Abstract
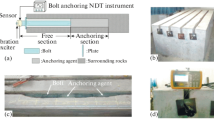
Bolts are utilised extensively in machinery and often bear large loads. Reliable connection of bolts is related to the effective functioning of machinery. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to detect bolt looseness in time. However, the identification of bolt looseness is typically challenging due to the strong background noise. Compared with Gaussian white noise, only few researches were conducted on Poisson white noise. To detect the looseness of the bolt in the presence of strong Poisson white noise, we propose a novel method based on sub-harmonic resonance, time-domain averaging and adaptive stochastic resonance. The disadvantages of damaging characteristic frequencies that exist in a majority of approaches are overcome. In addition, the looseness is assessed by the quality factor derived from physical science. To verify the efficacy of the method, we propose numerical simulations and experimental validations. The results demonstrate that the proposed method has effectively detected bolt looseness under strong Poisson white noise. The detection of bolt looseness might benefit greatly by adopting the suggested approach.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A Fuliński and P F Góra, J. Stat. Phys 101, 483 (2000)
Z Wang and X Shi, Cogn. Neurodyn. 14, 115 (2020)
C Q Li, Prob. Eng. Mech. 15, 359 (2000)
L R Russell, Waterw. Port. C-ASCE 97, 139 (1971)
B F Spencer, J Tang and C G Hilal, J. Sound Vib. 140, 163 (1990)
K Kyoung, E Powers, C Ritz, R Miksad and F Fischer, IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 12, 568 (1987)
C C Tung, J. Eng. Mech. Div. 95, 41 (1969)
J B Roberts, J. Sound Vib. 24, 23 (1972)
D Huang, J Yang, D Zhou, G Litak and H Liu, J. Comput. Nonlin. Dyn. 14, 031010 (2019)
G Muscolino, G Ricciardi and P Cacciola, Int. J. Nonliner Mech. 38, 1269 (2003)
S Chaki, G Corneloup, I Lillamand and H Walaszek, J. Press. Vess.- T. ASME 129, 383 (2006)
G C Johnson, A C Holt and B Cunningham, J. Test. Eval. 14, 253 (1986)
T Wang, G Song, Z Wang and Y Li, Smart. Mater. Struct. 22, 087001 (2013)
C Liang, F P Sun and C A Rogers, J. Int. Mater. Syst. Str. 8, 335 (1997)
T Wang, G Song, S Liu, Y Li and H Xiao, Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 9, 871213 (2013)
D Goyal, A Choudhary and B S Pabla, J. Int. Manuf. 31, 1275 (2020)
Q Jiang, F Chang and B Sheng, IEEE Access 7, 69795 (2019)
J Li, X Chen and Z He, J. Sound. Vib. 332, 5999 (2013)
L Gammaitoni, P Hänggi, P Jung and F Marchesoni, Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 223 (1998)
B McNamara and K Wiesenfeld, Phys. Rev. A 39, 4854 (1989)
S Mitaim and B Kosko, Proc. IEEE 86, 2152 (1998)
L He, X Liu and Z Jiang, Indian J. Phys. 77, 408 (2020)
P Xu, Y Jin and Y Zhang, Appl. Math. Comput. 346, 352 (2019)
Y Zhang, Y Jin and P Xu, Chaos 29, 023127 (2019)
S Wang, F Wang, S Wang and G Li, Chin. J. Phys. 56, 994 (2018)
G Zhang, D Hu and T Zhang, IEEE Access 7, 58435 (2019)
A S Pikovsky and J Kurths, Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 775 (1997)
C Yang, Z Wang and T Gong, Russ. J. Nondestruct. 59, 560 (2023)
Y K Lin and G Q Cai, Probabilistic structural dynamics: advanced theory and applications (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1995)
J J Meyer and D E Adams, Nonlinear Dyn. 81, 103 (2015)
M Zhang, Y Shen, L Xiao and W Qu, Nonlinear Dyn. 88, 1643 (2017)
J H Yang, M A F Sanjuán and H G Liu, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 30, 362 (2016)
E B Halim, M S Choudhury, S L Shah and M J Zuo, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 22, 261 (2016)
Y F Xu, Gao J, G C Chen and J S Yu, Appl. Mech. Mater. 63, 106 (2011)
S Yang, M Wang and L Jiao, Proceedings of the 2004 Congress on Evolutionary Computation (IEEE Cat. No. 04TH8753), IEEE 1, 320 (2004)
C Yang, J Yang, Z Zhu, G Shen and Y Zheng, Meas. Sci. Technol. 31, 045001 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12072362), the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. KYCX23-2683), the Graduate Innovation Program of China University of Mining and Technology (Grant No. 2023WLJCRCZL04) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, A., Gong, T. & Yang, J. Adaptive stochastic resonance under Poisson white noise background and its application for bolt looseness detection. Pramana - J Phys 98, 69 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-024-02757-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-024-02757-8