Abstract
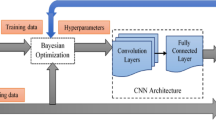
This study utilized AIML (artificial intelligence & machine learning) techniques to analyze 115 images of central perforation of tympanic membrane obtained from Telemyringoscopy through Borescope in order to establish a facilitation-model for the community ear diagnosis. The Modified VGG19 with batch normalization revealed the highest training accuracy of 85 as compared to other CNN techniques. The training accuracy started to saturate around mid-70% and the Test accuracy was around 50%. Although AIML did not reveal a high predictive value, its potential based on our observations cannot be underestimated considering many limitations (sample size, image-quality, associated pathologies, illumination-factor) in this study. Such limitations if resolved may revolutionize community ear care through a better cost effective tele-myringoscopy with innovations in AIML/ telemedicine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mishra A, Verma V, Shukla GK, Mishra SC, Dwivedi RC (2011) Prevalence of Deafness in Indian Population: an epidemiological study for Health Policy Considerations. Indian J Public Health 55(2):132–134
Cha D, Pae C, Seong SB, Choi JY, Park HJ (2019) Automated diagnosis of ear disease using ensemble deep learning with a big otoendoscopy image database. EBioMedicine 45:606–614
Myburgh HC, Jose S, Swanepoel DW, Laurent C (2018) Towards low cost automated smartphone- and cloud-based otitis media diagnosis. Biomed Sig Process Control 39:34–52
Lee JY, Choi S-H, Chung JW (2019) Automated classification of the tympanic membrane using a convolutional neural network. Appl Sci 9(9):1827
Tran T-T, Fang T-Y, Pham V-T, Lin C, Wang P-C, Lo M-T (2018) Development of an Automatic Diagnostic Algorithm for Pediatric Otitis Media. Otol Neurotol 39:1060–1065
Mironică I, Vertan C, Gheorghe DC (2011) Automatic pediatric otitis detection by classification of global image features. In Proceedings of the E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 24–26 November ; pp. 1–4
Kuruvilla A, Shaikh N, Hoberman A, Kovaˇcevi´c J (2013) 2013, 27
Pichichero ME, Poole MD (2001) Assessing diagnostic accuracy and tympanocentesis skills in the management of otitis media. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 155:1137–1142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK, PM, AK worked under supervision of DMK who was the overall authority for analyzing the image data. All the images were collected by AM who conceptualized the study and planned it with DMK. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest and no funding was obtained. Although no informed consent was taken as this distant method of assessment was in fact a necessity in covid phase but still an ethical clearance was applied for. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Katyayan, A., Mishra, P., Katyayan, A. et al. Augmenting Community Diagnosis of Safe Ear Disease Through Tele-Myringoscopy with Borescope Using AIML Techniques. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 1864–1869 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03769-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03769-3