Abstract
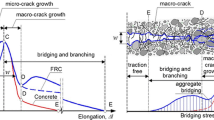
The article presents a novel hybrid concrete composite which is produced by combining glass and basalt textiles for achieving enhanced impact resistance compared to their independently reinforced counterparts. A full factorial analysis was performed to determine the synergy of two types of textiles and their combination on the impact strength and energy absorption. The two levels of key factors were considered for analysis such as the type of textile and impact energy level, and variance. The influencing parameters showed statistical significance with more than a 90% confidence level concerning impact resistance and energy absorption. The combination of two textiles showed the highest impact resistance irrespective of the energy levels, compared to the use of single textiles. The findings demonstrated that the energy absorption of hybrid textile reinforced concrete is not significantly enhanced with the increasing level of impact energy. At the high levels of impact energy, in comparison to the hybrid textile reinforced concrete slabs and basalt textile reinforced concrete, more energy is absorbed by the glass textile reinforced concrete slabs. Thus, in hybrid textile reinforced concrete, it is indicated by the failure pattern that combining basalt and glass textile influences the degree of local failure. Therefore, this research emphasizes on the synergy to customize and optimize textile reinforced concrete with superior impact resistance and energy absorption for the protection of structures in the event of impact loading.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bindiganavile V and Banthia N 2001 Polymer and steel fiber-reinforced cementitious composites under impact loading—Part 2: Flexural toughness. ACI Mater. J. 98: 17–24
Ugale V, Singh K, Mishra N and Kumar P 2013 Comparative study of carbon fabric reinforced and glass fabric reinforced thin sandwich panels under impact and static loading. J. Com. Mater. 49: 99–112
Zhu D, Gencoglu M and Mobasher B 2009 Low velocity flexural impact behavior of AR glass fabric reinforced cement composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 31: 379–387
Zhang Y, Kerr Z, Jarvis B and Volant R J 2017 High-velocity impact behaviour of a new hybrid fibre-reinforced cementitious composite. Adv. Struct. Eng. 21: 589–597
Yang E and Li V C 2012 Tailoring engineered cementitious composites for impact resistance. Cem. Concr. Res. 42: 1066–1071
Soe K T, Zhang Y X and Zhang L G 2013 High velocity impact responses of hybrid-fiber cementitious composite panels. Compos. Struct. 104: 320–330
Zhou X, Ghaffar SH, Dong W, Oladiran O and Fan M 2013 Fracture and impact properties of short discrete jute fibre-reinforced cementitious composites. Mater. Des. 49: 35–47
Brameshuber W (ed.) 2006 Report 36: textile reinforced concrete-state-of-the-art report of RILEM TC 201-TRC. 36 RILEM publications
Peled A and Bentur A 2000 Geometrical characteristics and efficiency of textile fabrics for reinforcing cement composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 30: 781–790
Peled A and Mobasher B 2005 Pultruded fabric-cement composites. ACI Mater. J. 102: 15–23
Maalej M, Quek S T and Zhang J 2005 Behavior of hybrid-fiber engineered cementitious composites subjected to dynamic tensile loading and projectile impact. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 17: 143–152
Padaki NV, Alagirusamy R, Deopura B and Fangueiro R 2010 Influence of preform interlacement on the low velocity impact behavior of multilayer textile composites. J. Ind. Tex. 40: 171–185
Yoo DY, Gohil U, Gries T and Yoon Y S 2016 Comparative low-velocity impact response of textile reinforced concrete and steel-fiber-reinforced concrete beams. J. Com. Mater. 50: 2421–2431
Dey V, Zani G, Colombo M, Di Prisco M and Mobasher B 2015 Flexural impact response of textile reinforced aerated concrete sandwich panels. Mater. Des. 86: 187–197
Liu S, Zhu D, Ou Y, Yao Y and Shi C 2018 Impact response of basalt textile reinforced concrete subjected to different velocities and temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 175: 381–391
Wang N, Mindess S and Ko K 1996 Fibre reinforced concrete beams under impact loading. Cem. Concr. Res. 26: 363–376
Arisoy B and Wu H C 2008 Material characteristics of high performance lightweight concrete reinforced with PVA. Constr. Build. Mater. 22: 635–645
Banthia N, Yan C, and Sakai K 1998 Impact resistance of fiber reinforced concrete at subnormal temperatures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 20: 393–404
Gopinath S, Prakash A, Aahrthy R and Bhavani H 2018 Investigations on the Influence of Matrix and Textile on the Response of Textile Reinforced Concrete Slabs under Impact Loading. Sādhanā 43: 172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopinath, S., Prakash, A. & Ahmed, A.K.F. Synergy of hybrid textile reinforced concrete under impact loading. Sādhanā 45, 72 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-020-1312-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-020-1312-9