 27:637–640
Lisowska G, Namysłowski G, Morawski K, Strojek K (2001) Cochlear dysfunction and diabetic microangiopathy. Scand Audiol 30(1):199–203
Alessandrini M, Bruno E, Parisi V, Uccioli L, Giacomini PG (2001) Saccadic eye movement and visual pathways function in diabetic patients. In Anal Otorrinolaringol Ibero-americs 28(3):269–280
Özel HE, ÖzkiriŞ M, Gencer ZK, Saydam L (2014) Audiovestibular functions in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Otolaryngol 134(1):51–57
Yilmaz S, Erbek S, Erbek SS, Ozgirgin N, Yucel E (2007) Abnormal electronystagmography in rheumatoid arthritis. Auris Nasus Larynx 34(3):307–311
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the HOD and in-charge head of department ASLP at SRM Institute of Science and Technology and the anonymous patient for generously sharing their time, experiences, and insights with us as we conducted this case study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Informed Consent
Patient assessment was carried out according to the protocol, and informed consent for using the data for publication after suitable anonymization was obtained.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramamoorthy, P., Ramamoorthy, S., Santhosh, T. et al. A Case Report of Auditory and Vestibular Findings in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Diabetes Mellitus. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04668-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04668-x