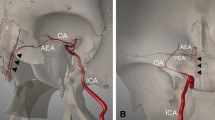
Abstract
The protocols for managing intractable idiopathic epistaxis have evolved with advances in endoscopic techniques. Transnasal endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation (TESPAL) has been the treatment of choice for idiopathic intractable epistaxis. If TESPAL fails, transantral ligation of internal maxillary artery (IMA) used to be the dictum along with radiological interventions. Here we discuss about the role of endoscopic IMA ligation in cases of failed TESPALs. Retrospective study at a tertiary hospital was performed. 28 cases of intractable idiopathic epistaxis underwent TESPAL in our institution of which 2 cases had rebleed. We also had two referred cases of failed TESPALS. Of this 4 patients, three patients underwent endoscopic IMA ligation and one patient underwent selective embolisation. All the patients who underwent endoscopic IMA ligation for failed TESPAL had no further episodes of epistaxis. One patient who underwent selective embolization also had no further episodes of bleed but had transient facial pain and trismus. When TESPAL fails, endoscopic IMA ligation can be considered as an alternative procedure before resorting to embolization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pallin DJ, Chng YM, McKay MP et al (2005) Epidemiology of epistaxis in US emergency departments, 1992 to 2001. Ann Emerg Med 46:77–81
Chandler JR, Serrins AJ (1965) Transantral ligation of the internal maxillary artery for epistaxis. Laryngoscope 75:1151–1159
Sokoloff J, Wickbom I, McDonald D, Brahme F, Goergen TG, Goldberger LE (1974) Therapeutic percutaneous embolization in intractable epistaxis. Radiology 111:285–287
Elden L, Montanera W, Terbrugge K, Willinsky R, Lasjaunias P, Charles D (1994) Angiographic embolization for the treatment of epistaxis: a review of 108 cases. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 111(1):44–50. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989411100110
Tseng EY, Narducci CA, Willing SJ, Sillers MJ (1998) Angiographic embolization for epistaxis: a review of 114 cases. Laryngoscope 108:615–619
Ram B, White PS, Saleh HA, Odutoye T, Cain A (2000) Endoscopic endonasal ligation of the sphenopalatine artery. Rhinology 38:147–149
Simpson GT, Janfaza P, Becker GD (1982) Transantral sphenopalatine artery ligation. Laryngoscope 92:1001–1005
Budrovich R, Saetti R (1992) Microscopic and endoscopic ligature of the sphenopalatine artery. Laryngoscope 102:1390–1394
Strong EB, Bell DA, Johnson LP, Jacobs JM (1995) Intractable epistaxis: transantral ligation versus embolization: efficacy review and cost analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113:674–678
Gilyoma JM, Chalya PL (2011) Etiological profile and treatment outcome of epistaxis at a tertiary care hospital in Northwestern Tanzania: a prospective review of 104 cases. BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 11:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6815-11-8
Darlene Lubbe, The open access of otolaryngology, head and neck operative surgery by Johan Fagan (editor) https://vula.uct.ac.za/access/content/group/ba5fb1bd-be95-48e5-81be-586fbaeba29d/Sphenopalatine%20artery%20_SPA_%20ligation.pdf
Metson R, Hanson DG (1983) Bilateral facial nerve paralysis following arterial embolization for epistaxis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 91:299–302
Kim JK, Cho JH, Lee Y et al (2010) Anatomical variability of the maxillary artery: findings from 100 Asian cadaveric dissections. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136(8):813–818. https://doi.org/10.1001/archoto.2010.121
Pritkin JB, Caldarelli DD, Panje WR (1998) Endoscopic ligation of internal maxillary artery for treatment of intractable posterior epistaxis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 107:85–92
Willems PW, Farb RI, Agid R (2009) Endovascular treatment of epistaxis. Am J Neuroradiol 30:1637–1645
Hervochon R, Khoueir N, Le Clerc N, Clément J, Kania R, Herman P, Verillaud B (2018) Unilateral vs bilateral sphenopalatine artery ligation in adult unilateral epistaxis: a comparative retrospective study of 83 cases. Clin Otolaryngol 43:1591–1594. https://doi.org/10.1111/coa.13183
MacArthur FJD, McGarry GW (2017) The arterial supply of the nasal cavity. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol 274(2):809–815
Ntomouchtsis A, Venetis G, Zouloumis L et al (2010) Ischemic necrosis of nose and palate after embolization for epistaxis: a case report. Oral Maxillofac Surg 14(2):123–127
Elsheikh E, El-Anwar MW (2013) Septal perforation and bilateral partial middle turbinate necrosis after bilateral sphenopalatine artery ligation. J Laryngol Otol 127(10):1025–1027
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasindran, V., John, M.S. Role of Endoscopic Internal Maxillary Artery Ligation in Intractable Idiopathic Epistaxis. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 72, 228–233 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01788-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01788-y